Haryana Board Class 10 Biology Solutions For Sample Question Paper
Question 1. When sodium bicarbonate reacts with dilute hydrochloric acid, the gas evolved is:
- Hydrogen; it gives pop sound with burning match stick.
- Hydrogen; it turns lime water milky.
- Carbon dioxide; it turns lime water milky.
- Carbon dioxide; it blows off a burning match stick with a pop sound.
Answer: 3. Carbon dioxide; it turns lime water milky.
Question 2. When aqueous solutions of potassium iodide and lead nitrate are mixed, an insoluble substance separates out. The chemical equation for the reaction involved is:
- \(\mathrm{KI}+\mathrm{PbNO}_3 \rightarrow \mathrm{Pbl}+\mathrm{KNO}_3\)
- \(2 \mathrm{KI}+\mathrm{Pb}\left(\mathrm{NO}_3\right)_2 \rightarrow \mathrm{Pbl}_2+2 \mathrm{KNO}_3\)
- \(\mathrm{KI}+\mathrm{Pb}\left(\mathrm{NO}_3\right)_2 \rightarrow \mathrm{Pbl}+\mathrm{KNO}_3\)
- \(\mathrm{KI}+\mathrm{PbNO}_3 \rightarrow \mathrm{Pbl}_2+\mathrm{KNO}_3\)
Answer: 2. \(2 \mathrm{KI}+\mathrm{Pb}\left(\mathrm{NO}_3\right)_2 \rightarrow \mathrm{Pbl}_2+2 \mathrm{KNO}_3\)
Question 3. A metal ribbon ‘X’ burns in oxygen with a dazzling white flame forming a white ash Y. The correct description of X, Y and the type of reaction is:
- X = Ca; Y = CaO; Type of reaction = Decomposition
- \(2 \mathrm{KI}+\mathrm{Pb}\left(\mathrm{NO}_3\right)_2 \rightarrow \mathrm{Pbl}_2+2 \mathrm{KNO}_3\)
- X = Al; Y= Al203; Type of reaction = Thermal decomposition
- X = Zn; Y = ZnO; Type of reaction = Endothermic
Answer: 2. \(2 \mathrm{KI}+\mathrm{Pb}\left(\mathrm{NO}_3\right)_2 \rightarrow \mathrm{Pbl}_2+2 \mathrm{KNO}_3\)
Question 4. Acid present in tomato is:
- Methanoic acid
- Acetic acid
- Lactic acid
- Oxalic acid
Answer: 4. Oxalic acid
Question 5. Sodium hydroxide is termed an alkali while Ferric hydroxide is not because:
- Sodium hydroxide is a strong base, while Ferric hydroxide is a weak base.
- Sodium hydroxide is a base which is soluble in water while Ferric hydroxide is also a base but it is not soluble in water.
- Sodium hydroxide is a strong base while Ferric hydroxide is a strong acid.
- Sodium hydroxide and Ferric hydroxide both are strong base but the solubility of Sodium hydroxide in water is comparatively higher than that of Ferric hydroxide.
Answer: 2. Sodium hydroxide is a strong base, while Ferric hydroxide is a weak base.
Question 6. The name of the salt used to remove permanent hardness of water is:
- Sodium hydrogen carbonate (NaHC03)
- Sodium chloride (NaCI)
- Sodium carbonate decahydrate (Na2C03.10H20)
- Calcium sulphate hemihydrate (CaS04. 12H2O)
Answer: 3. Sodium carbonate decahydrate (Na2C03.10H20)
Question 7. The electron dot structure of chlorine molecule is:
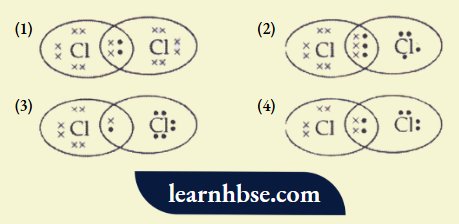
Answer: 3.
