Haryana Board Class 10 Biology Solutions For Chapter 3 Heredity And Evolution Multiple Choice Questions And Answers
Question 1. Which statement explains the Mendel’s law of segregation?
- A trait in an offspring is due to the combination of an allele each from both the parent.
- A trait in an offspring is due to the combination of two alleles each from both the parent.
- A trait in an offspring is due to the combination of two alleles each from either of the parent.
- A trait in an offspring is due to the combination of one allele each from either of the parent.
Answer: 1. A trait in an offspring is due to the combination of an allele each from both the parent.
Question 2. The inheritance of color trait in flower is as shown.
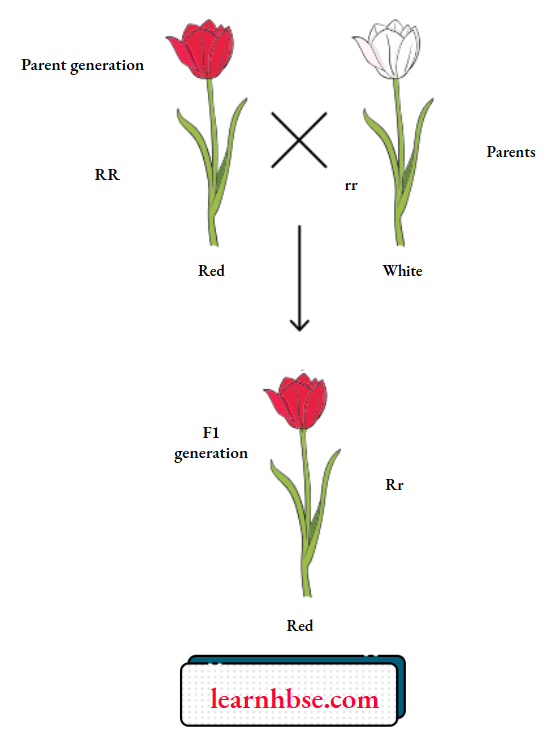
R and r denote two different genes for color. Which law of Mendel can be explained using the image?
- Only Law of segregation
- Only Law of independent assortment
- Law of segregation and Law of dominance
- Law of segregation and Law of independent assortment
Answer: 3. Law of segregation and Law of dominance
Question 3. Humans have two different sex chromosomes, X and Y. Based on the Mendel’s laws, a male offspring Will inherit which combination of chromosomes?
- Both the x chromosomes from one of its parents
- Both the y chromosomes from one of its parents
- Combination of x chromosomes from either of its parents
- Combination of x and y chromosome from either of its parents.
Answer: 4. Combination of x and y chromosome from either of its parents.
Question 4. Two individuals are as shown using geometric shapes
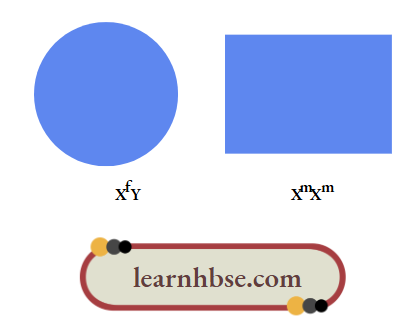
Their sex chromosomes are respectively denoted by Xf Xm, and Y. What are the possible combinations of sex chromosomes for their male and female offspring respectively?
- Xf Xm and XmXm
- XmY and XmXm
- Xf Y and XmY
- XmY and XmXf
Answer: 4. XmY and XmXf
Question 5. An individual is tall with black hair, and free earlobes. The individual learnt to play football from his father and got a scar on his forearm in a match. Which table shows the correct classification of his traits into acquired traits and inherited traits.
