Chapter 1 Life Processes Multiple Choice Questions And Answers
Question 1. Which statement can be concluded from the image?

- Plants absorb CO2 from air and H2O from the soil as raw materials and convert them into glucose
- Plants absorb CO2 from the soil and H2O from air as raw materials and convert them into glucose
- plants absorb O2 from air and glucose from the soil as raw materials and convert them into light energy
- Plants absorb O2 from air and minerals from the soil as raw materials and convert them into heat energy.
Answer: 1. plants absorb CO2 from air and H2O from the soil as raw materials and convert them into glucose
Question 2. A student sets up an experiment to study the importance of nutrition in plants. The student takes 2 pots, pot 1 and pot 2 each with the same healthy plant. Both the pots were placed in the garden and watered properly. Pot1 was kept as such, while pot 2 was kept in an air tight glass box with caustic soda. Caustic soda absorbs carbon dioxide present in the surrounding. After 2 days, the student observes that the plant kept in the garden is healthy while the plant placed in container shed leaves and droops. What is the likely reason for this observation?
- Lack of nutrients in the soil
- Absence of oxygen for survival
- Inability to perform photosynthesis
- Absorption of light by caustic soda restricting growth
Answer: 3. Inability to perform photosynthesis
Question 3. Which of the equation show correct conversion of CO2 and H2O into carbohydrates in plants?
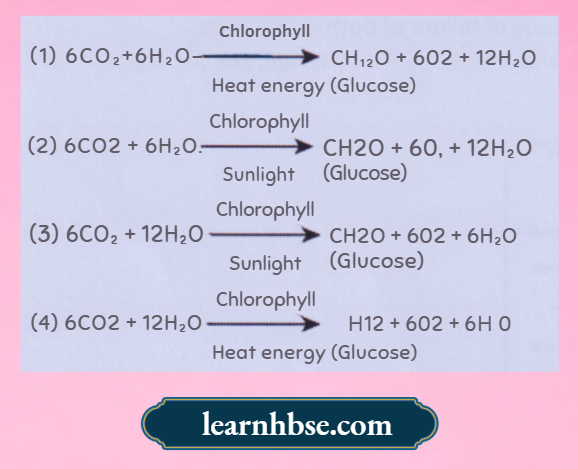
Answer: 3. 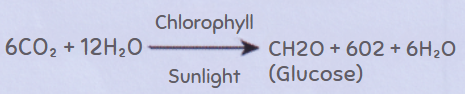
Question 4. A student sets up an experiment to study the photosynthesis in plants. The student destarched a potted plant by keeping it in a dark room for 3 days. Half of the portion of destarched leaf was placed in a bottle containing caustic potash (absorbs CO2) as shown:
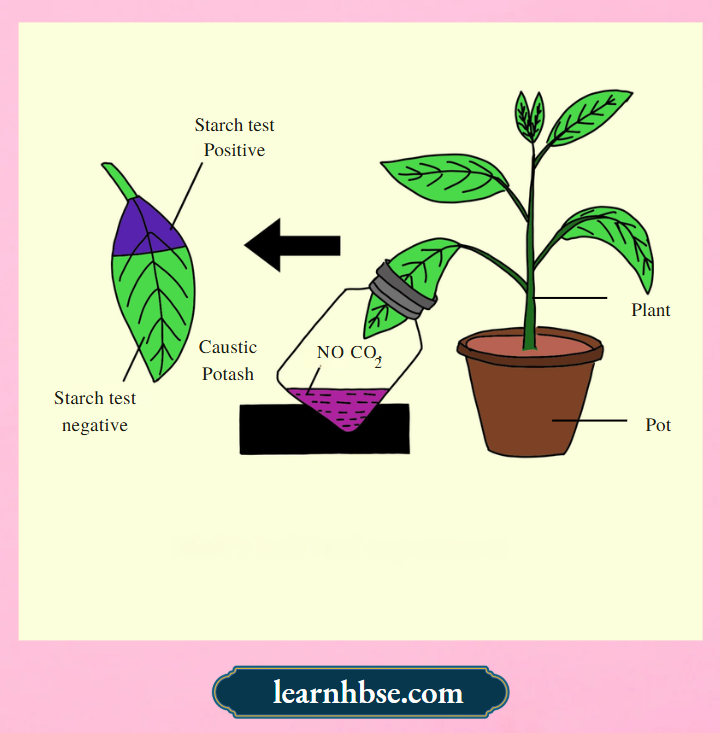
The student then places the plant in light and tests the leaf after 5 hours for the presence of starch. The portions inside the bottle shows negative starch test by reflecting no change in colour when react with iodine, however, other upper portions of the leaf gave positive starch test showing blue-black colour with iodine. What can be evaluated from this experiment?
- Carbon dioxide is directly linked with the colour of leaf
- Carbon dioxide is necessary for preparing carbohydrate
- Lack of carbon dioxide increases amount of starch in plant
- Lack of carbon dioxide slows the process of photosynthesis
Answer: 2. Carbon dioxide is necessary for preparing carbohydrate
Question 5. The image shows the bread moulds on a bread.
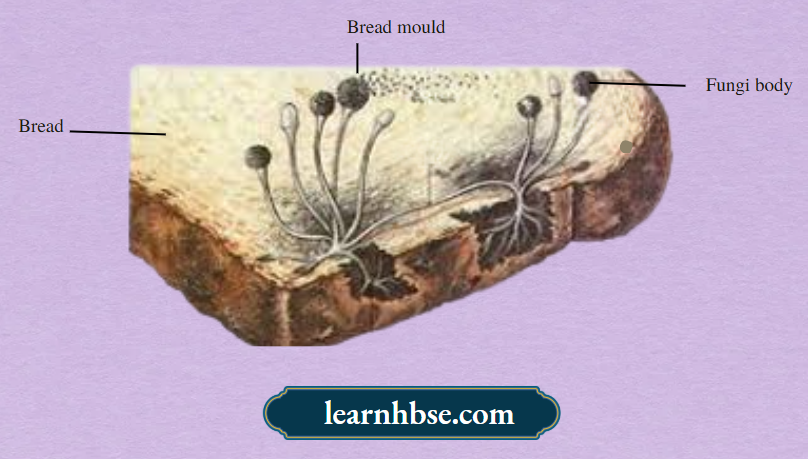
How these fungi obtain nutrition?
- By eating the bread on which it is growing
- By using nutrients from the bread to prepare their own food
- By breaking down the nutrients of bread and then absorbing them
- By allowing other organisms to grow on the bread and then consuming them
Answer: 3. By breaking down the nutrients of bread and then absorbing them
Question 6. The image shows how Amoeba obtains nutrition.
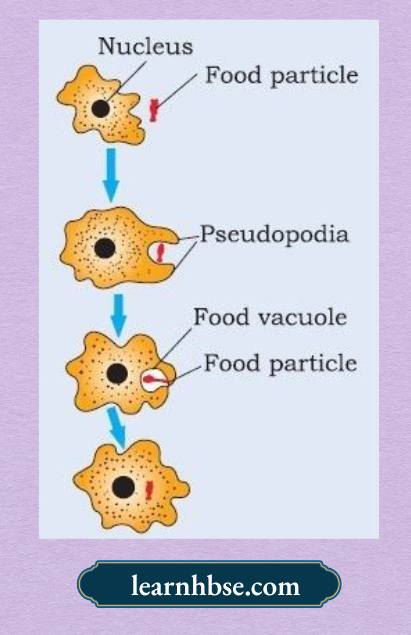
How this process is advantageous for Amoeba?
