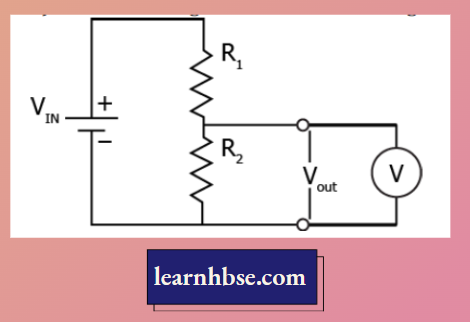
Haryana Board Class 10 Physics Solutions For Chapter 4 Magnetic Effects Of Current Multiple Choice Questions And Answers
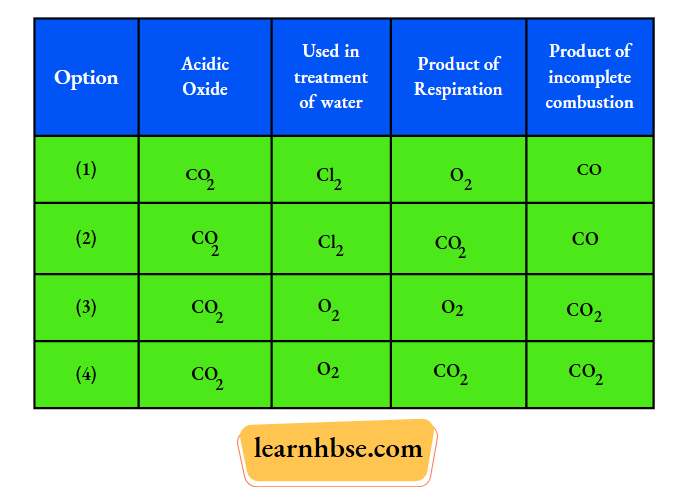
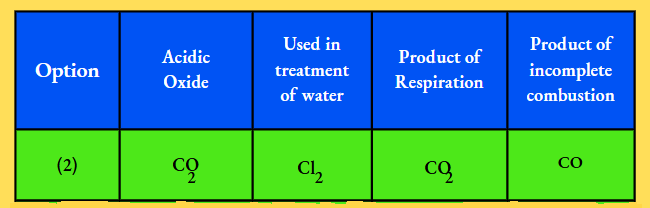
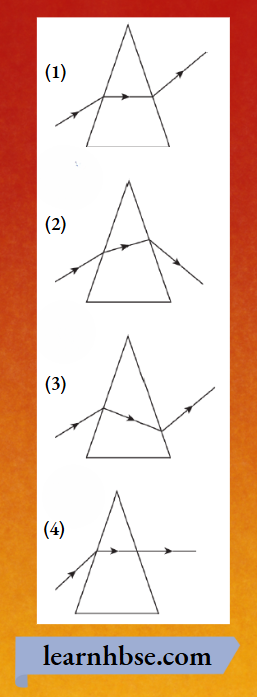
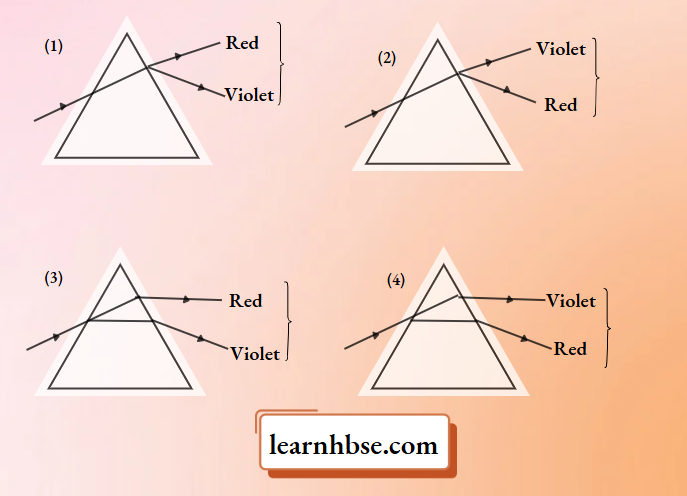
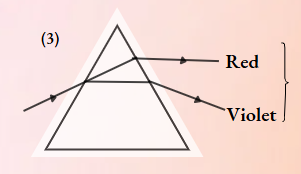
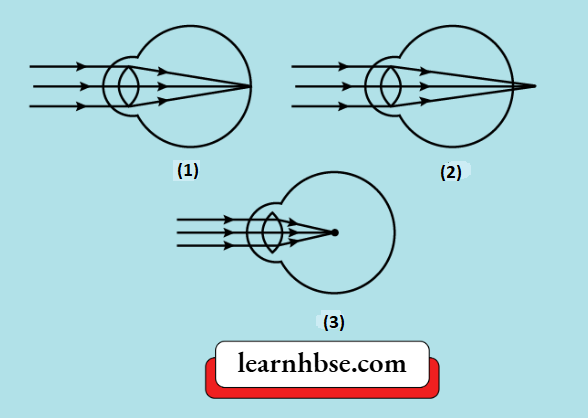
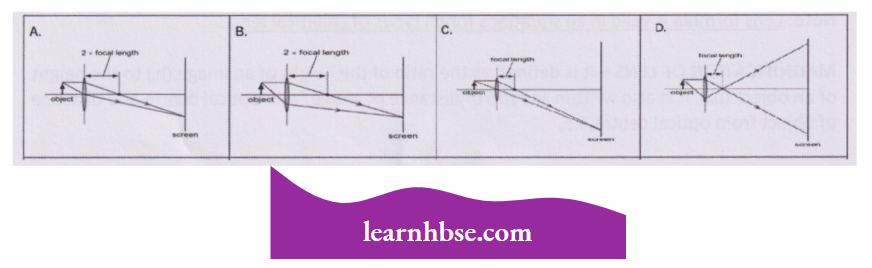
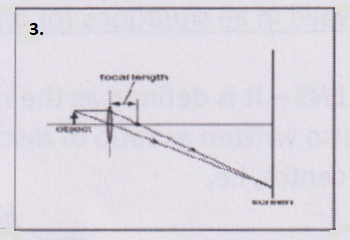
Question 1. A student learns that the magnetic field strength around a bar magnet is different at every point. Which diagram shows the correct magnetic field lines around a bar magnet?