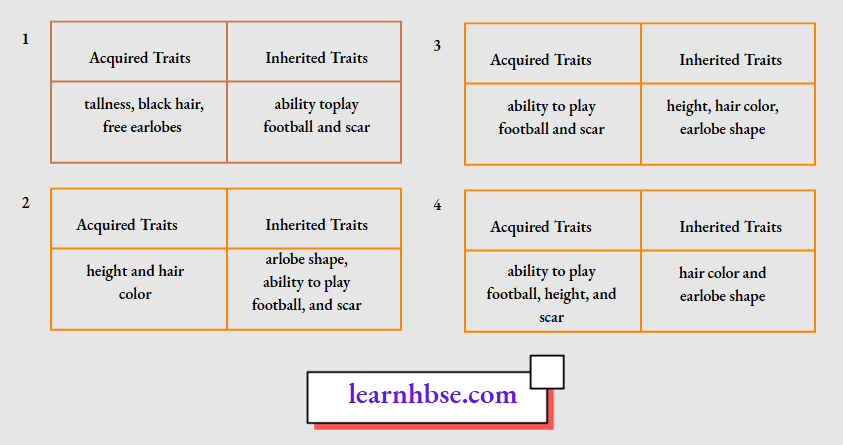
Answer: 4. 
Question 6. The image shows the traits present across generations of a family.
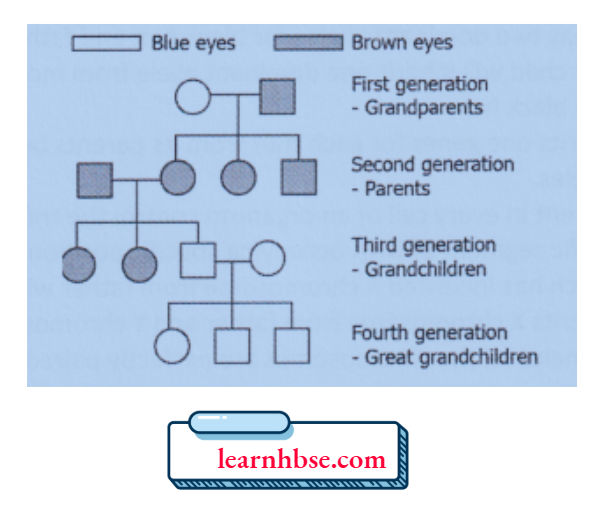
Based on the image, what can be inferred about the eye color trait?
- Acquired trait because both male and females have it.
- Acquired trait because it is expressed in all the generations.
- Inherited trait because it is expressed in two different colors.
- Inherited trait because it depends on the traits of preceding generation.
Answer: 4. Inherited trait because it depends on the traits of preceding generation.
Question 7. In which case does the change in DNA contributes to speciation?
- Changes in the DNA of zygote
- Changes in the DNA of brain cells
- Changes in the DNA of bone cells
- Changes in the DNA of sperm cells.
Answer: 4. Changes in the DNA of sperm cells.
Question 8. The image shows the extent of similarity in the DNA of humans and the organisms.
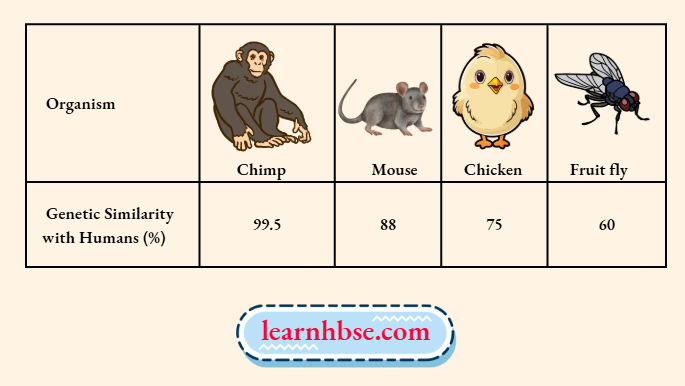
Based on the image, what can be inferred about DNA changes in context of speciation?
- Newly evolved species have inactive ancestral genes.
- Species retain their DNA and evolve new proteins with time.
- Some of the genes remain conserved during the evolution of species.
- Species undergo a complete change of DNA sequences as they evolve.
Answer: 3. Species undergo a complete change of DNA sequences as they evolve.
Chapter 3 Heredity And Evolution Very Short Questions And Answers
Question 1. A normal pea plant bearing coloured flowers suddenly start producing white flowers. What could be the possible cause?
Answer: The appearance of white flowers is due to mutation
Question 2. How does the creation of variations in a species promote survival?
Answer: Variations enable a species to adapt according to the changes and new needs and thus provide better chances for the survival of the species.