- Capturing of food takes less time
- Complex food can be digested easily
- More amount of food can be consumed
- Fast distribution of nutrition within the body
Answer: 4. Fast distribution of nutrition within the body
Question 7. The image shows the human digestive system.
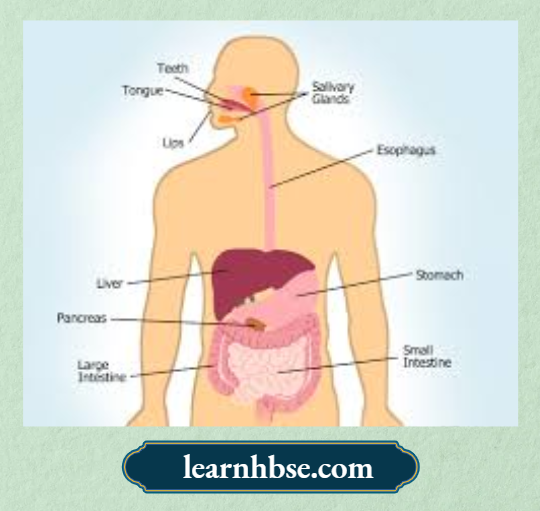
Digestion of food starts from which organ of the digestive system?
- Mouth due to the presence of saliva
- Oesophagus that moves the food in gut
- That releases juices for fat breakdown
- Which helps in mixing food with digestive juices
Answer: 1. Mouth due to the presence of saliva
Question 8. The image shows a cross section of small intestine.
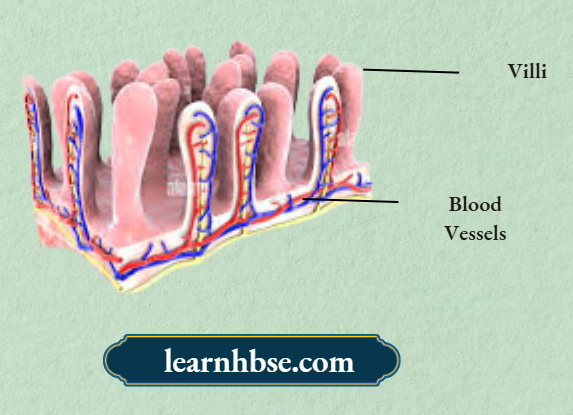
What will be the likely happen if the number of villi increases in the intestine?
- Increase in the absorption of food
- Fast elimination of waste from the body
- Increase in flow of blood in the small intestine
- Fast breakdown of larger food particles into smaller ones
Answer: 1. Increase in the absorption of food
Question 9. An incomplete equation for the digestion of starch using saliva is shown as:
Saliva + Starch (in test tube)→ What will be the likely outcome of this?
- Saliva will convert starch into complex fat molecules.
- Saliva will convert starch into complex sugar molecules.
- Saliva will breakdown starch into simple sugar molecules.
- Saliva will breakdown starch into simple protein molecules.
Answer: 3. Saliva will breakdown starch into simple sugar molecules.
Question 10. A student sets up an experiment to study the role of enzymes in digestion of food. In which test tube, the digestion of protein will occur?

- Test tube A as pepsin will breakdown into simple molecules.
- Test tube B as HCI will breakdown protein into simple molecules.
- Test tubes A as pepsin will breakdown protein into simple molecules.
- Test tube B as HCI will activate pepsin for breakdown of protein into simple molecules.
Answer: 2. Test tube B as HCI will breakdown protein into simple molecules.
Question 11. The image shows the flow diagram for the breakdown of glucose in yeast.

Under which condition these types of products are obtained?
- In the presence of oxygen
- In the absence of oxygen
- The presence of carbon dioxide
- In the absence of carbon dioxide
Answer: 2. In the absence of oxygen
Question 12. Which pathway will occur in the cell of an athlete who is performing 100m sprint?
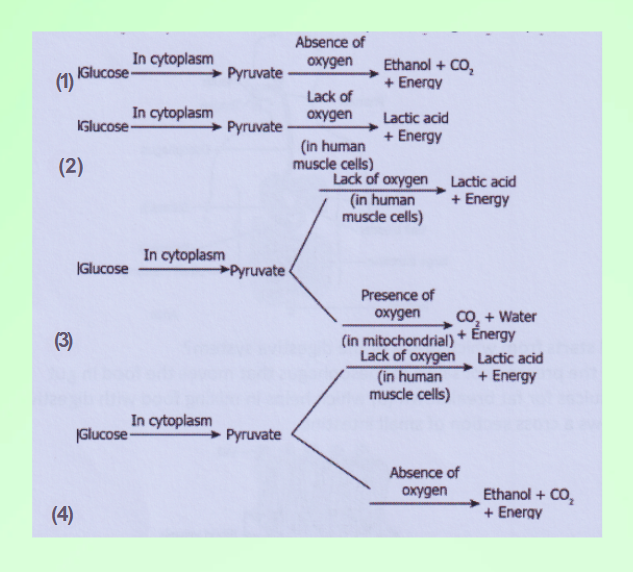
Answer: 3. 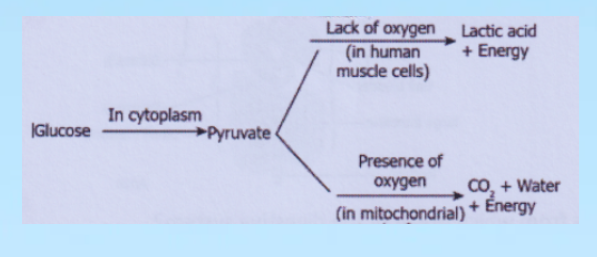
Question 13. A student setup an experiment to study the human respiratory system. In the experiment, the student places candle and a living cockroach in the flask A, while a candle and a dead cockroach in flask B. The burning of candle needs oxygen.
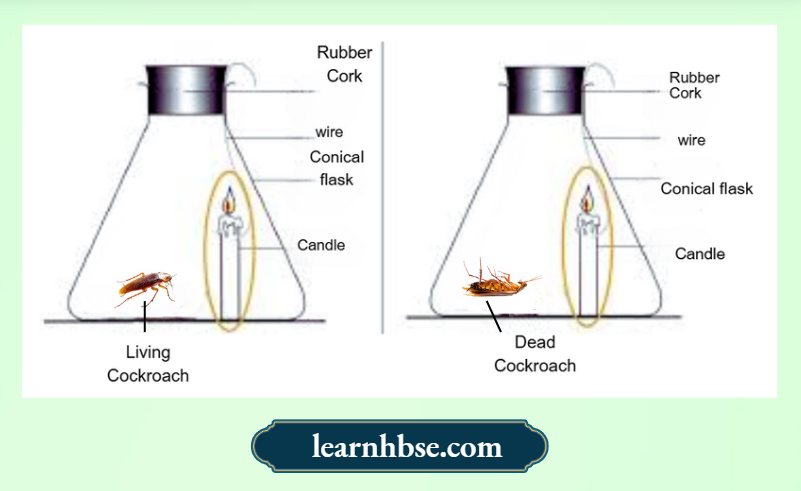
After 10 minutes, the student observes that the candle in flask A extinguish faster while candle in flask B keeps burning for a longer time. What can be evaluated from this experiment?
