Haryana Board Class 10 Biology Solutions For Chapter 4 Control And Coordination Multiple Choice Questions And Answers
Question 1. The image shows the structure of a neuron.
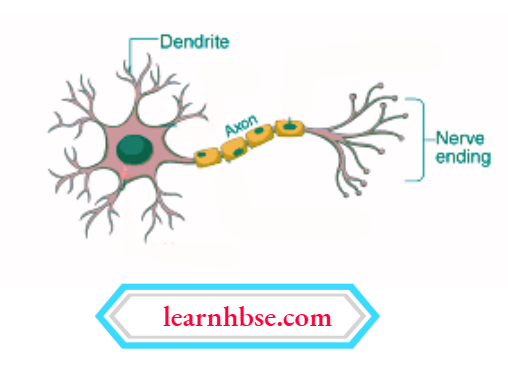
How will information travel within a neuron?
- Dendrite → cell body → axon → nerve ending
- Dendrite → axon → cell body → nerve ending
- Axon → dendrite → cell body → nerve ending
- Axon -> cell body -> dendrite -> nerve ending
Answer: 1. Dendrite → cell body → axon → nerve ending
Question 2. The image shows structure of a neuron.
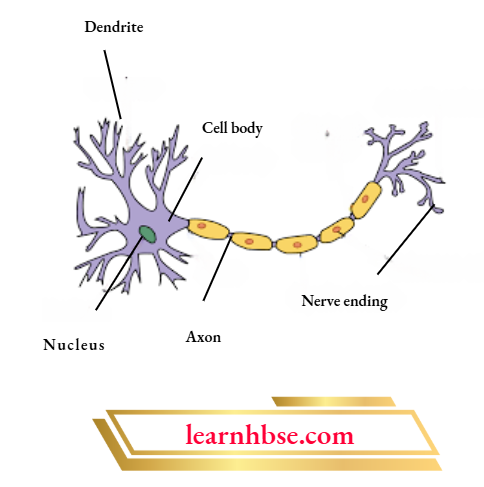
After our nose senses a smell, which option shows the mechanism of the travelling of sense in our body?
- Olfactory receptors- dendritic tip of a nerve cell- – axon- nerve ending-release of signal -dendritic tip of other nerve cell
- Olfactory receptors- dendritic tip of a nerve cell- axon- cell body- release of signal-dendritic tip of other nerve cell
- Gustatory receptors- dendritic tip of a nerve cell- cell body- axon- release of signal-dendritic tip of other nerve cell
- Gustatory receptors- dendritic tip of a nerve cell- axon- cell body- release of signal-dendritic tip of other nerve cell
Answer: 1. Olfactory receptors- dendritic tip of a nerve cell- – axon- nerve ending-release of signal -dendritic tip of other nerve cell
Question 3. Which option correctly shows the sequence of events that occur when we touch a hot utensil?
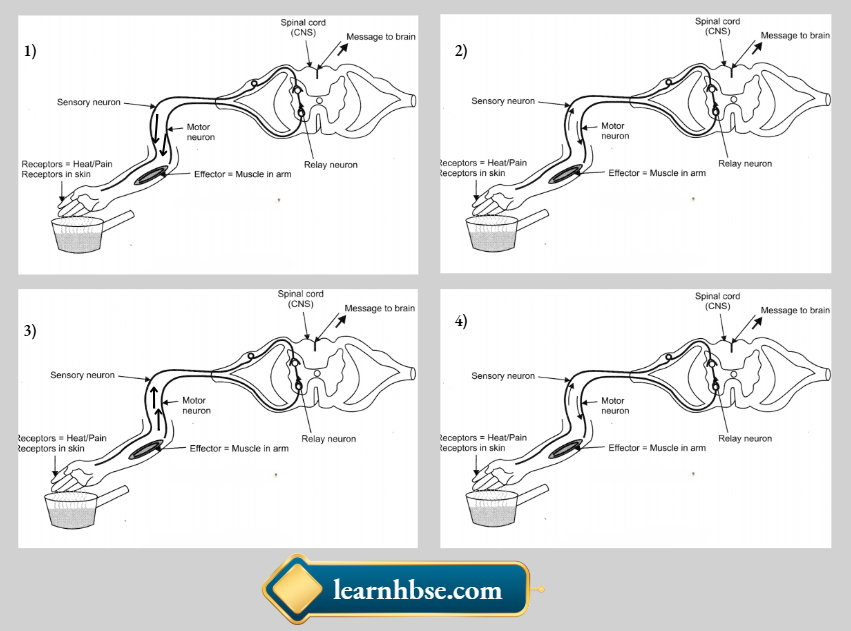
Answer: 2.