Question 8. Observe the following diagram and identify the process and its significance from the following
options:
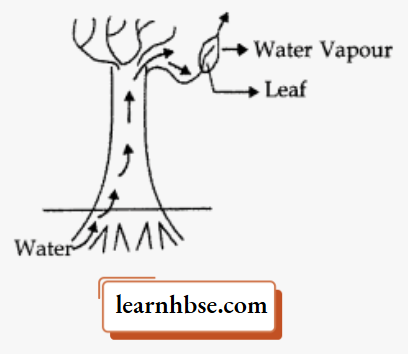
- Evaporation: maintains water contents in leaf cells.
- Transpiration: creates a suction force which pulls water inside the plant.
- Excretion: helps in excreting out waste water from the plant.
- Translocation: helps in transporting materials from one cell to another.
Answer: 2. Transpiration: creates a suction force which pulls water inside the plant.
Question 9. Opening and closing of stomata is due to:
- High pressure of gases inside the cells.
- Movement of water in and out of the guard cells.
- Stimulus of light in the guard cells.
- Diffusion of C02 in and out of the guard cells.
Answer: 2. Movement of water in and out of the guard cells.
Question 10. A cross between pea plant with white flowers (vv) and pea plant with violet flowers (W) resulted in F2 progeny in which ratio of violet (VV) and white (w) flowers will be:
- 1 : 1
- 2 : 1
- 3 : 1
- 1 : 3
Answer: 1. 1 : 1
Question 11. In plants the role of cytokinin is:
- Promote cell division
- Wilting of leaves
- Promote the opening of stomatal pore
- Help in the growth of stem
Answer: 1. Promote cell division
Question 12. The number of chromosomes in parents and offsprings of a particular species undergoing sexual reproduction remain constant due to:
- Doubling of chromosomes after zygote formation.
- Halving of chromosomes after zygote formation.
- Doubling of chromosomes before gamete formation.
- Halving of chromosomes at the time of gamete formation.
Answer: 4. Halving of chromosomes at the time of gamete formation.
Question 13. Two LED bulbs of 12W and 6W are connected in series, if the current through 12W bulb is 0.06A the current through 6W bulb will be:
- 0.04A
- 0.06A
- 0.08A
- 0.12A
Answer: 2. 0.06A
Question 14. The correct pattern of magnetic field lines of the field produced by a current carrying circular
loop is:
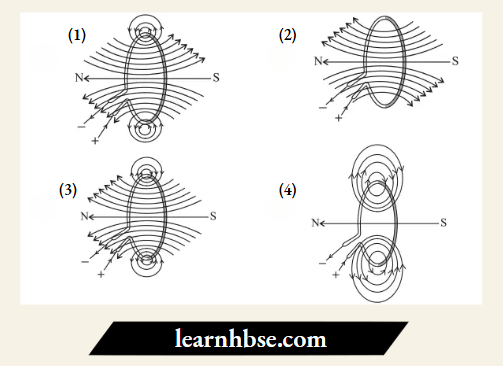
Answer: 3.
Question 15. The resistance of a resistor is reduced to half of its initial value. If other parameters of the electrical cirenit remain unaltered, the amount of heat produced in the resistor will become:
- Four times
- Two times
- Half
- One fourth
Answer: 2. Two times
Question 16. An alpha particle enters a uniform magnetic field as shown. The direction of force experienced by the alpha particle is:
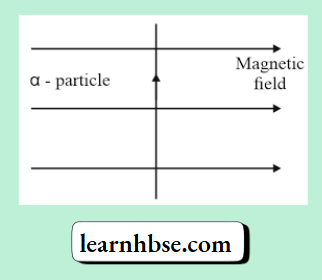
- Towards right
- Towards left
- Into the page
- Out of the page
Answer: 4. Out of the page
Assertion – Reasoning based questions. These consist of two statements Assertion (A) and Reason (R). Answer these questions selecting the appropriate option given below.
- Both (A) and (R) are true and (R) is the correct explanation of (A).
- Both (A) and (R) are true but (R) is not the correct explanation of (A).
- (A) is true but (R) is false.
- (A) is false but (R) is true.
Question 1. Assertion (A): Reaction of quicklime with water is an exothermic reaction.