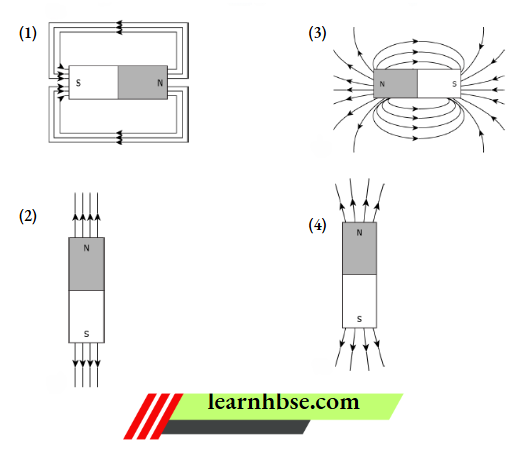
Answer: 3.
Question 2. A student places some iron fillings around a magnet. The iron fillings arrange themselves as shown in image.
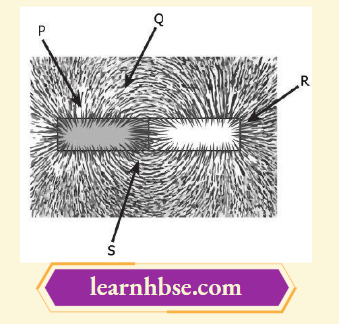
The student labelled four different regions around the magnet. Where would be the magnetic be the strongest?
- P
- Q
- R
- S
Answer: 3. R
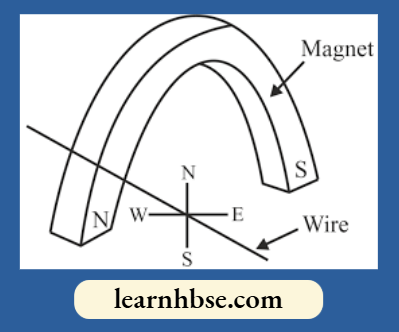
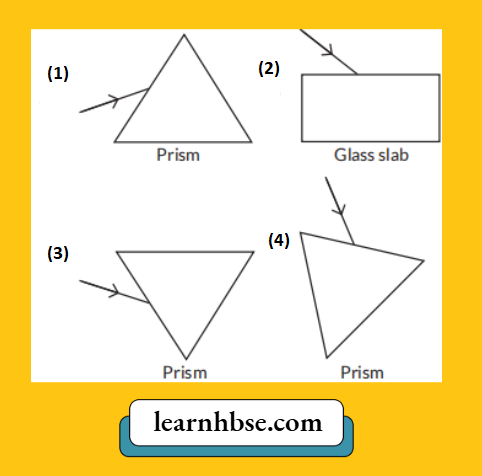
Question 3. A student placed a magnetic compass around a straight current carrying wire. The student noticed when he moved the compass away from the wire, the deflection in compass decreases. How would be the magnetic field lines around the conductor?
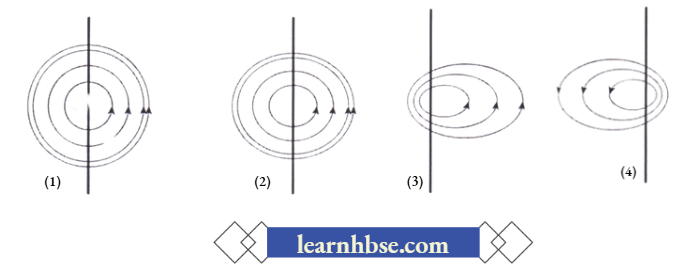
Answer: 2.