- Candle produces high amount of carbon dioxide
- Living beings consumes oxygen during respiration
- Burning of candle decreases the life span of cockroach
- Water vapours produced by living beings prevents burning of candle
Answer: 2. Living beings consumes oxygen during respiration
Question 14. A student sets up an experiment to study human respiration using lime water, test tube and a straw. Lime water is colourless in the absence of CO2 and is milky in its presence. The student fills a freshly prepared limewater in a test tube and blows air through straw into the limewater. It was observed that the solution turns cloudy as shown.
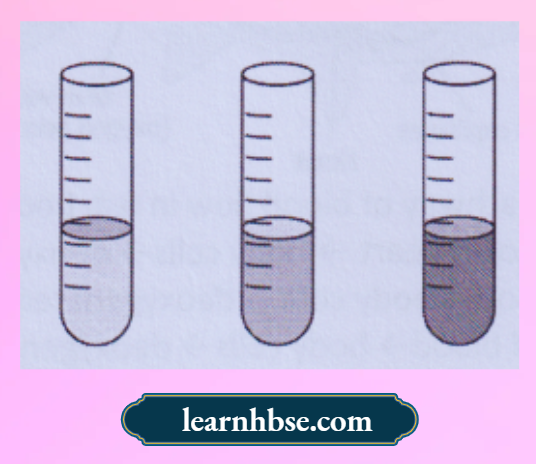
What can be evaluated from this observation?
- Oxygen is exhaled during respiration
- Glucose is produced during respiration
- Dioxide is exhaled during respiration
- Water vapours are produced during respiration
Answer: 3. Dioxide is exhaled during respiration
Question 15. The image shows the transport of gases in body through heart and lungs.
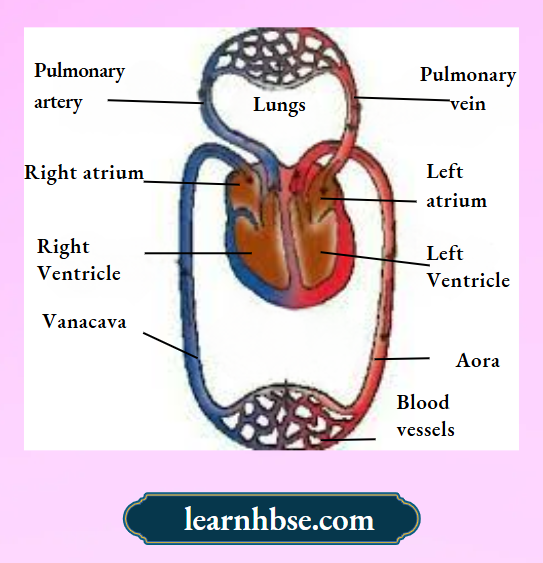
Which option correctly shows the transport of oxygen to the cell?
- Lungs →pulmonary vein →left atrium →left ventricle →aorta → body cells
- Lungs vein →right atrium →right ventricle → aorta body cells
- Lungs →pulmonary artery →left atrium → left ventricle→ venacava → body cells
- Lungs →pulmonary artery →right atrium → right ventricle→ venacava → body cells
Answer: 1. Lungs →pulmonary vein→left atrium →left ventricle →aorta → body cells
Question 16. The image shows oxygenated and de-oxygenated blood in the human heart.
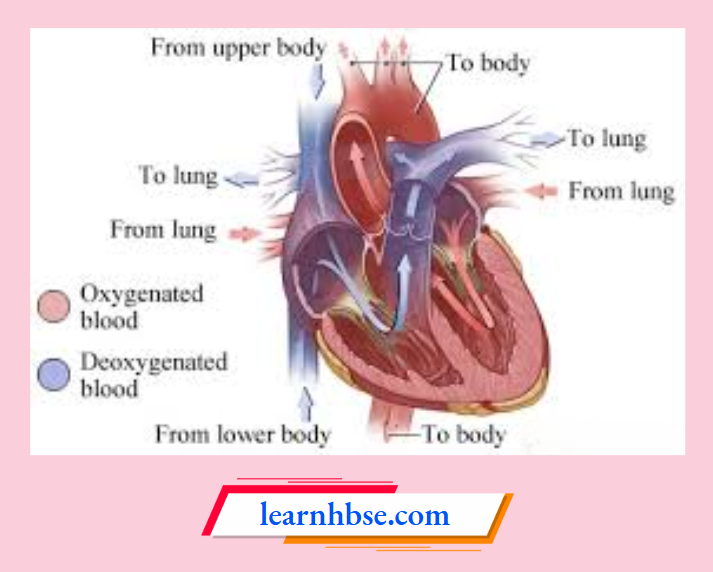
What is the direction of deoxygenated blood from right atrium of the heart?
- Towards the lungs
- Towards the lower body
- Towards the upper body
- Towards the left atrium of heart
Answer: 1. Towards the lungs
Question 17. The image shows the circulation of blood in fishes.
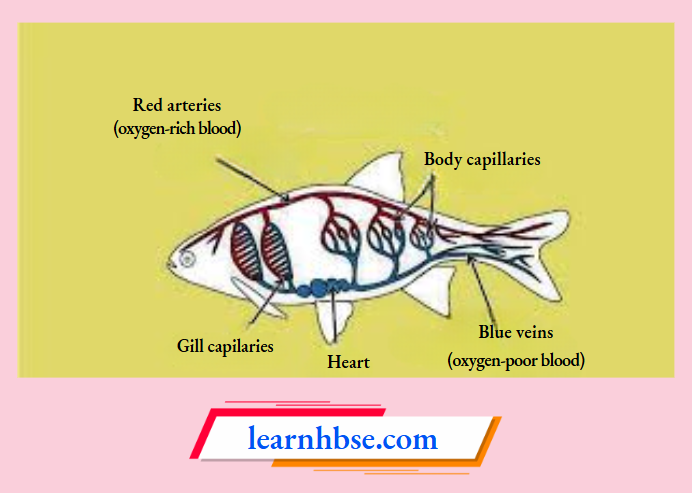
Which option correctly traces the pathway of blood flow in fish body?
- Gill capillaries→ oxygenated blood→heart → body cells→ deoxygenated blood-*gills
- Gill capillaries→oxygenated blood→ body cells→ deoxygenated blood→ heart→gills
- capillaries→ heart blood→ body cells→ deoxygenated blood→heart→gills
- Gill capillaries→ oxygenated blood→heart → body cells→ deoxygenated blood→heart→gills
Answer: 2. Gill capillaries→ oxygenated blood→ body cells→ deoxygenated blood→ heart→gills
Question 18. The image shows the circulation of blood in fishes and humans.