Reason (R): Quicklime reacts vigorously with water releasing a large amount of heat.
Answer: 1. Both (A) and (R) are true and (R) is the correct explanation of (A).
Question 2. Assertion (A): In humans, if gene (B) is responsible for black eyes and gene (b) is responsible for brown eyes, then the colour of eyes of the progeny having gene combination Bb, bb or BB will be black only.
Reason (R): The black colour of the eyes is a dominant trait.
Answer: 4. (A) is false but (R) is true.
Question 3. Assertion (A): The inner walls of the small intestine have finger like projections called villi which are rich in blood.
Reason (R): These villi have a large surface area to help the small intestine in completing the digestion of food.
Answer: 1. Both (A) and (R) are true and (R) is the correct explanation of (A).
Question 4. Assertion (A): A current carrying straight conductor experiences a force when placed perpendicular to the direction of magnetic field.
Reason (R): The net charge on a current carrying conductor is always zero.
Answer: 2. Both (A) and (R) are true but (R) is not the correct explanation of (A)
Very Short Answer Questions
Question 1.
1. A student took a small amount of copper oxide in a conical flask and added dilute hydrochloric acid to it with constant stirring. He observed a change in colour of the solution.
- Write the name of the compound formed and its colour.
- Write a balanced chemical equation for the reaction involved.
OR
2. The industrial process used for the manufacture of caustic soda involves electrolysis of an aqueous solution of compound ‘X’, In this process, two gases Y and ‘Z’ are liberated. Y is liberated at cathode and which is liberated at anode, on treatment with dry slaked lime forms a compound ‘B’. Name X, Y, Z and B.
Answer:
The compound formed is Copper Chloride or cupric chloride (CuCI2). The colour of CuCI2 is blue-green.
The balanced chemical equation is: CuO(s) + 2HCI(aq) CuCI2(aq) + H20(l)
OR
Compound X is NaCI(aq), which is a concentrated aqueous solution of sodium chloride in water.
Compound Y is H2 (Hydrogen gas), liberated at cathode.
Compound Z is Cl2, (Chlorine gas), liberated at anode.
Treatment of gas Z (Cl2) with dry slaked lime, Ca(OH)2, gives bleaching powder (CaOCI2).
\(\mathrm{Ca}(\mathrm{OH})_2+\mathrm{Cl}_2 \rightarrow \mathrm{CaOCl}_2+\mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{O}\)Hence, Compound B is CaOCI2
The overall balanced chemical equation is: \(2 \mathrm{NaCl}(\mathrm{aq})+2 \mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{O}(\mathrm{l}) \rightarrow 2 \mathrm{NaOH}(\mathrm{aq})+\mathrm{Cl}_2(\mathrm{~g})+\mathrm{H}_2(\mathrm{~g})\)
Question 2.
1. Name the part of brain which is responsible for the following actions:
- Maintaining posture and balance
- Beating of heart
- Thinking
- Blood pressure
OR
2. Where are auxins synthesized in a plant? Which organ of the plant shows:
- Positive phototropism
- Negative geotropism
- Positive hydrotropism
Answer:
- Cerebellum
- Medulla
- Cerebrum
- Medulla
OR
Auxins are synthesized in the growing regions at the tip of the shoot and root in a plant.
- Positive phototropism -Shoot
- Negative geotropism- Shoot
- Positive hydrotropism- Root
Question 3. Write one specific function each of the following organs in relation with excretion in human beings:
- Renal Artery
- Urethra
- Glomerulus
- Tubular part of nephron
Answer:
- Renal artery carries nitrogenous excretory wastes towards the kidneys.
- Urethra releases urine out of the body.
- Glomerulus helps infiltration of blood passing through it and passes it on to the Bowman’s capsule.
- The tubular part of nephron reabsorbs useful products like glucose, amino acids, ions and a large amount of water into blood capillaries.
Question 4. Two green plants are kept separately in oxygen free containers, one in the dark and other in sunlight. It was observed that plant kept in dark could not survive longer. Give reason for this observation.
Answer:
Plants release oxygen during photosynthesis, which can be utilized by the plant for respiration. The plant kept in dark was not able to perform photosynthesis to generate some oxygen for respiration.