Question 4. The image shows the magnetic field lines around a straight current-carrying conductor.
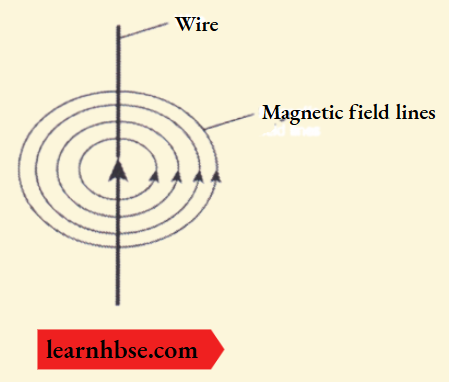
If the direction of the current in the straight wire is changed, what change in the magnetic field line will be observed?
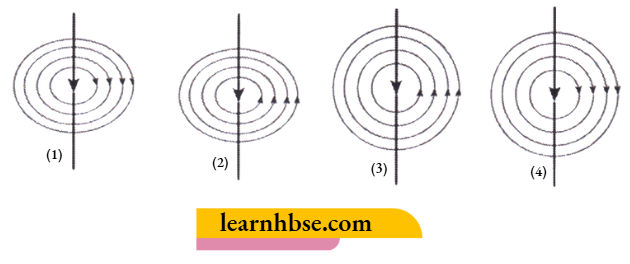
Answer: 1.
Question 5. Which diagram shows the magnetic field lines around a current-carrying circular loop?
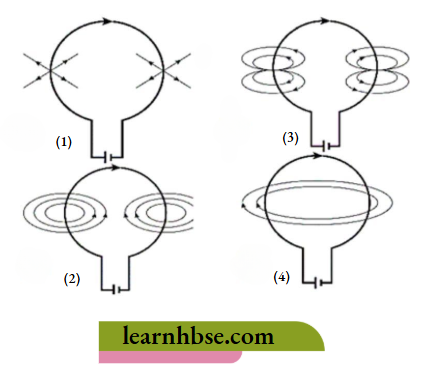
Answer: 2.
Question 6. Which diagram shows the correct direction of the magnetic field lines at point P and Q in current carrying circular loop?
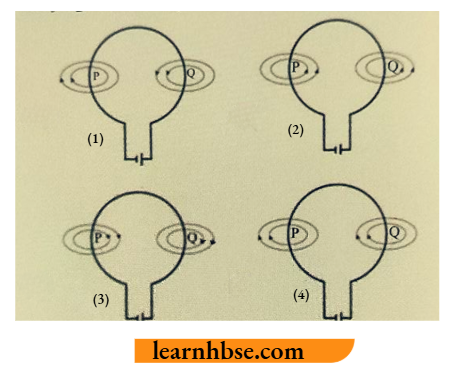
Answer: 2.
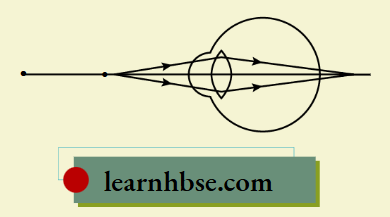
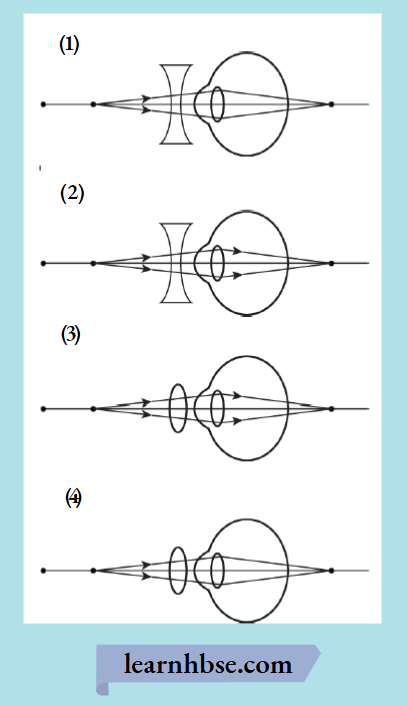
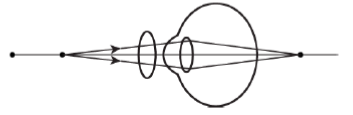
Question 7. The magnetic field lines of solenoid are similar to the magnetic field lines of bar magnet. Which image correctly shows the solenoid as a bar magnet?
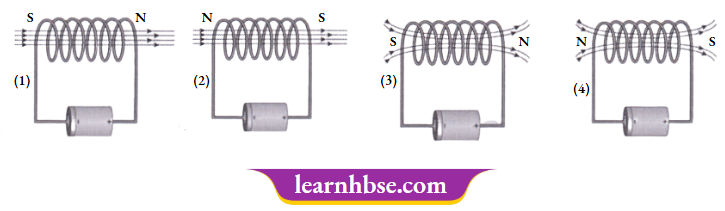
Answer: 3.