Question 3. Two pea plants one with round green seeds (RRyy) and another with wrinkled yellow (rrYY) seeds produce FI progeny that have round, yellow (RrYy) seeds. When FI plants are selfed, what will be the ratio of the F2 progeny?
Answer: 9:3:3:1.
Question 4. List any two characters used by Mendel to conduct experiments on pea plants.
Answer: Seed colour and Flower colour.
Question 5. Do genetic combination of mothers play a significant role in determining the sex of new born?
Answer: No, mothers have no role in determining the sex of the new born. Mothers have a pair of X chromosome. And all children will inherit an ‘X’ chromosome from their mother regardless of whether they are boys or girls.
Question 6. Give reason for the appearance of new combinations of characters in the F2 progeny.
Answer: Since an organism can inherit each character independently. So, in the F2 progeny new combination of character appears, e.g. Tall/Short and round/wrinkled seed trait are independently inherited.
Question 7. Newly formed DNA copies may not be identical at times. Give reason.
Answer: Newly formed DNA copies may not be identical at times if there are errors or inaccuracies in DNA copying.
Question 8. If a tall pea plant is crossed with a dwarf pea plant, what is the ratio of dwarf plants in the F2 generation?
Answer: 3 Tall : 1 Dwarf
Question 9. No two individuals are absolutely alike in a population. why?
Answer: No two individuals are absolutely alike in a population as there are variation in the DNA due to the crossing-over and recombination during the DNA copying process.
Chapter 3 Heredity And Evolution Short Questions And Answers
Question 1. What are the two possible sources of variation?
Answer: Two possible sources of variation are Errors in DNA copying and Random fertilisation.
Question 2. Why did Mendel choose pea plants for his experiments?
Answer: Mendel choose pea plants for his experiments because of the following reasons: Easy to grow; Flowers have bisexual characteristics; Easy to obtain pure breed plant through self-fertilization; Generation time is less.
Question 3. An animal (guinea pig) having black colour is crossed with guinea pig having the same colour. They produced 100 offsprings, of which 75 were black and 25 were white. Find out
- What is the possible genotype?
- Which trait is dominant and which is recessive? How is this determined?
Answer:
Let BB/ Bb be the dominant colour (black) of guinea pig and bb be the recessive trait which codes for white colour of guinea pig.
- The possible genotype of the parent pigs is Bb i.e. the animals are heterozygous dominant as they produced offspring in the ratio of 3: 1. The 25 of the black pigs have the gene BB whereas the rest 50 of the black pigs have genes Bb and the white pigs have bb.
- The trait coding for black colour is dominant while the one coding for white is recessive. Traits are defined to be dominant when they are present in more individuals than the recessive trait-bearing individuals in the wild (i.e. not in human regulated breeding).
Question 4. ‘Different species use different strategies to determine the sex of a new born individual. It can be environmental cues or genetically determined’. Explain the statement by giving example for each strategy.
Answer: Environmental cue: In some animals, the temperature at which fertilised eggs are incubated determines whether the developing animal in egg is a male or a female. In some animals like snail, individuals can change sex.
Genetic cue: A child who inherits an X chromosome from the father will be a girl and the one who inherits a Y chromosome from the father will be a boy
Question 5. “It is possible that a trait is inherited but may not be expressed.” Give a suitable example to justify this statement.
Answer: Yes, it is possible that a trait is inherited but may not be expressed, e.g. when pure tall pea plants are crossed with pure dwarf pea plants, only tall pea plants are obtained in FI generation. The trait for dwarfness was present but could not express itself in the presence of the dominant trait for tallness. On selfing the tall plants of FI generation, both tall and dwarf plants are obtained in F2 generation in the ratio 3 : 1. Reappearance of the dwarf character, a recessive trait in F2 generation shows that the dwarf trait was present in individuals of FI, but it did not express. It got suppressed in the presence of the dominant trait.
Question 6. “A brother and sister are more related to each other as compared to the case when any one of them is related with his/her cousin”. Through this statement what will we get to know about their ancestors?
Answer: A brother and sister are more closely related to each other which mean that they have common ancestors more recently as compared to the case when any one of them (brother or sister) is related to the cousin. A brother and sister have their “parents” in common while a brother or sister and cousin have “grandparents” in common.