The carbon dioxide released by the plant after respiration was utilized by the plants to photosynthesize food, hence, the plant was able to survive.
Question 5.
Observe the following diagram and answer the questions following it:
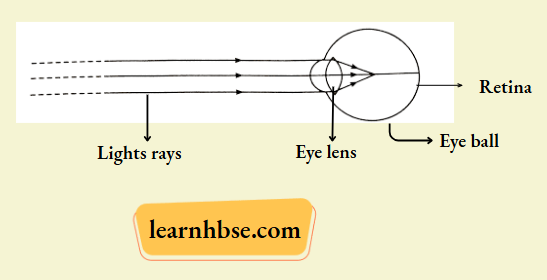
- Identify the defect of vision shown,
- List its two causes,
- Name the type of lens used for the correction of this defect.
OR
The colour of clear sky from the earth appears blue but from the space it appears black. Why?
Answer:
- Myopia, as image is formed before the retina for far away objects.
- Possible causes are:
- Elongation of eyeballs.
- Excessive curvature of eye lens.
- Correction: Using concave lens of suitable focal length.
OR
2. The sky appears blue because of the presence of atmosphere, which scatters maximum blue light. Since, Earth has atmosphere, so particles present in it, make scattering of light possible for blue colour.
Space has no atmosphere so there is no intervening particle to obstruct light so as to scatter light. Hence, it appear dark from space.
Question 6. Use of several pesticides which results in excessive accumulation of pesticides in rivers or ponds, is a matter of deep concern. Justify this statement.
Answer:
Pesticides are toxic, non-biodegradable substances that often run off into water bodies. Once, the toxin enters the body of living organisms, it is not metabolized or excreted, leading to its accumulation inside the body.
The accumulation increases the concentration of toxin with each successive trophic level of the food chain, leading to a phenomenon called biological magnification. The topmost trophic level accumulates the maximum amount of toxin, leading to severe health issues and sometimes the death of the individual.
Short Answer Questions
Question 1.
While electrolysing water before passing the current some drops of an acid are added.
- Why ? Name the gases liberated at cathode and anode. Write the relationship between the volume of gas collected at anode and the volume of gas collected at cathode.
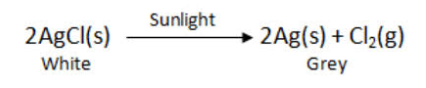
- What is observed when silver chloride is exposed to sunlight ? Give the type of reaction involved.
Answer:
1. Water is a non-electrolyte so, the addition of acid will make it a good conductor of electricity. By this action, ions will be produced due to dissociation of acidified water that acts as a charge carriers for the faster conduction of electricity.
The gas liberated at the cathode is Hydrogen gas. The gas liberated at the anode is Oxygen gas. In the electrolysis of water, the ratio of volumes of hydrogen and oxygen obtained is 2:1 i.e. 2 volumes of hydrogen and 1 volume of oxygen combines to form water.
2. When silver chloride is exposed to light, it decomposes to form silver metal and chlorine gas. The type of reaction is photolytic decomposition.
Question 2.
- Suggest a safe procedure of diluting a strong concentrated acid.
- Name the salt formed when sulphuric acid is added to sodium hydroxide and write its pH.
- Dry HCI gas does not change the colour of dry blue litmus paper. Why?
Answer:
The acid is always diluted by adding the acid to water slowly and with constant stirring. In addition to it, it is advised to wear gloves and goggles and maintain safe distance.
The salt formed when sulphuric acid is added to sodium hydroxide is sodium sulphate. The balanced equation is:
\(2 \mathrm{NaOH}+\mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{SO}_4 \rightarrow \mathrm{Na}_2 \mathrm{SO}_4+2 \mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{O}\)Its pH is approximately equal to 7.
The colour of litmus paper changes only in the presence of ions like hydrogen (H+) or hydronium (H30+) ions. HCI can produce these ions only in the form of aqueous solution. Hence, dry HCI gas does not change the colour of dry litmus paper.
Question 3.
1. (1) How does Paramecium obtain its food ?