Question 4. Which option correctly shows the order of events when a bright light is focused on our eyes?
- Bright light- receptors in eyes – sensory neuron – spinal cord – motor neurons – eyelid closes
- Bright light – receptors in eyes – spinal cord -sensory neuron – motor neurons – eyelid closes
- Bright light – receptors in eyes – sensory neuron – motor neurons – spinal cord – eyelid closes
- Bright light – receptors in eyes – spinal cord – motor neurons – sensory neuron – eyelid closes
Answer: 1. Bright light- receptors in eyes – sensory neuron – spinal cord – motor neurons – eyelid closes
Question 5. The image shows the labelled structure of a brain.
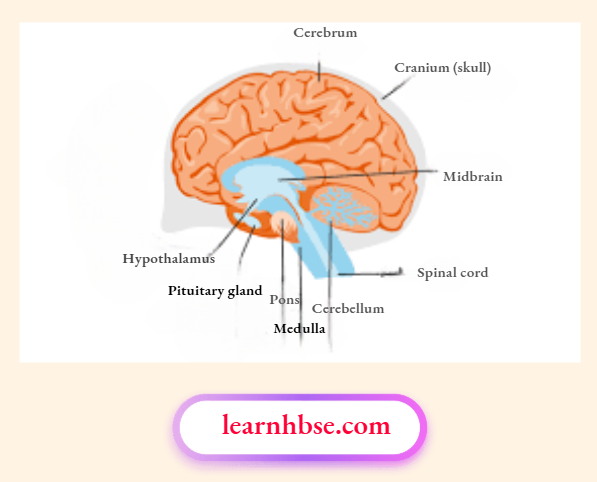
Which parts of the brain controls the blood pressure?
- Spinal cord, skull, hypothalamus
- Cord, skull, cerebrum
- Pons, medulla, cerebellum
- Pons, medulla, pituitary
Answer: 3. Pons, medulla, cerebellum
Question 6. Which option illustrates the location of centre that controls the feelings associated with hunger (M) and the centre that allows a person to walk in a straight line (N)?
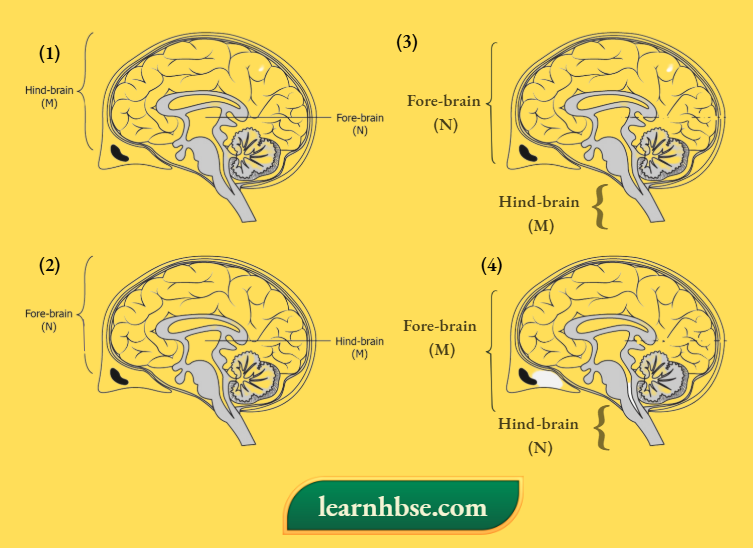
Answer: 4.
Question 7. When we touch the leaves of “touch-me-not” plant, they began to fold up and droop. How does the plant communicate the information of touch?
- The plant uses electrical signals to transfer information from external environment to cells.
- The plant uses electrical- chemical signals to transfer information from cell to cell.
- The plant uses electrical- chemical signals to transfer information from tissue to specialized cells.