Question 7. How are variant genotypes produced?
Answer: Variant genotypes are produced by the following mechanisms: Mutation in genes and chromosomes; Recombination of genes; Hybridization of genes
Question 8. A woman with blonde curly hair married a man with black soft hair. All of their children in the first generation had black soft hair but in next generation children had different combinations in the ratio of 9:3:3:1. State the law that governs this expression.
Answer: The law of independent inheritance governs the given situation. The law states that the factors of different pairs of contrasting characters do not influence each other. They are independent of one another in the inheritance.
Question 9. The genotype of green stemmed tomato plants is denoted as GG and that of purple stemmed tomato plants as gg. When these two are crossed:
- What is the percentage of purple stemmed plants in F2 progeny if FI plants are self-pollinated?
- In what ratio would you find the genotype of GG and Gg in the F2 progeny?
Answer:
- Purple stemmed plants in F2 progeny – 25%
- Ratio of GG and Gg in the F2 progeny- 1:2:1
Question 10. A child questioned his teacher that why do organisms resemble their parents more as compared to grandparents. In which way will the teacher explain to the child?
Answer: The two parents involved in sexual reproduction produce gametes which fuse together forming a zygote. It gradually develops into a young child showing certain similarities with the parents. Since, a child inherits its characters from both the parents the resemblance with them is very close. The grandparents and the child resemble less closely because a gap of gene pool is created by the parents of the child. Since the child is immediate generation next to his parent thus to carry more similar genes as that of parents. Variations are more with grandparents.
Question 11. Mustard was growing in two fields- A and B, while field A produced brown coloured seeds, field B produced yellow coloured seeds. It was observed that in field A, the offsprings showed only the parental trait for consecutive generations, whereas in field B, majority of the offsprings showed a variation in the progeny. What are the probable reasons for these?
Answer: Self-pollination in field A; Cross pollination in field B.
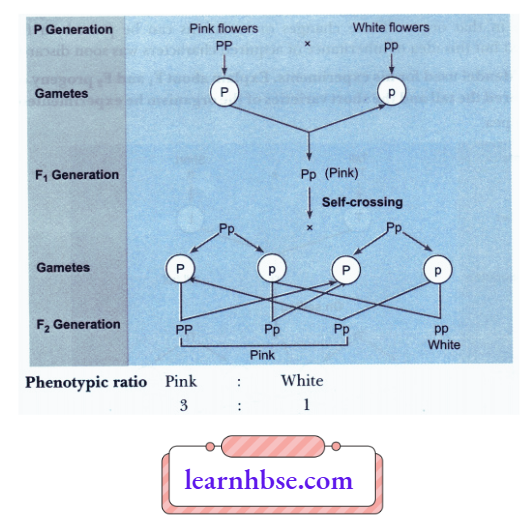
Question 12. In a cross between plants with homozygous pink flowers and plants with homozygous white flowers, all the offsprings ofFI generation had pink flowers. When the FI generation was self-crossed, it was observed in the F2 generation that out of 100, 75 flowers were pink. Make a cross and answer the following questions:
- What are the genotypes of the F2 progeny?
- What is the ratio of Pink: White flowers in the F2 generation?
Answer:
1. Genotypes of F2 progeny are PP, Pp and pp.
2. 
Question 13.
- If a purple-flowered pea plant (PP) is crossed with a white-flowered pea plant (pp), will we have white-flowered pea plants in the FI generation? Explain.
- What do you mean by dominant and recessive traits
Answer:
- No. We will not have white-flowered pea plants in the FI generation. This is because all the FI progeny plants show genetic makeup Pp. Since P is a trait dominant over p, all the plants in the FI generation have purple flowers.
- A dominant trait is a genetic trait which is expressed in a person who has only one copy of that gene. A recessive trait is a genetic trait which is expressed only when two copies of the gene are present.
Question 14. A pea plant with blue flowers denoted by BB is cross-bred with a pea plant with white flowers denoted by ww.
- What is the expected flower colour in the FI progeny?
- What will be the percentage of plants bearing white flowers in the F2 generation when the flowers of FI plants are self-pollinated?