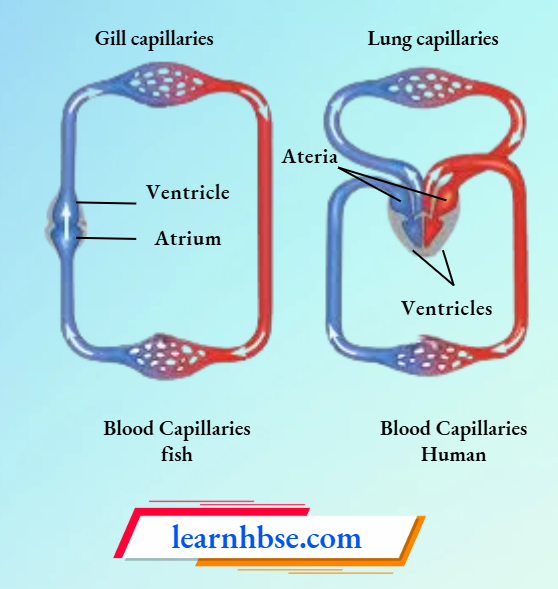
How is the circulations of blood in fish different from that in humans?
- The heart in fish is bigger in size.
- The flow of blood in fish is unidirectional.
- The blood goes through heart only once in fishes.
- The heart of fish has more chambers compared to that of a human.
Answer: 3. The blood goes through heart only once in fishes.
Question 19. The image shows the structure of an artery.
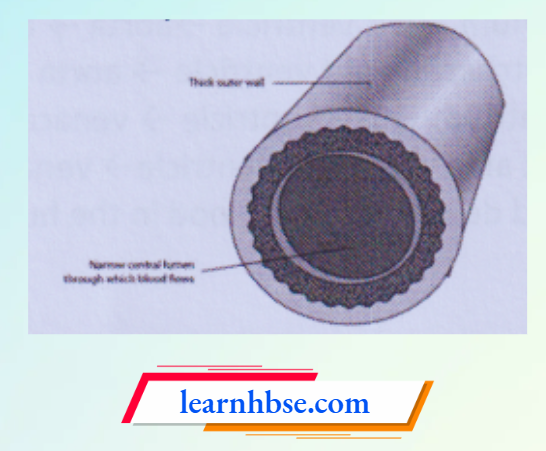
Which statement supports the likely reason for thick walls in arteries?
- To Carry Large Amount Of Blood
- To Allow Easy Exchange Of Gases With Cells
- To Ensure Blood Flows In Only One Direction
- To Sustain The High-Pressure Blood From The Heart
Answer: 4. To Sustain The High-Pressure Blood From The Heart
Question 20. The image shows the healing of a wound.
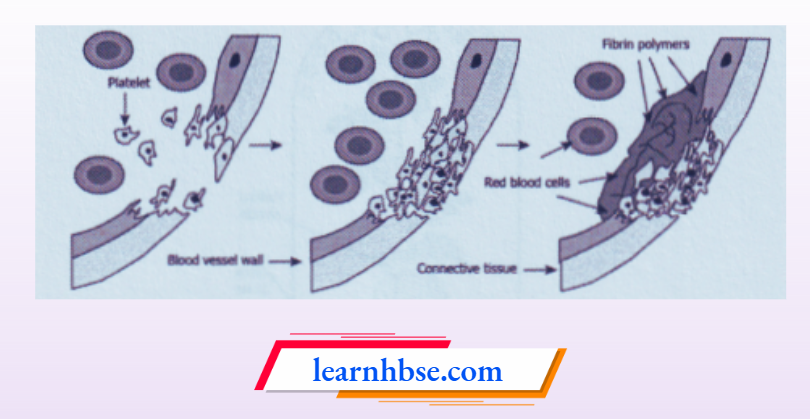
Based on the image, what explains the process?
- Platelets form clot by plugging the site of injury
- Platelets uses component of broken vessel to form clot
- Red blood cells divide and replace the broken vessel at the site of injury
- Red Blood Cells And Platelets Migrate To Site Of Injury And Secrete Substance That Forms New Vessel
Answer: 1. Platelets form clot by plugging the site of injury
Question 21. How water is taken up from soil to the xylem tissue of the plant roots?
- Xylem attracts water molecules
- Roots act as a suction pump for taking water
- Soil expels the water with pressure to the xylem
- Difference in the ion concentration creates a gradient for water movement
Answer: 4. Difference in the ion concentration creates a gradient for water movement
Question 22. A student performs an experiment using a balsam plant with intact stem, leaves, roots and flowers. The plant was kept in a test tube containing eosin solution (a pink colour dye). The test tube mouth was covered using cotton plug as shown
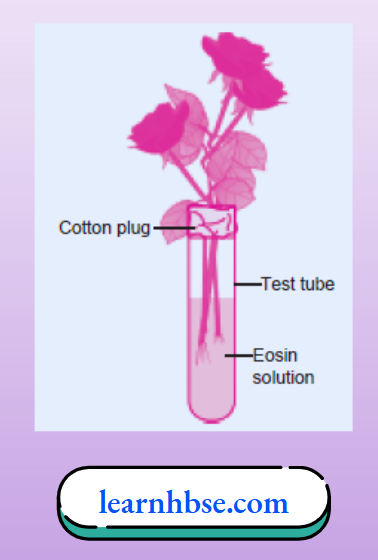
The student kept the plant undisturbed in the lab. After 2-3 hours, a transverse section of stem was obtained using sharp scissors and studied under microscope. The studies reveal the presence of pink colour in the vessels of xylem. What does this observation explain?
- Eosin solution gets stored in the xylem
- Water moves through xylem in the plant
- Xylem reacts with eosin and gives colour
- Most portion of the plant stem is occupied by xylem
Answer: 2. Water moves through xylem in the plant
Question 23. The loss of water from the leaves of the plant is transpiration. How this process is advantageous for the plant?
- It helps in the downward movement of the water.
- It helps the plant to maintain temperature in hot sunny days.
- It acts as a driving force for distribution of food in plant’s body.
- Helps maintain a constant level of water in the soil around the plant.
Answer: 2. It helps the plant to maintain temperature in hot sunny days.
Question 24. A student setup an experiment using a well-watered plant. The plant’s roots and soil were covered with a rubber sheet. The plant was then kept in a glass bell jar and sealed with Vaseline at the bottom part to prevent the flow of air. The student keeps the apparatus in the light and observes water drops inside the jar after 2 hours as shown in the image.

What can be evaluated about transpiration from this experiment?
- Plant leaves give off water in form of vapours.
- Heat from the outside warms the jar which melts the vaseline into vapours.
- Plant absorbs water from environment thus extra water appears on the inside of jar.
- Covered roots and stem of the plant decreases the temperature of jar resulting in condensation of moisture into vapours.
Answer: 1. Plant leaves give off water in form of vapours.
Question 25. The image shows the transport of food material inside plant body with the help of phloem.
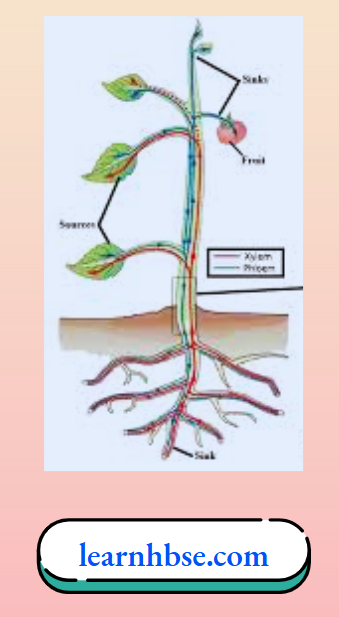
How is food transported from phloem to the tissues according to plants need?