Question 8. Where should the magnetic compass be placed in solenoid to get maximum deflection in the magnetic compass?
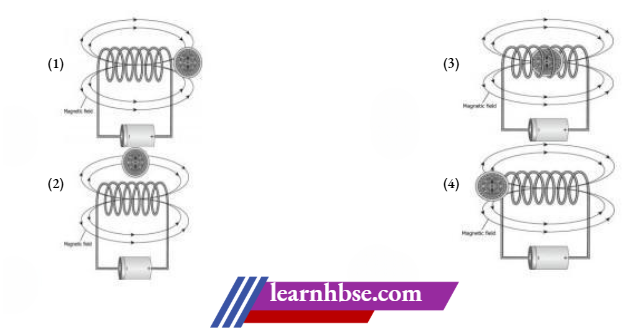
Answer: 3.
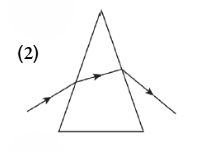
Question 9. The image shows Fleming’s left-hand rule.
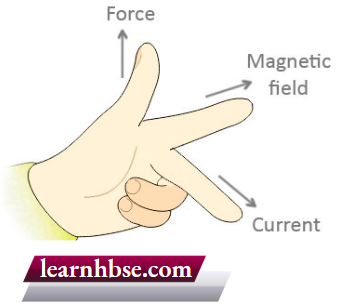
Which option explains the rule to understand the working of the motor?
- When a current-carrying conductor is moved with a force, it creates a magnetic field.
- When a conductor is moved inside a magnetic field, current is produced in the conductor.
- When a magnetic field is moved relative to the conductor, current is produced in the conductor.
- When a current carrying conductor placed in a magnetic field, it experiences a force by magnetic field.
Answer: 4. When a current carrying conductor placed in a magnetic field, it experiences a force by magnetic field.
Question 10. A metal rod PQ. is placed in the magnetic field. The ends of the rod are connected with a battery using wires.
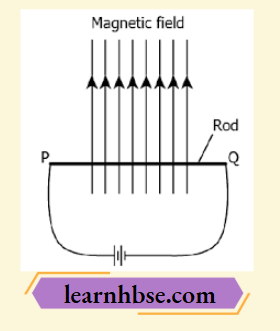
Where will the rod move?
- Upward
- Downwards
- Into the field
- Out of the field
Answer: 4. Out of the field
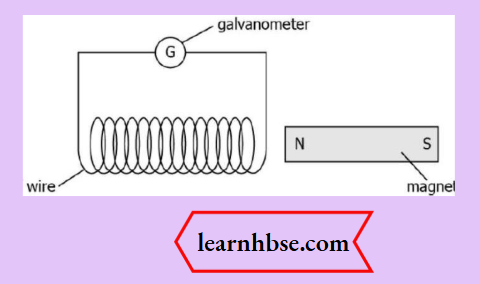
Question 11. A student inserts a bar magnet in the coil. The student observes deflection in the galvanometer connected to the coil. What will happen if the magnet is continuously getting in and out of the coil?
- The current induced in the coil will increase
- The current will change its direction continuously
- The magnetic field will create a motion in the coil
- The magnetic field of the bar magnet would keep decreasing
Answer: 2. The current will change its direction continuously
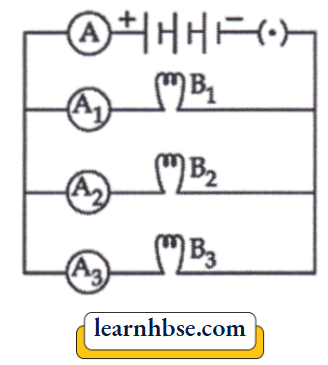
Question 12. A student makes an arrangement to study electromagnetic induction, as shown.
She changes the arrangement in four different ways.

In which trial would the galvanometer remain undeflected?
- Trial 1
- Trial 2
- Trial 3
- Trial 4
Answer: 4. Trial 4
Question 13. The image shows the components of an electric generator.
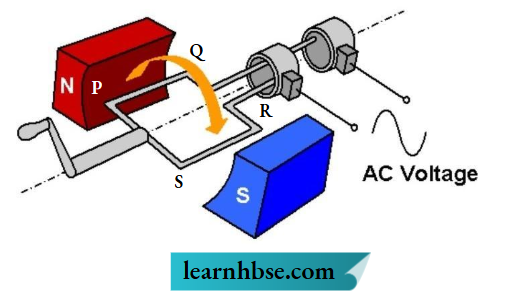
When the coil PQRS is rotated as shown. What is the direction of electric current when coil completes half cycle of the rotation?