- State the expected ratio of the genotypes BB and Bw in the F2 progeny.
Answer:
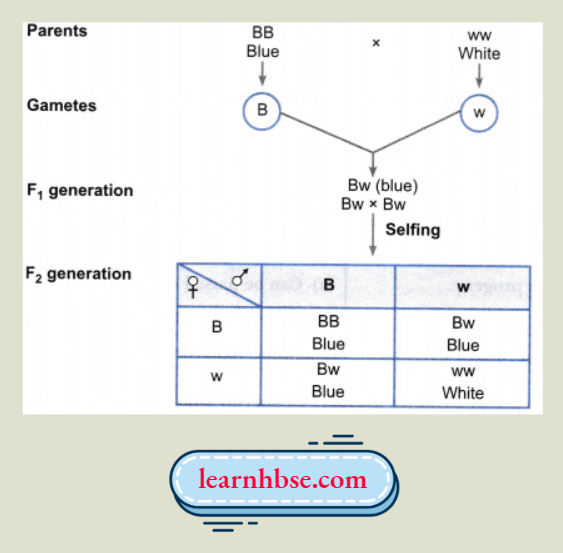
- The F1 progeny is expected to have plants with blue flowers.
- % of the F2 generation bears white flowers. So, 25% of the F2 progeny bears white flowers in the F2 generation when the flowers of F1 plants are self-pollinated.
- The ratio of the genotype BB and Bw in the F2 progeny is 1 (BB):2 (Bw).
Question 15. A cross was carried out between a pure-bred pea plant with axial flowers and a purebred pea plant with terminal flowers, and the FI progeny was obtained. This progeny was selfed to obtain the F2 progeny. Answer the following questions:
- What is the phenotype of the FI progeny and why?
- Give the phenotypic ratio of the F2 progeny.
- Why is the F2 progeny different from the FI progeny?
Answer:
A pea plant with axial flowers (AA; dominant) was crossed with a pea plant with terminal flowers (aa, recessive).
1. All the FI progeny would bear axial flowers because the trait for axial flowers is dominant over the trait for terminal flowers.
2. In the F2 generation. Parents → Aa x Aa Gametes → A, a A, a
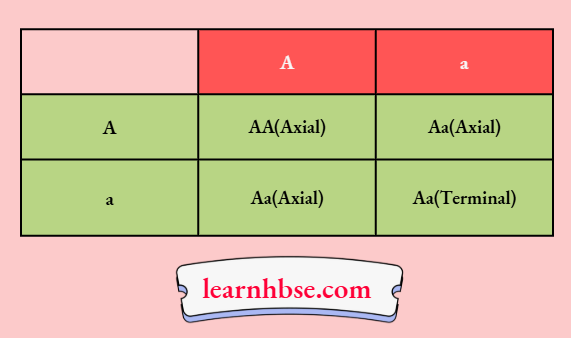
3. Phenotypic ratio → Axial : Terminal = 3:1
FI plants are heterozygous (Aa), and hence, only the dominant trait is visible in the FI generation. In the F2 generation, factors responsible for the two traits are segregated and recombined to form a homozygous recessive trait for terminal flowers (aa).
Question 16. A blue-flowered plant denoted by BB is crossbred with a white-flowered plant denoted by bb.
- State the colour of the flowers you would expect in the FI generation plants.
- What must be the percentage of white-flowered plants in the F2 generation if flowers of FI plants are self-pollinated?
- State the expected ratio of the genotypes BB and Bb in the F2 progeny.
Answer:
The cross between blue-flowered plant (BB) and white-flowered plant (bb) is a monohybrid cross which involves a single trait, i.e. colour of the flower under study.
- All the FI generation plants would be blue.
- If flowers of FI plants are self-pollinated, then we would have 75% plants with blue flowers and 25% plants with white flowers in the F2 generation.
- The expected ratio of the genotypes BB and Bb in the F2 progeny is 1:2.
Question 17. Basis the understanding of size of the organism and chromosome number, answer the following
questions:
- Do larger organisms have more number of chromosomes/cells?
- More the number of chromosomes/cells greater in the DNA content. Justify.
Answer:
- No, there is no relationship between size of organism and its chromosome number.