- Food is transported along with the water in plant’s body.
- Food is transported in only direction like water in the plant body through xylem.
- Food is transported from a region with low concentration to higher concentration.
- Food is transported from a region where it is produced to other parts of the plants.
Answer: 4. Food is transported from a region where it is produced to other parts of the plants.
Question 26. The image shows the movement of sucrose into phloem against the concentration gradient which also leads to the movement of water due to osmotic difference. This osmotic pressure allows movement of material in plant body.
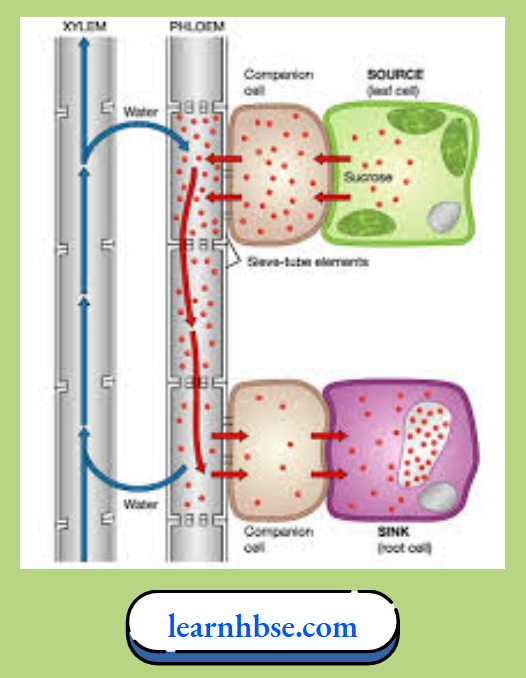
How the movement of sucrose into phloem takes place initially?
- With the help of transpiration
- With the help of water gradient
- With the help of atp molecules
- With the help of adp molecules
Answer: 3. With the help of atp molecules
Question 27. The image shows the excretory system in humans.
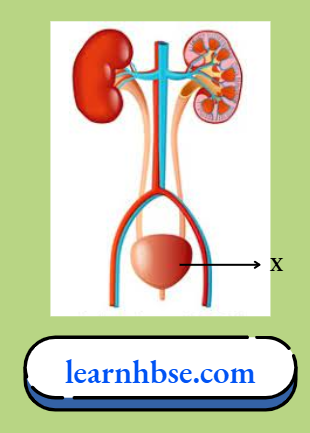
What is the importance of the labelled part in the excretory system?
- It produces urine.
- It filters waste from the blood.
- It stores the urine till urination.
- It carries urine from kidney to outside.
Answer: 3. It stores the urine till urination.
Question 28. The image shows the structure of a nephron.
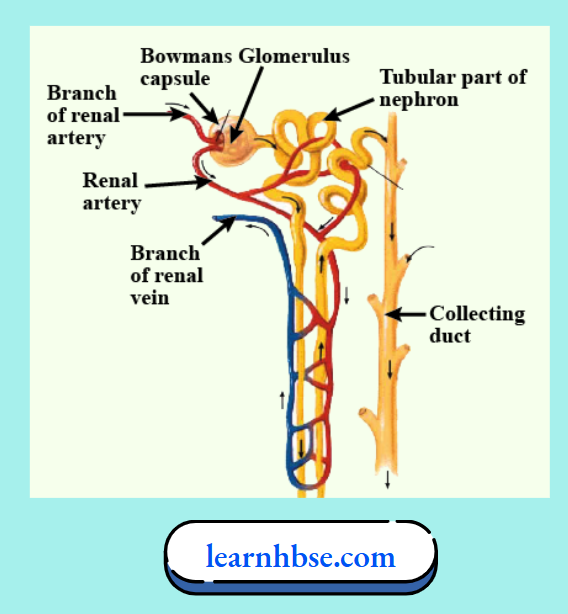
Nephron is a unit of filtration in kidneys that filters waste material. It selectively reabsorbs or excretes water with the help of capillaries that surround it. What is the likely benefit of this?
- It makes the process of filtration at Bowman’s capsule easier.
- It helps keep the output of urine constant throughout the day.
- It helps to uptake and store excess amount of water in the body for later use.
- It maintains the concentration of urine based on the amount of water present in the body.
Answer: 4. It maintains the concentration of urine based on the amount of water present in the body.
Question 29. The image shows the process of photosynthesis in plants

Based on the image, which component is excreted by plants during photosynthesis?
- Carbon dioxide
- Glucose
- Light energy
- Oxygen
Answer: 4. Oxygen
Question 30. A plant gets rid of excess water through transpiration. Which is a method used by plants to get rid of solid waste products?
- Shortening of stem
- Dropping down of fruits
- Shedding of yellow leaves
- Expansion of roots into the soil
Answer: 3. Shedding of yellow leaves
Question 31. The given graph indicates the effect of exercise intensity on carbohydrate consumption.
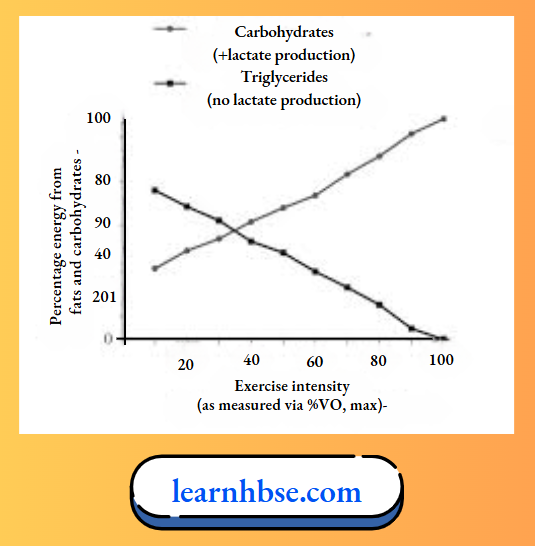
At high intensity of exercise
- The anaerobic consumption of sugars increases
- The aerobic consumption of sugars increases
- The anaerobic consumption of sugars decreases
- No consumption of sugars takes place
Answer: 1. The anaerobic consumption of sugars increases
Chapter 1 Life Processes Very Short Questions And Answers
Question 1. In which of the following group/groups of animals, heart does not pump oxygenated blood to different parts of the body?
- Pisces
- Amphibians
- Amphibians and reptiles
- Pisces and amphibians
Answer: 1. Pisces
Question 2. What processes would you consider essential for maintaining life?
Answer: Nutrition, respiration, transportation and excretion.
Question 3. Which organ of male reproductive system acts as thermoregulator?
Answer: Scrotum acts as thermoregulator.
Question 4. Why is DNA copying an essential part of the process of reproduction?
Answer: DNA copying is essential for inheritance of features from parents to the next generation.
Question 5. What is dialysis?
Answer: The process by which blood is cleared of metabolic wastes in case of a kidney failure is called dialysis.
Question 6. Where do plants get each of the raw materials required for photosynthesis?
Answer: Plants get carbon dioxide and sunlight from atmosphere. It gets water and minerals from the soil.
Question 7. What is the mode of nutrition in fungi and plasmodium?
Answer: Modes of nutrition: Fungi- Saprophytic; Plasmodium- Parasitic
Question 8. Which of the following carries only deoxygenated blood?