- The plant uses electrical signals to transfer information from cell to specialized tissues.
Answer: 2. The plant uses electrical- chemical signals to transfer information from cell to cell.
Question 8. Aditya potted some germinated seeds in a pot. He put the pot in a cardboard box that was open from one side. He keeps the box in a way that the open side of box faces sunlight near his window. After 2-3 days he observes the shoot bends towards light as shown in image.
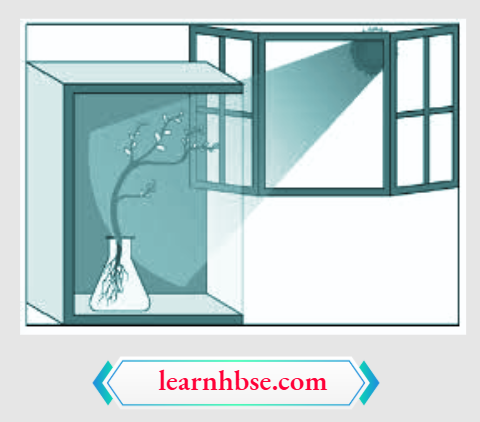
Which type of tropism he observes?
- Geotropism
- Phototropism
- Chemotropism
- Hydrotropism
Answer: 2. Phototropism
Question 9. What is a likely limitation of electric impulses?
- The electric impulses travel slowly between the neurons.
- The electric impulses allow signal transmission in multiple directions.
- The electric impulses are transmitted to only those body parts that are connected to neurons.
- The electric impulses once generated needs to be transmitted quickly within the body.
Answer: 3. The electric impulses are transmitted to only those body parts that are connected to neurons.
Question 10. Organisms depend on hormones as well as electric impulses for the transmission of signals from brain to rest of the body. What can be a likely advantage of hormones over electric impulses?
- It is secreted by all types of cells present in the body.
- It is secreted by stimulated cells and reaches all cells of the body.
- It is relayed to the target organ at a faster rate than electric impulses
- It does not depend on an external stimulus to be generated in the cells.
Answer: 2. It is secreted by stimulated cells and reaches all cells of the body.
Question 11. What is the function of pituitary gland?
- To develop sex organs in males
- To stimulate growth in all organs
- To regulate sugar and salt level in the body
- To initiate metabolism in the body
Answer: 2. To stimulate growth in all organs
Question 12. A female is suffering from irregular menstrual cycle. The doctor prescribed her some hormonal tablets. Which option shows the hormone she lacks in her body from the endocrine gland?
- Oestrogen
- Testosterone
- Adrenalin
- Thyroxin
Answer: 1. Oestrogen
Question 13. The movement of a plant part in response to the force of attraction exerted by the earth is called:
- Hydrotropism
- Geotropism
- Chemotropism
- Phototropism
Answer: 2. Geotropism
Question 14. A big tree falls in a forest, but its roots are still in contact with the soil. The branches of this fallen tree grow straight up (vertically). This happens in response to:
- Water and light
- Water and minerals
- Gravity and water
- Light and gravity
Answer: 4. Light and gravity
Question 15. The main function of the plant hormone called abscisic acid is to:
- Increase the length of cells
- Promote cell division
- Inhibit growth
- Promote growth of stem and roots
Answer: 3. Inhibit growth
Question 16. The growth of tendrils in pea plants is due to the:
- Effect of sunlight on the tendril cells facing the sun
- Effect of gravity on the part of tendril hanging down towards the earth
- Rapid cell division and elongation in tendril cells that are away from the support
- Rapid cell division and elongation in tendril cells in contact with the support
Answer: 3. Rapid cell division and elongation in tendril cells that are away from the support
Question 17. The plant hormone which triggers the fall of mature leaves and fruits from the plant body is:
- Auxin
- Gibberellin
- Abscisic acid
- Cytokinin
Answer: 3. Abscisic acid
Chapter 4 Control And Coordination Very Short Questions And Answers
Question 1. Why is it advised to use iodised salt in our diet?
Answer: Iodine stimulates the thyroid gland to produce thyroxin hormone. Deficiency of this hormone results in the enlargement of the thyroid gland. This can lead to goitre.
Question 2. Give an example of a plant hormone that promotes its growth. Where it is synthesized?