- Yes, since the major component of chromosome is DNA, if there are more chromosomes in a cell, the quantity of DNA will also be more.
Question 18. A potato is cut into a number of small pieces. These potato pieces are placed on wet cotton kept in a tray. After a few days, green shoots and roots appear only from some potatoes and not from all potato pieces. Why?
Answer: The pieces of potato that bear nodes only can give rise to new plants by producing shoots and roots. But the pieces not bearing nodes cannot produce new plants. Thus from a whole potato only some pieces that bear nodes give rise to roots and shoots. This is an example of vegetative propagation which is an asexual mode of reproduction in plants.
Question 19. In a tobacco plant, the male gametes have 24 chromosomes. What is the number of chromosomes in the female gamete? What is the number of chromosomes in the zygote?
Answer: Number of chromosomes in female gamete is 24. Number of chromosomes in zygote is 48.
Question 20. A man with blood group A marries a woman with blood group 0 and their daughter has blood group 0. Is this information enough to tell you which of the traits-blood group A or O- is dominant? Why or why
not?
Answer: No. This information is not sufficient to determine which of the traits – blood group A or 0 – is dominant. This is because we do not know about the blood group of all the progeny. Blood group A can be genotypically AA or AO. Hence, the information is incomplete to draw any such conclusion.
Chapter 3 Heredity And Evolution Long Questions And Answers
Question 1. Sex determination is the method by which distinction between males and females is established in a species. The sex of an individual is determined by specific chromosomes. These chromosomes are called sex chromosomes or allosomes. X and Y chromosomes are called sex chromosomes. The normal chromosomes other than the sex chromosomes of an individual are known as autosomes.
In XX-XY type of sex determination who produces two different types of gametes?
A couple has six daughters. What is the possibility of their having a girl next time?
What is the number of autosomes present in the liver cells of a human female?
Answer:
- Males produce two different types of gametes.
- 50% The possibility of having a girl or boy child is equal i.e., 50%, as 50% male gametes are Y type and 50% are X type.
- 22 pairs In humans, the number of autosomes are 2n = 44 or 22 pairs regardless of the sex.
Question 2.
- How many characters are transmitted in the following cross? Name them.
- Define dominant trait and recessive trait.
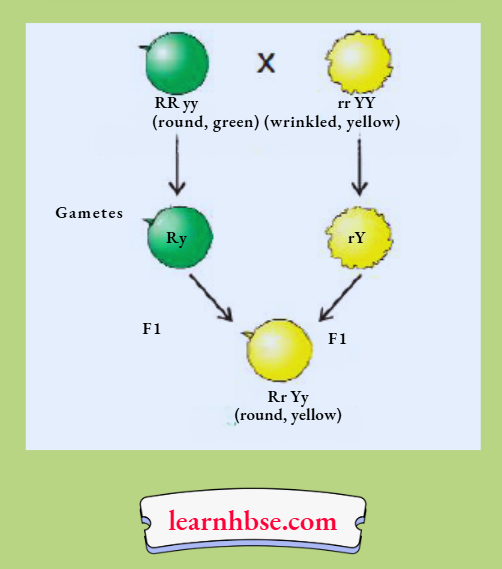
Answer:
- Two characters are transmitted. They are shape of seed and colour of seed.
- A dominant trait is a genetic trait which is considered dominant if it is expressed in a person who has only one copy of that gene. A recessive trait is a genetic trait which is expressed only when two copies of the same gene are present.
Question 3. Explain Mendel’s experiment on inheritance of characters considering only one visible contrasting character in pea plant.
Answer:
Mendel’s experiment can be studied in the following ways:
- Mendel first crossed pure-bred, tall pea plants with pure-bred, short pea plants and found that tall pea plants were produced in the FI generation.
- Mendel crossed tall pea plants of the FI generation and found that tall plants and dwarf plants are in the ratio 3:1. Mendel observed that the dwarf trait of the pea plant which had disappeared in the FI generation progeny reappeared in the F2 generation. He concluded by saying that traits are inherited independently.