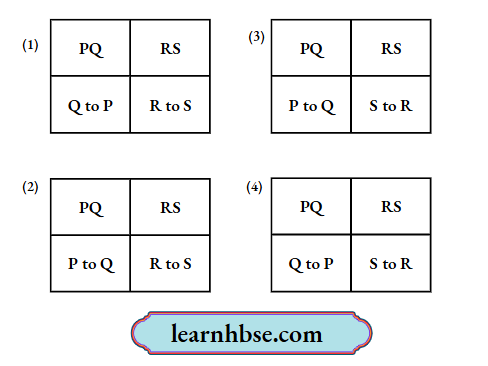
Answer: 2.
Question 14. Appliances that have a metal body are generally connected to the earthing wire. What is the reason to earth these wires?
- To prevent an excess of current
- To prevent the leakage of current
- To provide extra current to appliance
- To provide high resistance to the appliance
Answer: 2. To prevent the leakage of current
Question 15. Which diagram shows the domestic electric circuit?
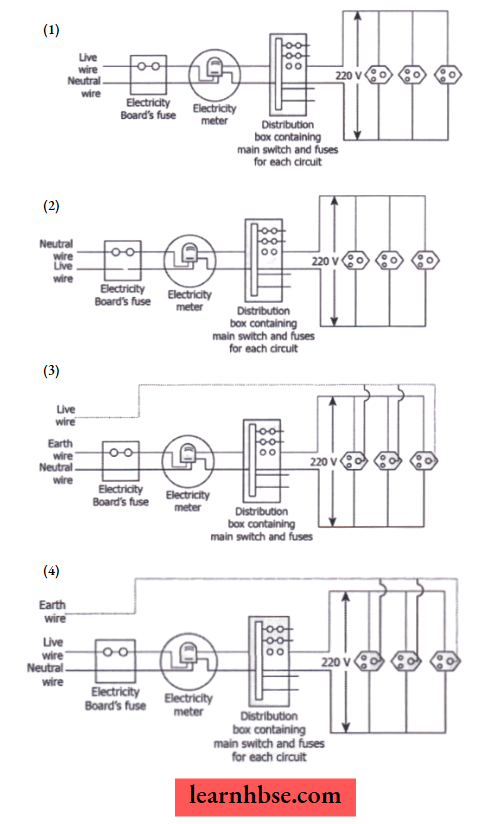
Answer: 4.
Chapter 4 Magnetic Effects Of Current Very Short Questions And Answers
Question 1. Why does a compass needle show deflection when brought near a current carrying conductor?
Answer: The magnetic field is produced around the current carrying conductor.
Question 2. Positively charged particles moving towards the west are deflected towards the north by a magnetic field. What will be the direction of the magnetic field?
Answer: Upward direction in accordance with Fleming’s left hand rule.
Question 3. If you hold a coil of wire next to magnet, no current will flow in the coil. What else is needed to induce a current?
Answer: Relative motion between the coil and the magnet.
Question 4. What is the qualitative effect of inserting an iron core into a current-carrying solenoid?
Answer: Magnetic field becomes very strong.
Question 5. How is the magnetic field inside the long solenoid carrying current?
Answer: The Magnetic field is uniform inside the long solenoid carrying current.
Question 6. Name the rule for finding the direction of the magnetic field produced by a straight current-carrying conductor.
Answer: Maxwell’s right-hand thumb rule.
Question 7. What is the shape of a current-carrying conductor whose magnetic field pattern resembles that of a bar magnet?
Answer: Solenoid
Question 8. A circular conducting coil has ‘n’ turns. If the magnitude of the magnetic field produced by a single coil is B, then what is the magnetic field of the entire coil?
Answer: Since the magnetic field produced by current-carrying wire at a given point depends directly on the current passing through it. Therefore, if there is a circular coil having “n” turns, the field produced is “n” times as large as that produced by a single turn. This is because the current in each circular turn has the same direction, and the field due to each turn then just adds up.
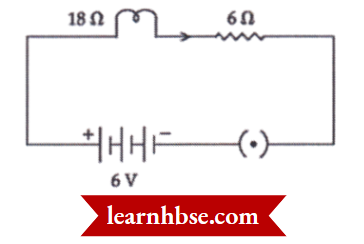
Question 9. A soft iron bar is enclosed by a coil of insulated copper wire as shown in the figure. When the plug of the key is closed, then where would the face B of the iron bar be marked?
Answer: N-Pole
Chapter 4 Magnetic Effects Of Current Short Questions And Answers
Question 1. For the coil in the diagram below, when the switch is pressed:
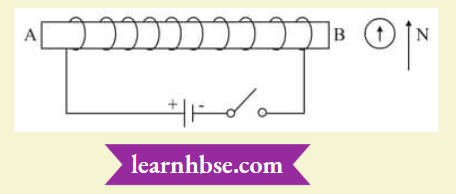
- What is the polarity of end A?
- Which way will the compass point then?