(2) List the role of each of the following in our digestive system:
- Hydrochloric acid
- Trypsin
- Muscular walls of stomach
- Salivary amylase
OR
2. (1) What is double circulation ?
(2) Why is the separation of the right side and the left side of the heart useful? How does it help birds and mammals?
Answer:
1. (1) Paramecium takes its food at a specific spot by endocytosis. Food is moved to this spot by the movement of cilia which cover the entire surface of the cell.
(2) Hydrochloric acid: The hydrochloric acid creates an acidic medium which facilitates the action of enzyme pepsin and it also kills the germs in the food.
- Trypsin: Trypsin helps in digestion of proteins into smaller peptides.
- Muscular wall of stomach: The muscular wall of stomach help in mixing the food thoroughly with more digestive juices.
- Salivary amylase: Saliva contains an enzyme called salivary enzyme which breaks down starch to give simple sugar.
or
2. (1) Double circulation is the process during which blood passes twice through the heart during one complete cycle. Blood is circulated to the body tissues through systemic circulation and to the lungs through pulmonary circulation.
(2) The separation of right side and left side of the heart helps in separation of oxygenated and deoxygenated blood, which allows a more efficient supply of oxygen to the body cells. 1 Birds and mammals are warm blooded animals. Since, they require more energy to maintain a constant body temperature; hence, the separation provides availability of oxygen during respiration to generate more energy for thermoregulation.
Question 4.
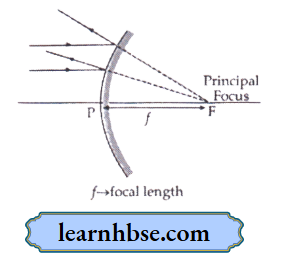
1. Define the following terms in the context of a diverging mirror:
- Principal focus
- Focal length Draw a labelled ray diagram to illustrate your answer.
OR
2. An object of height 10 cm is placed 25 cm away from the optical centre of a converging lens of focal length 15 cm. Calculate the image-distance and height of the image formed.
Answer:
- Principal focus: It is the point on the axis of a mirror to which parallel rays of light appear to diverge after reflection from diverging mirror.
- Focal length: The distance between pole of convex mirror and principal focus.
2. Given, Object’s height h0 = 10 cm; Object distance, u = -25 cm; Focal length of convex lens; f = 15 cm
Image distance v = ? Height of image hi = ?
Using the lens formula:
\(\frac{1}{f}=\frac{1}{v}-\frac{1}{u}\)or, \(\frac{1}{v}=\frac{1}{f}+\frac{1}{u}=\frac{1}{15}+\frac{1}{-25}\)
or, \(v=\frac{75}{2}=37.5 \mathrm{~cm}\)
From the magnification formula
\(\frac{h_i}{h_{\mathrm{o}}}=\frac{\mathrm{v}}{\mathrm{u}}\)or, \(h_i=\frac{v}{u} \times h_o=\frac{37.5 \times 10}{-25.0}\)
or, hi = —15 cm
An inverted image of 15 cm will be formed at a distance of 37.5 cm from the given lens.
Question 5. The power of a lens is +4D. Find the focal length of this lens. An object is placed at a distance of 50 cm from the optical centre of this lens. State the nature and magnification of the image formed by the lens and also draw a ray diagram to justify your answer.
Answer:
Power of lens, P = +4D
Since \(\)
Or, f = 0.25 m = 25 cm
Since power is positive, so the lens is convex lens.
Now using lens formula,
\(\frac{1}{f}=\frac{1}{v}-\frac{1}{u}\)or, \(\frac{1}{v}=\frac{1}{f}+\frac{1}{u}=\frac{1}{25}+\frac{1}{-50}\)
or, v = 50 cm
Magnification, \(m=\frac{v}{u}=\frac{50}{-50}=-1\)
Since, image distance is positive and its magnification is -1, it indicates a real, inverted and image of same size.
Question 6.
Why is an alternating current (A.C.) considered to be advantageous over direct current (D.C.) for the long distance transmission of electric power?
How is the type of current used in household supply different from the one given by a battery of dry cells?