Answer: Plant hormone that promotes growth is auxin. It is synthesized at the tip of the plant stem.
Question 3. State the function of:
- Gustatory receptors, and
- Olfactory receptors.
Answer:
- Gustatory receptors – these are sensitive to taste;
- Olfactory receptors – these are sensitive to smell.
Question 4. Name the part of the brain which controls posture and balance of the body.
Answer: Cerebellum
Question 5. Mention the part of the body where gustatory and olfactory receptors are located.
Answer: Gustatory receptors are located in Cerebrum of fore-brain. Olfactory receptors are located in Olfactory lobe of fore-brain.
Question 6. How is the spinal cord protected in the human body?
Answer: Spinal cord is enclosed in a bony cage called vertebral column.
Question 7. A potted plant is made to lie horizontally on the ground. Which part of the plant will show
- Positive geotropism?
- Negative geotropism?
Answer:
- Root
- Shoot.
Question 8. Mention the function of the hind-brain in humans.
Answer: Hind brain controls respiration, cardio-vascular reflexes and gastric secretions. It also modulates the motor commands initiated by the cerebrum.
Question 9. A young green plant receives sunlight from one direction only. What will happen to its shoots?
Answer: Shoots will bend towards the light and roots away from the light.
Question 10. What is the function of thyroxine hormone in our body?
Answer: Thyroxine hormone regulates the carbohydrate, protein and fat metabolism in the body so as to provide the best growth balance.
Question 11. Name two tissues that provide control and coordination in multicellular animals.
Answer: Nervous tissue and Muscular tissue
Chapter 4 Control And Coordination Short Questions And Answers
Question 1.
- Name the hormones that are released in human males and females when they reach puberty.
- Name a gland associated with brain. Which problem is caused due to the deficiency of the hormone released by this gland?
Answer:
- Testes in males produces hormone testosterone. Ovaries in females produces hormone
oestrogen. - Pituitary gland present in the brain is responsible for body growth, development of bones and muscles (if excess-gigantism) (if less-dwarfism).
Question 2. Which part of the brain controls involuntary actions? Write the function of any two regions of it.
Answer: Hind-brain controls the involuntary actions. Cerebellum controls the coordination of body movement and posture. Medulla oblongata regulates center for swallowing, coughing, sneezing and vomiting.
Question 3. Mention the functions of adrenaline hormone.
Answer: Adrenaline hormone is released into the blood from the adrenal gland during stimulation of the nervous system on seeing any adverse situation of fight or fright, it: Increases the blood pressure; Increases heart beat rate; Increases breathing rate; Diverts blood to essential organs including the heart, brain and skeletal muscles by dilating their blood vessels and constricting those of less essential organs, such as the skin and digestive system.
Question 4. Name, the two main organs of our central nervous system. Which one of them plays a major role in sending command to muscles to act without involving thinking process? Name the phenomenon involved.
Answer: Brain and Spinal cord. Spinal cord plays a major role in sending command to muscles to act without involving thinking process. This phenomenon is called reflex action.
Question 5. What is the need for a system of control and coordination in human beings?
Answer: A living being does not live in isolation. It has to constantly interact with its external environment and has to respond properly for its survival, e.g. when a hungry lion spots a deer, the lion has to quickly make a move so that it can have its food. On the other hand, the deer needs to quickly make a move to run for its life. The responses which a living being makes in relation to external stimuli are controlled and coordinated by a system; especially in complex animals. So, control and coordination is essential in maintaining a state of stability and a steady state between the internal conditions of an organism and the external environment.
Chapter 4 Control And Coordination Short Questions And Answers
Question 1. State how concentration of auxin stimulates the cells to grow longer on the side of the shoot which is away from light?
Answer: When light falls on the side of the shoot auxin diffuses towards the shady side of the shoot. This concentration of the auxin stimulates the cell to grow longer on the side of the shoot which is away from light. Thus plant appears to bend towards light
Question 2. Write one example each of the following tropic movements :
- Positive phototropism
- Negative phototropism
- Positive geotropism
- Negative geotropism
- Hydrotropism
- Chemotropism
Answer:
- Positive phototropism: shoots growing towards light.