- Pulmonary artery
- Pulmonary vein
- Capillary
- Aorta
Answer: 1. Pulmonary artery
Question 9. Which of the following makes a 3-chambered heart less efficient as compared to a 4- chambered heart?
Answer: In a 3-chambered heart, due to mixing of blood in a single ventricle, the parts of the body do not get blood saturated with oxygen. Therefore, a 3-chambered heart is less efficient as compared to a 4- chambered heart.
Question 10. What regulates the opening and closing of stomata?
Answer: The opening and closing of stomata is regulated by kidney-shaped cells called guard cells
Question 11. What will happen in the absence of anther?
Answer: If anther is absent, then pollen grain will not be produced.
Question 12. How do woody plants carry out gaseous exchange?
Answer: Woody plants carry out gaseous exchange through the lenticels.
Question 13. Name the excretory organ in Amoeba.
Answer: Cell membrane.
Question 14.Where does digestion of starch begin in human body?
Answer: The digestion of starch begins inside the mouth.
Question 15. Name the structure through which pollen tube enters the ovule.
Answer: The pollen tube enters the ovule through the stigma.
Question 16. During contraction of heart, what prevents the backflow of blood?
Answer: During contraction of heart, the valves in heart prevent the backflow of blood.
Question 17. Why is potassium hydroxide used in photosynthesis experiments?
- It reacts with carbon dioxide.
- It reacts with oxygen produced.
- It helps in destarching the leaf.
- It eliminates the interference of sunlight
Answer: 1. It reacts with carbon dioxide.
Chapter 1 Life Processes Short Questions And Answers
Question 1. Why do fish die when taken out of water?
Answer: Fish utilise the oxygen dissolved in water for their respiration. When fish are taken out of water, the supply of oxygen to the fish is cut as they cannot absorb and breathe using the oxygen present in the atmosphere. Hence, the fish die after some time.
Question 2. What is the role of HCI in our stomach?
Answer: HCI makes the medium inside the stomach acidic, which is necessary for the activation of enzyme pepsin. HCI also kills the bacteria, which may enter the stomach along with food.
Question 3. How is oxygen and carbon dioxide transported in human beings?
Answer: Oxygen and carbon dioxide are transported in human beings with the help of transportation system. Transport of oxygen: The air present in the alveolar sacs have high concentration of oxygen, while the blood capillaries surrounding the alveolar sacs are deficient in oxygen.
Oxygen diffuses from the alveoli to the blood capillaries where it combines with the haemoglobin to form oxyhaemoglobin. Then the blood reaches the tissues where oxyhaemoglobin breaks into haemoglobin and oxygen. This oxygen enters the cells.
Transport of carbon dioxide: The tissues have high concentration of carbon dioxide than the blood entering them. Therefore, carbon dioxide diffuses from the tissues into the blood. Then it reaches the lungs where it diffuses into the alveoli, and expelled out into the atmosphere through the respiratory tract.
Question 4. Differentiate between single and double circulation found in vertebrates.
Answer:
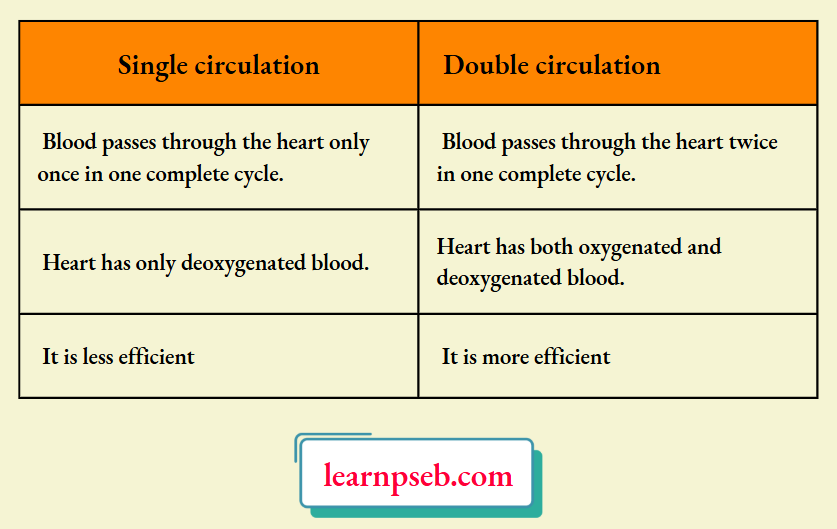
Question 5. How is food transported in plants?
Answer: The food is transported in plants both in upward and downward direction through phloem tissues, which consist of sieve tubes and companion cells.
Question 6. The diagram given below represents a system in the human body. Study the diagram and answer the following questions:
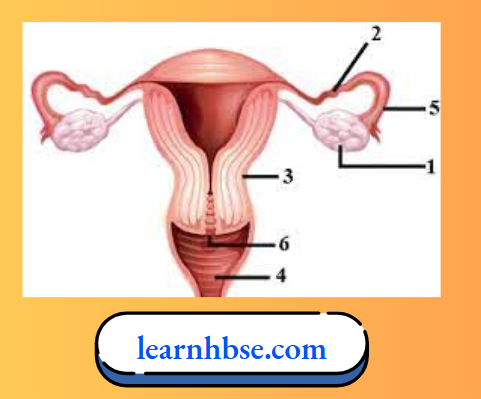
- Label the parts marked 5 and 6.
- Name the two hormones secreted by 1.
Answer:
- Part 5: Oviduct; Part 6: Cervix
- Hormones secreted by 1 (ovary): Oestrogen and Progesterone
Question 7. What is the significance of the testes being located in the scrotal sac outside the abdomen?
Answer: The production and survival of sperm require a temperature which is lower than the normal body temperature. So, the testes are located in the scrotal sac which is outside the abdomen to maintain the temperature at 3*ÿ below the normal body temperature.
Question 8. Why does blood in the arteries flow with jerks and is under pressure?
Answer: Blood in the arteries moves because of the pressure of blood from the heart. Each time the heart pumps, it pushes the blood a little further. Due to this reason it flows with jerks.
Question 9. Do veins rely on heart for movement of blood? Justify your answer.
Answer: Veins do not rely on the heart to move blood. Veins have a system of valves to keep the blood from not moving backward. Movement of blood in veins occurs due to contraction of muscles.
Question 10. What is translocation? Why is it essential for plants?
Answer: Transportation of organic solutes in plants is called translocation. It occurs in the upward as well as downward directions and in the storage organs of roots, fruits, seeds and growing organs.Translocation is necessary because all the plant cells need food to carry out their vital functions.
Question 11. What are villi? Mention their functions.
Answer: Villi are tiny finger-like projections present in the walls of small intestine. The function of villi is to increase the surface area of intestines for efficient food absorption.
Question 12. What is saliva? State its role in the digestion of food.
Answer: Saliva is a watery fluid secreted by the salivary glands in the mouth. Functions of Saliva:
- Moistening food, and helping to create a food bolus, so it can be swallowed easily.
- Saliva contains the enzyme amylase that breaks down starch into simple sugars.
Question 13. How are the alveoli designed to maximise the exchange of gases?
Answer: Alveoli have thin walls and a close network of blood arteries to allow gas exchange between blood and air-filled alveoli. They have a balloon-like structure to maximize surface area in exchange for gas.