Answer:
- End A becomes the S-pole because current flows in a clockwise direction at A.
- When A becomes S-pole, the other end becomes N-pole. So, the tip of the compass (which also has North polarity) moves away from this end i.e., the tip moves towards the right.
Question 2. What, according to Maxwell’s Right Hand Thumb rule, will be the direction of the current when lines of the magnetic field are in the anti-clockwise direction?
Answer:
The current will be flowing in the upward direction when the direction of the magnetic field is in the anti-clockwise direction.
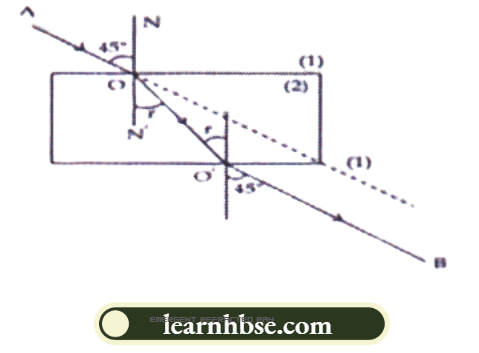
Question 3. The figure given below shows the magnetic field between two magnets:
- Label the other poles of the magnets.
- Which is the weaker magnet?
Answer:
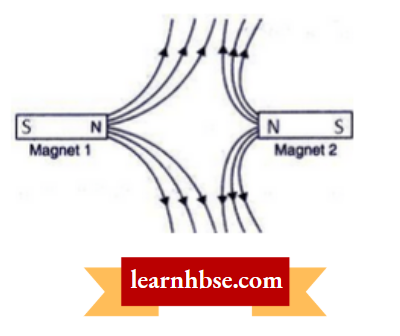
Magnet 2 is weaker.
Question 4. What are the two ways in which you can trace the magnetic field pattern of a bar magnet?
Answer:
- By using iron filings
- By using compassion
Question 5. Copy the figure below which shows a plotting compass and a magnet. Label the North pole of the magnet and draw the field line on which the compass lies.
image
Answer:
image
Question 6.
- Mention the factors on which the direction of force experienced by a current-carrying conductor placed in a magnetic field depends.
- A proton beam is moving along the direction of a magnetic field. What force is acting on the proton beam?
Answer:
- The direction of the force exerted on experienced by a current carrying conductor mainly depends on the two factors:
- The direction of the current , the direction of flow of positive charge determine the direction of the force as described by the Flemings left hand rule,
- The direction of the magnetic field; the force exerted on the conductor depends on the orientation of the magnetic field. This is also defined according to the Flemings left hand rule,
- As the proton beam is moving along the direction of the magnetic field it will experience no force. The strength of the magnetic field depends on the orientation of the conductor in the magnetic field.
It experiences maximum force when the direction of flow of current and the magnetic field is perpendicular to each other i.e. the angle between the two is, let’s say θ = 90° as shown in the figure (2). If the direction of the current and the magnetic field is parallel i.e. θ = 0° as shown in the figure (1), the conductor will experience no force.
image
Question 7. What are the three factors which cause a change in magnetic flux of the coil?
Answer:
Changes in the magnetic flux of a coil occur due to:
- Relative motion between a coil and a magnet placed near it.
- Relative motion between a coil and a current-carrying conductor placed near it.
- Change of current in the conductor placed near the coil.
Question 8. The diagram below shows a bar magnet surrounded by two compasses numbered 2 and 4. What directions will these compasses show?
image
Answer:
Directions shown by the needle of compasses 2 and 4 would be as shown below.
image
This is because the magnetic field lines arise from the North Pole and end at the South Pole.
Question 9. A simple motor is made in a school laboratory. A coil of wire is mounted on an axle between the poles of a horseshoe magnet, as illustrated.
image
In the example above, coil ABCD is horizontal and the battery is connected as shown.
- For this position, state the direction of the force on the arm AB.
- Why does the current in the arm BC not contribute to the turning force on the coil?
Answer:
- Downwards
- Because BC is in the same direction as the direction of field lines. Force is minimum when the direction of current in the conductor is the same as that of the magnetic field. BC will not contribute as the force on this part of the coil will be cancelled by the force on DA.
Question 10. Geeta performed an activity in the school laboratory to observe the effects of magnetic field lines. Based on her observation, she has drawn the magnetic field lines of two magnets as shown in fig. 1 and fig. 2.
image
- Select the figure that represents the correct pattern of field lines. Give reasons for your answer.
- Also, name the poles of the magnets facing each other.
Answer:
- Figure B represents the correct pattern of field lines. In figure A, field lines cross each other which is not possible because if they cross each other, at the point of intersection, there would be two directions of field lines,
- In figure B, field lines are emerging in nature, so poles of magnet facing each other are north poles while opposite faces will have south polarity.