- Negative phototropism: roots growing away from light towards ground,
- Positive geotropism: growth of roots towards earth due to the pull of the
earth. - Negative geotropism: shoots growing away from the earth,
- Hydrotropism: roots growing towards the source of water.
- Chemotropism: growth of pollen tubes towards the ovules.
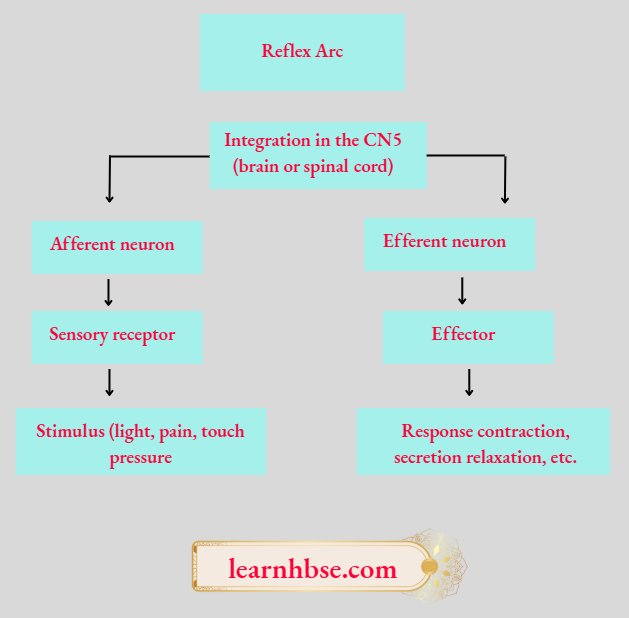
Question 3. List the components of reflex arc in correct sequence. State in brief the role of brain in reflex action.
Answer: The reflex arc pathway is shown in the flow chart as follows: The Reflex arc does not involve brain. It minimises the overloading of brain.
Question 4. Smita’s father has been advised by a doctor to reduce his sugar intake.
- Name the disease he is suffering from and name the hormone whose deficiency is?
- Identify the gland that secretes it and mention the function of this hormone.
- Explain how the time and amount of secretion of this hormone is regulated in human system.
Answer:
- He is suffering from diabetes. Deficiency of insulin causes diabetes,
- Pancreas secretes insulin. Insulin helps in regulating blood sugar,
- When the sugar level in blood increases, it is detected by the acells of the pancreas which responds by producing more insulin. As the blood sugar level falls, insulin secretion is reduced.
Question 5.
- Which plant hormone is present in greater concentration in the areas of rapid cell division?
- Give one example of a plant growth promoter and a plant growth inhibitor.
Answer:
- Cytokinin is present in greater concentration in the areas of rapid cell division,
- An example of a plant growth promoter is gibberellins and example of a plant growth inhibitor is abscisic acid.
Question 6. Which organ secretes a hormone when blood sugar rises in our body? Name the hormone and name one enzyme released by this organ.
Answer: Pancreas. Insulin is the hormone released by this organ and the name of the enzyme is pancreatic juice.
Question 7. What causes a tendril to encircle or coil around the object in contact with it is? Explain the process involved.
Answer: When a tendril comes in contact with any support, the part of the tendril in contact with the object does not grow as rapidly as the part away of the tendril away from the object. This causes the tendril to circle around the object and cling to it.
Chapter 4 Control And Coordination Long Questions And Answers
Question 1.
- Name the hormone which is released into the blood when its sugar level rises.
- Explain the need of Chemical communication in multicellular organisms.
- Name the organ which produces this hormone and its effect on blood sugar level. Also mention the digestive enzymes secreted by this organ with one function of each.
Answer:
- Insulin
- Since nerves cannot reach each and every part of the body of multicellular organisms, chemical communication is important for communication of messages between the central nervous system (brain and spinal cord) and other parts of the body
- Pancreas.
Question 2.
- How is brain protected from injury and shock?
- Name two main parts of hind brain and state the functions of each.
Answer:
- Skull and cerebrospinal fluid protect the brain from injury and shock.
- Two main parts of hind-brain are- Medulla and Cerebellum. Their functions are: medulla: Invounatary actions such as blood pressure, salivation and vomiting. Cerebellum: It is responsible for precision of voluntary actions and maintaining the posture and balance of the body.