Question 14. The diagrams given below are cross-sections of blood vessels:
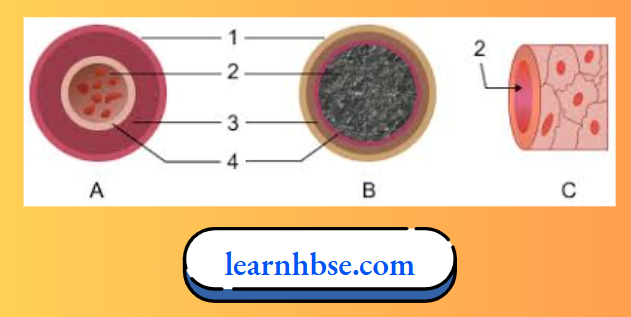
- Identify the blood vessels A, B and C.
- Mention one structural difference between A and B.
Answer:
- A- Artery, B- Vein, C- Blood capillary
- Structural difference between A (artery) and B (vein): In artery valves are not present, whereas in veins, valves are present.
Question 15. State the role of the placenta in the development of the embryo.
Answer: Placenta is a disc-like tissue which develops between the uterus wall and the embryo. Role Of Placenta: Exchange of water between the mother and the foetus; Exchange of nutrients; Exchange of respiratory gases; Removal of nitrogenous wastes from the foetus.; Antibodies cross the placenta and provide immunity to the baby.
Question 16. Explain the cause of cramps after excessive physical exercise.
Answer: During heavy exercise, the demand for energy is high but the supply of oxygen to produce energy is limited. Therefore, anaerobic respiration takes places in the muscles cells to fulfil the demand for energy. This anaerobic breakdown of glucose leads to the formation of lactic acid in muscles. The accumulation of lactic acid in muscles leads to muscle cramps.
Question 17. Pre-natal sex determination has been prohibited by law. State two reasons.
Answer:
- To prevent female foeticide in desire for a male child.
- Declining female-male sex ratio.
Question 18. Rahul complained of acidity on reaching home after a marriage. Explain the reason for acidity.
Answer: When we eat more food or spicy food, our digestive system has to work more by releasing more enzymes for digestion. The stomach releases more HCI to digest more food because of which a lot of acid is formed. This may cause acidity.
Question 19. Most of the CO2 produced in a tissue enters the red blood cells by diffusion. What happens to this CO2?
Answer: The pigment haemoglobin present in RBCs binds with CO2 and gets transported to the lungs through blood from where it is released out through the nostrils.
Question 20. Study the diagram given below and answer the following questions
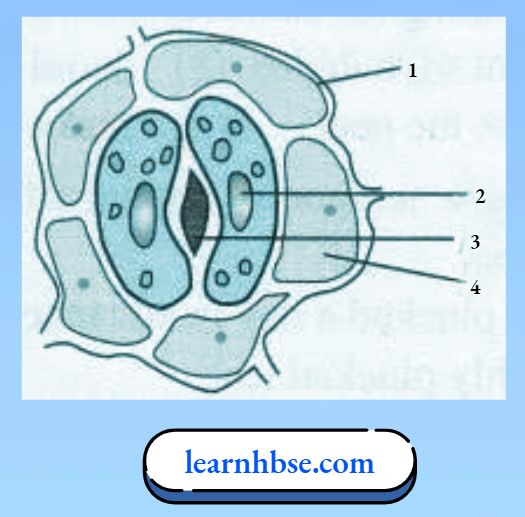
- Name the parts labelled 1, 2, 3, and 4.
- State the function of (2).
Answer:
- 1- Epidermal cell, 2- guard cells, 3- stoma, 4 – chlorophyll.
- Guard cells help in the opening and closing of stomata
Question 21. What is excretion? How do unicellular organisms remove their wastes?
Answer: The biological process of removing harmful metabolic wastes from the body is called excretion. Unicellular organisms remove their wastes through simple diffusion.
Question 22. If you consume butter during lunch, how will it get digested in your body?
Answer: Butter consists of fat, which is digested by bile released from the liver.
- Fats are present in the intestines in the form of large globules, making it difficult for enzymes to act on them.
- Bile salts present in the bile break fats into smaller globules to increase the action of enzymes. This process is known as emulsification.
- Later, lipase acts on the emulsified fats and breaks them down into fatty acids and glycerol.
Question 23. What is the role of the following in the human digestive system?
- Mucus
- Bicarbonate
- Trypsin
Answer:
- Mucus: It protects the inner lining of the stomach from HCI.
- Bicarbonate: It makes the acidic food alkaline so that pancreatic enzymes can act on it.
- Trypsin: It converts proteins into amino acids.
Question 24. You have visited a zoo where you have observed that a fish is respiring at a faster rate as compared to a dog. Explain the reason for this.
Answer: Fish is an aquatic animal, while dog is a terrestrial animal. Aquatic organisms obtain oxygen dissolved in water, while terrestrial organisms use oxygen present in the air for respiration. As compared to air, the availability of oxygen in water is low. Hence, aquatic organisms like fish have to breathe faster as compared to terrestrial organisms like dog. A faster rate of breathing provides more oxygen to aquatic animals.
Question 25. What are the consequences of deficiency of haemoglobin in our body?
Answer: Deficiency of haemoglobin in our body causes anaemia. In anaemia, the blood is unable to transport sufficient amount of oxygen required by the body. As a result, respiration will be less, and hence, less energy will be available for the body. A haemoglobin-deficient person will feel weak, pale, lethargic, and will not be able to do heavy physical work.
Question 5.
- Write the three main steps which take place in the chloroplast during photosynthesis.
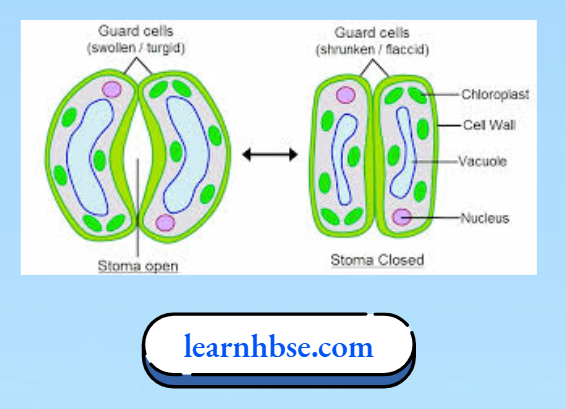
- How do stomata open and close?
Answer:
- Steps which take place inside the chloroplast during photosynthesis:
- Absorption of sunlight energy by chlorophyll.
- Conversion of light energy to chemical energy, and splitting of water into hydrogen and oxygen by light energy.
- Reduction of carbon dioxide by hydrogen to form carbohydrates like glucose by utilising chemical energy.
- The opening and closing of stomata is controlled by guard cells. When water flows into the guard cells, they swell, become curved and cause the stomata to open. When the guard cells lose water, they shrink, become straight and the stomata close.
Question 26. What are the methods used by plants to get rid of excretory products?
Answer:
Methods used by plants to get rid of excretory products:
- Oxygen produced during photosynthesis is removed by diffusion through stomata and lenticels.
- Excess water is removed by transpiration.
- Many waste products are stored in cell vacuoles.
- Some waste products are removed in the falling leaves.
- Some wastes are stored as resins and gums, especially in old xylem.
- Plants also get rid of some waste products by excreting into the surrounding soil.