Question 4. After self-pollination in pea plants with round, yellow seeds, following types of seeds were obtained by Mendel:
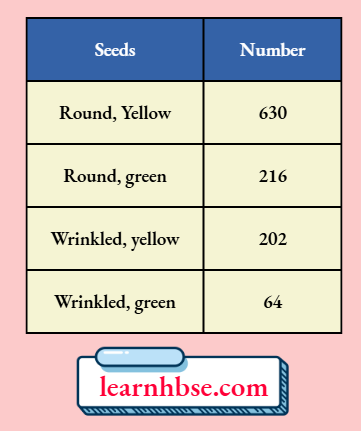
Analyse the result and describe the mechanism of inheritance which explains these results.
Answer: The ratio obtained is 9:3:3:1 in which parental as well as new combinations are observed. This indicates that progeny plants have not inherited a single whole gene set from each parent. Every germ cell takes one chromosome from the pair of maternal and paternal chromosomes. When two germ cells combine, segregation of one pair of characters is independent of other pair of characters.
Question 5. In humans, there is a 50% probability of the birth of a boy and 50 % probability that a girl will be born. Justify the statement on the basis of the mechanism of sex-determination in human beings.
Answer: In human beings, the genes inherited from the parents decide whether the child born will be a boy or a girl. Women have a perfect pair of sex chromosomes (XX). But, men have a mismatched pair (XY) of sex chromosomes. All children will inherit an X chromosome from their mother regardless of whether they are boys or girls. Thus, the sex of the children will be determined by what they inherit from their father. A child who inherits an X chromosome from her father will be a girl, and one who inherits a Y chromosome from him will be a boy.
Question 6. A blue colour flower plant denoted by BB is cross bred with that of white colour flower plant denoted by bb.
- State the colour of flower you would expect in their FI generation plants.
- What must be the percentage of white flower plants in F2 generation if flowers of F1 plants are selfpollinated?
- State the expected ratio of the genotypes BB and Bb in the F2 progeny.
- State the type of plants which are not found in FI generation but reappeared in F2 generation. Write the reason for the same.
Answer:
- All flowers will be blue.
- White: 25%
- Genotype ratio in F2: BB: Bb :: 1:2
- White flowering plants; White flower being a recessive trait can only be expressed in the recessive homozygous condition.
Question 7. Fertilization and implantation are the most critical events in the reproduction process. In this process, both egg and sperm are fused together to form a zygote. Later, it gets implanted into the uterus and the development of an organism starts.
The given flowchart explains the process. Study the chart and answer the questions given below:
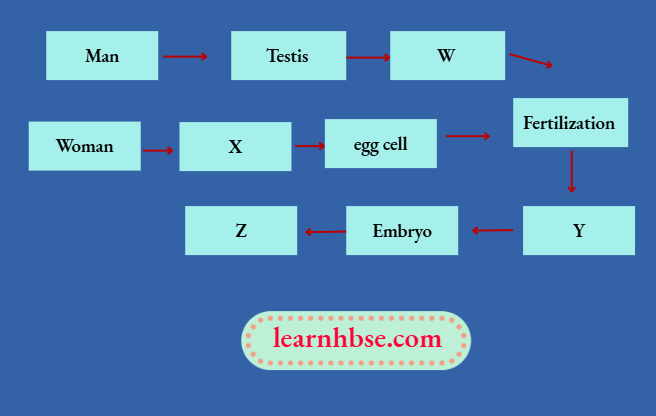
- Identify the labels X, Y and Z.
- Where does the process of fertilisation takes place in female body?
Answer:
- W: Sperm; X: Ovary; Y: Zygote; Z: Foetus;
- Fallopian Tubes
Question 8. A horticulturist took stems of two different plants, plant X with roots and plant Y without roots. He fixed the cut stem X in soil and fitted and bound tightly the other cut stem Y over the surface of X. He fastened the joint properly with the help of polythene. The cut soon healed and the two plant stems (X and Y) grew together as one plant.
- What are stems X and Y respectively known as?
- Why the area where two stems are joined is covered with polythene?
Answer:
- The cut stem of a plant having roots (X) and is fixed in soil is called stock. The cut stem of another plant (without roots) (Y) is called scion.
- The area where two stems are joined is covered with polythene to prevent the loss of water and cell sap from the cut and joined ends of the stems. It also helps to prevent harmful infection by bacteria or fungi.