Question 11. A student drew three magnetic field lines 1, 2 and 3 of a bar magnet with the help of a compass needle as shown in the figure.
image
Is this configuration possible? If not, then what is wrong in the given figure and why?
Answer:
No, this type of configuration is not possible as:
Two field lines cannot intersect each other,
Direction of field line as it emerged from south pole and merged at north pole. ‘3’ is wrong as, it emerged from south pole and merged at north pole.
Question 12.
- What are the patterns formed by the circular loop carrying current?
- Which rule is used to find the direction of the magnetic field produced due to the electric current in a circular loop?
- On which factors does the strength of a magnetic field depend?
Answer:
- The circular loops carrying current forms concentric circular patterns of the magnetic field due to electric current.
- The direction of the magnetic field of the loop carrying current can be determined by the clock face rule.
- The strength of the magnetic field due to current depends on the
- Number of turns of wire in the coil
- Radius of the coil
- Current flowing in the coil.
Question 13. How does the strength of the magnetic field at the centre of a circular coil of a wire depend on?
- Radius of the coil
- Number of turns of wire in the coil
- Draw the magnetic lines of force in case of a circular coil of wire
Answer:
- The strength of the magnetic field (B) is inversely proportional to the radius of the circular loop (r).
- The strength of the magnetic field (B) is directly proportional to the number of turns in the coil (N).
- The magnetic field lines will be as shown below.
image
Question 14. A coil of insulated copper wire is connected to a galvanometer. What will happen if a bar magnet is held stationary inside the coil?
Answer:
When a bar magnet is held stationary inside the coil, there will be no deflection in the galvanometer indicating that no current is produced in the coil.
Question 15.
- If a current carrying straight conductor is placed in east-west direction, then find the direction of the force experienced by the conductor due to earth’s magnetic field.
- Mona draws magnetic field lines of field close to the axis of a current carrying circular loop. As she moves away from the centre of the circular loop she observes that the lines keep on diverging. How will you explain her observation?
Answer:
- The force will act in upward direction perpendicular to both, the direction of current as well as to the field. The direction of force experienced by the conductor gets reversed, i.e., in the downward direction.
- Strength of the magnetic field decreases as distance increases. This is indicated by the decrease in degree of closeness of the lines of field.
Question 16. A magnetic field is described by drawing the magnetic field lines. When a small north magnetic pole is placed in the magnetic field created by a magnet, it will experience a force. And if the North Pole is free, it will move under the influence of the magnetic field. The path traced by a north magnetic pole free to move under the influence of a magnetic field is called a magnetic field line.
image
Since the direction of magnetic field line is the direction of force on a north pole, so the magnetic field lines always begin from the N-pole of a magnet and end on the S-pole of the magnet. Inside the magnet, however the direction of magnetic field lines is from the S-pole of the magnet to the N-pole of the magnet. Thus, the magnetic field lines are closed curves. When a small compass is moved along a magnetic field line, the compass needle always sets itself along the line tangential to it. So, a line drawn from the south pole of the compass needle to its north pole indicates the direction of the magnetic field at that point.
- Do the magnetic field lines intersect? If not, why?
- A strong bar magnet is placed vertically above a horizontal wooden board. What would be the magnetic lines of force?
- Where do we use Magnetic field lines?
Answer:
- No two magnetic field lines are found to cross each other. If two field lines crossed each other, it would mean that at the point of intersection, the compass needle would point in two directions at the same time, which is not possible.
- The magnetic field and hence the magnetic line of force exist in all the planes all around the magnet.
- The relative strength of the magnetic field is shown by the degree of closeness of the field lines and the direction of the magnetic field is obtained by the tangent to the field lines at the point of intersection.
Question 17. Diagram below shows a circuit containing a coil wound over a long and thin hollow cardboard tube.
image
- Show the polarity acquired by each face of the solenoid.
- Draw the magnetic field lines of force inside the coil and also show their direction.
Answer:
- The polarity acquired by the two ends is as shown below. (A shows North and South polarity).
image
Question 18. Identify the poles of the magnet in the given figures:
image
Answer:
1. Field lines emerge from north pole (N) and merge at the south pole (S) in figure (1), So the poles of the magnet are:
image
2. Field lines emerge from north pole (N) and merge at the south pole (S) in figure (2), So the poles of the magnet are:
image
Question 19. Richa is performing an experiment on magnetism for which she has used two magnets A and B. She felt that there was an attraction between the magnets. So, she drew the magnetic field lines as below.
image
But her teacher said that the diagram was wrong.
- Why was the diagram wrong?
- Draw the correct diagram.
- What does the direction of thumb indicate in the right-hand thumb rule. In what way this rule is different from Fleming’s left-hand rule?
Answer:
1. From the drawing of Richa it is clear that the magnetic north poles are facing each other. But there was an attraction between the magnets. So, north pole of one magnet was facing the south pole of the other magnet.