Question 27. Tooth enamel is one of the hardest substances in our body. How does it undergo damage due to eating chocolates and sweets?
Answer:
Dental caries or tooth decay occurs when bacteria acting on sugars produce acids due to which food particles stick to the teeth to form dental plaque. When plaque covers the teeth, saliva (which is alkaline in nature) cannot reach the tooth surface to neutralise the acid. This may cause gradual softening of enamel.
Question 28. Give reasons for the following:
- Diffusion is insufficient to meet the oxygen requirements of multicellular organisms.
- People living in the mountains have more red corpuscles in their blood than people living in the plains.
- Energy requirement is less for amphibians than for birds.
Answer:
- Diffusion is insufficient to meet the oxygen requirement of multicellular organisms because the volume of the human body is so large that oxygen cannot diffuse into all the cells of the body quickly.
- People living in the mountains have more RBCs in their blood than people living in the plains because the low air pressure requires more RBCs to supply the body cells with oxygen.
- Amphibians are cold-blooded animals whose body temperature depends on the temperature in the environment. They do not need energy to maintain their body temperature, and hence, their requirement of energy is less.
Question 29.
- What is regeneration of an organism? With a neat diagram, describe regeneration in Planaria.
- How does the embryo get nourishment inside the mother’s body?
- List the changes seen in the ovule and ovary after fertilisation.
Answer:
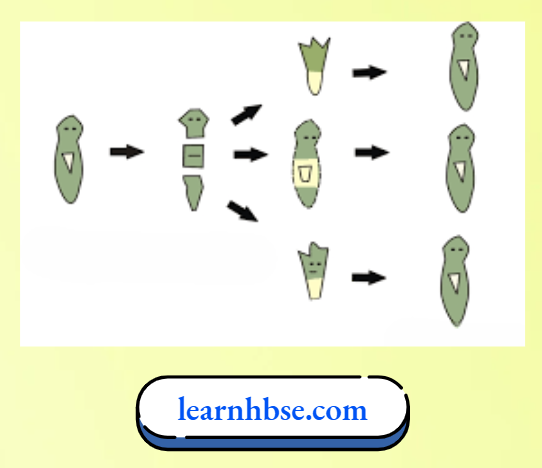
1. Planaria can be cut into any number of pieces, and each piece grows into a complete organism. This process is called regeneration. It is carried out by specialised cells in the organism.
Regeneration in Planaria
2. The embryo gets nutrition from the mother’s blood with the help of a special tissue called the placenta. It provides a large space and area for glucose and oxygen to pass from the mother to the embryo. The developing embryo also produces waste substances which can be moved by transferring them into the mother’s blood through the placenta.
3. The ovule develops a tough coat and is gradually converted to a seed. The ovary grows rapidly and ripens to form a fruit.
Question 30. Name the end products formed during:
- Oxidation of glucose in the muscles
- Oxidation of glucose in body cells
- Breakdown of glucose anaerobically
Answer:
- Lactic acid and ATP.
- Water, carbon dioxide and ATP.
- Ethanol, carbon dioxide and ATP.
Chapter 1 Life Processes Long Questions And Answers
Question 1. What happens to the pollen which falls on a suitable stigma?
Answer:
Reproduction in flowering plants begins with pollination, the transfer of pollen from anther to stigma of the flower. If the transfer takes place to the stigma of flower of the same plant, it is called self-pollination. If the transfer takes place to the stigma of flower of another plant, it is called cross-pollination. Once the pollen grain reaches the stigma, a pollen tube grows from the pollen grain to an ovule. Two sperm nuclei develop. One of them unites with the egg nucleus and produces a zygote. The other unites with two polar nuclei to produce an endosperm that stores food for the development of a plant. Zygote develops into seed and seedling.
Question 2. What is the advantage of having a four-chambered heart? Support your answer with a diagram of the section of the human heart.
Answer:
In a four-chambered heart, the left half is completely separated from the right half by septa. This prevents oxygenated and deoxygenated blood from mixing. It allows a highly efficient supply of oxygenated blood to all parts of the body. This is useful in animals that have energy needs, such as birds and mammals.
Question 3. What could be the possible reason for the declining female-male sex ratio in our country? Suggest two measures to achieve the 1:1 ratio.
Answer:
The reason for declining females in India is sex-selective abortions of the female foetus through surgeries (female foeticides). This can be avoided by banning prenatal sex determination. Everyone in society needs to be educated about the equality of gender and the health of women.
Question 4. Where does fertilisation occur in the female reproductive tract?
Answer:
Fertilisation occurs in the fallopian tube or oviduct of the female reproductive tract.
Question 5.
- What happens if an egg is not fertilised?
- Why do we need to adopt contraceptive measures?
- Name one bacterial and one viral sexually transmitted disease.
- How does the embryo get nourishment inside the mother’s body?
- The embryo gets its nourishment inside the mother’s body with the help of the placenta.
Answer:
- If an egg is not fertilised by a sperm, then blood along with cellular debris comes out through the vagina; this process is called menstruation.
- Need to adopt contraceptive measures:
- To prevent unwanted pregnancies
- To prevent sexually transmitted diseases
- Spacing between children
- Sound health
- Sexually transmitted diseases: Bacterial- Gonorrhea; Viral- AIDS
- The embryo gets its nourishment inside the mother’s body with the help of the placenta
Question 6. Study this diagrammatic representation of the process of fertilisation and answer the questions which follow.
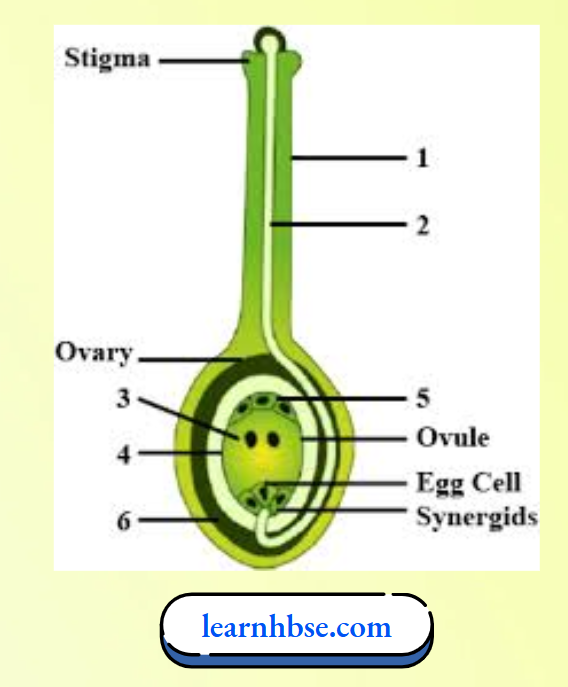
- Name the parts labelled 1, 2, and 4.
- What happens to the ovary and the ovule after fertilisation?
- What part does the stigma play in the process of fertilisation?
Answer:
- 1 : Style; 2 : Pollen tube; 4 : Embryo sac;
- After fertilisation, the ovary enlarges to form the fruit and the ovarian wall forms the fruit wall. The ovule becomes the seed.
- Pollen grain is transferred to the stigma during pollination. Germination of pollen grain takes place only if it falls on the stigma. After germination, the pollen tube grows through the stigma and reaches the ovary for the fertilisation of the egg cell.