2. The correct diagram is either of the two diagrams shown below:
image
3. In the right-hand thumb rule the r thumb indicates the direction of current in the straight conductor held by curled fingers, whereas in Fleming’s left-hand rule the thumb gives the direction of force experienced by current-carrying conductor placed in an external magnetic field.
Chapter 4 Magnetic Effects Of Current Long Questions And Answers
Question 1. Is the magnetic field same all around a bar magnet? Explain with reasons.
Answer:
No, magnetic field strength varies at every point around it. Magnetic field strength depends on the number of field lines per unit area.
If the field lines per area is more, then the magnetic strength in that area is strong, and if the field lines per area is less, then the magnetic strength is weak.
As the magnetic field lines per unit area is maximum at the poles, the magnetic strength is also maximum in that region.
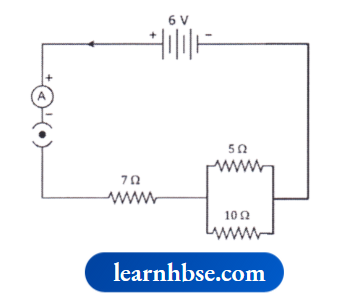
Question 2. PQ is a current-carrying conductor in the plane of the paper as shown in the figure below.
image
- Find the directions of the magnetic fields produced by it at points R and S.
- Given r1 > r2, where will the strength of the magnetic field be larger? Give reasons.
- If the polarity of the battery connected to the wire is reversed, how would the direction of the magnetic field be changed?
- Explain the rule that is used to find the direction of the magnetic field for a straight current-carrying conductor.
Answer:
- The magnetic field lines are produced is into the plane of the paper at R and out of it at S.
- Field at S > Field at P The Magnetic field strength for a straight current-carrying conductor is inversely proportional to the distance from the wire.
- If polarity is reversed, the current will go from top to bottom in the wire and the magnetic field lines goes in the clockwise direction on the plane which is perpendicular to the wire carrying current,
- According to the Right-Hand thumb rule, the thumb is aligned to the direction of the current, and the direction in which the fingers are wrapped around the wire will give the direction of the magnetic field.
Question 3. An insulated copper wire wound on a cylindrical cardboard tube such that its length is greater than its diameter is called a solenoid. When an electric current is passed through the solenoid, it produces a magnetic field around it. The magnetic field produced by a current-carrying solenoid is similar to the magnetic field produced by a bar magnet. The field lines inside the solenoid are in the form of parallel straight lines. The strong magnetic field produced inside a current-carrying solenoid can be used to magnetise a piece of magnetic material like soft iron when placed inside the solenoid. The strength of the magnetic field produced by a current-carrying solenoid is directly proportional to the number of turns and the strength of the current in the solenoid.
- What would be the strength of the magnetic field inside a long current-carrying straight solenoid?
- By using which rule we can find the north-south polarities of an electromagnet?
- A long solenoid carrying a current produces a magnetic field B along its axis. If the current is double and the number of turns per cm is halved, then what will be the new value of magnetic field?
- A soft iron bar is enclosed by a coil of insulated copper wire as shown in figure.
image
When the plug of the key is closed, then where would the face B of the iron bar be marked?
Answer:
- Magnetic field inside an infinite solenoid is uniform. Hence it is same at all points.
- Clock face rule
- For a long solenoid, magnetic field B oc In; where I is the flowing current and n is number of turns per unit length in the solenoid. Therefore, in the given case magnetic field will remain unchanged.
- N-pole.
Question 4.
1. An induced emf is produced when a magnet is plunged into a coil. On which factor or factors does the magnitude of induced emf depend?
2. The wire in the figure below is being moved downwards through the magnetic field, so as to produce an induced current.
image
- What would be the effect of using a stronger magnet?
- What would be the effect of holding the wire still in the magnetic field?
Answer:
1. The number of turns of the coil, the speed with which the magnet is moved, and the strength of the magnet.
- The magnitude of the induced current increases.
- The induced current is zero.
Question 5. When a current is passed through the circular loop of wire, the magnetic field lines near the coil are nearly circular and concentric. At the centre of the circular loop, the magnetic field lines are straight. The strength of the magnetic field produced by a current-carrying circular coil (or circular wire) depends on:
- Radius of the circular coil.
- Number of turns of wire in the circular coil. The direction of the field lines can be found by applying the Right-Hand Thumb Rule.
image
- A long horizontal power line is carrying a current of 100 A in the east-west direction. What is the direction of the magnetic field at a point 1.0 m below it?
- What type of curve we get, between magnetic field and distance along the axis of a current-carrying circular coil?
Answer:
- The current flows in the east-west direction. From the right-hand rule, we get the direction of the magnetic field as from north to south. The direction of the magnetic field will be the same at every point below the power line.
- At smaller distances, the magnetic field will be described by concentric circles around the wire. As the distance increases, the circles become larger and larger. At the centre of the loop or coil, the magnetic field will appear as a straight line.