How does an electric fuse prevent the electric circuit and the appliances from a possible damage due to short circuiting or overloading.
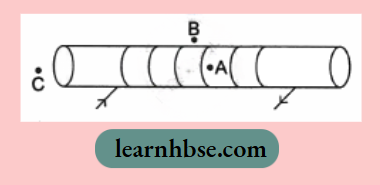
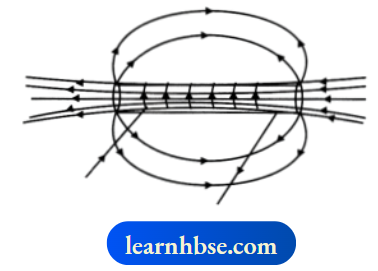
OR
For the current carrying solenoid as shown, draw magnetic field lines and give reason to explain that out of the three points A, B and C, at which point the field strength is maximum and at which point it is minimum?
Answer:
- Alternating current can be transmitted over long distances at very high voltages so as to ensure that current value is very low and as a result very low amount of energy is lost during transmission. When it reaches near the household, the voltage can be stepped down to restore required value of current whereas the voltage of direct current cannot be stepped up and down.
- The type of current used in domestic household supply is alternating while a battery of dry cells supplies direct current.
- Electric fuse is made of wires of very low melting point. If there is a current larger than the specified value, the temperature of fuse wire increases and it melts to break the electric circuit and stop the flow of unduly high electric current. This saves appliances from possible damage.
or
- The field strength will be maximum at point A as A is inside the solenoid where the field lines have highest density.
- The field strength will be minimum at point B as field lines have least density.
Question 7. Write one difference between biodegradable and non-biodegradable wastes. List two impacts of each type of the accumulated waste on environment if not disposed off properly.
Answer:
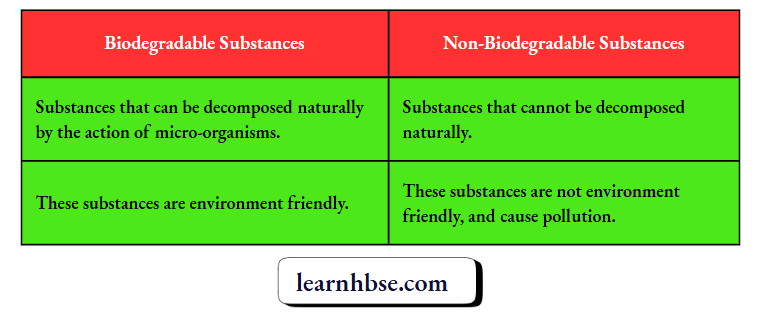
Effects of biodegradable substances on environment:
- Decomposition of biodegradable wastes is accompanied by foul smell which spreads in the environment and affects the people of nearby areas.
- It act as breeding grounds for houseflies, etc. which act as vectors of various diseases.
Effects of non-biodegradable substances on environment:
- Excessive use of non-biodegradable pesticides increases the soil pollution and also affects the soil fertility.
- Certain non-biodegradable wastes enter the food chains and affects the various biotic components of the environment.
Long Answer Questions And Answers
Question 1.
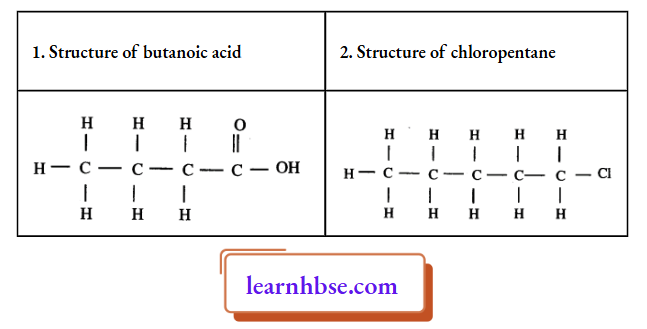
1. Draw the structure of the following components?
- Butanoic acid
- Chloropentane
2. How are structure
- And structure
- Given below related to one another ? Give reason to justify your answer.
image
Draw one more possible structure for above case.
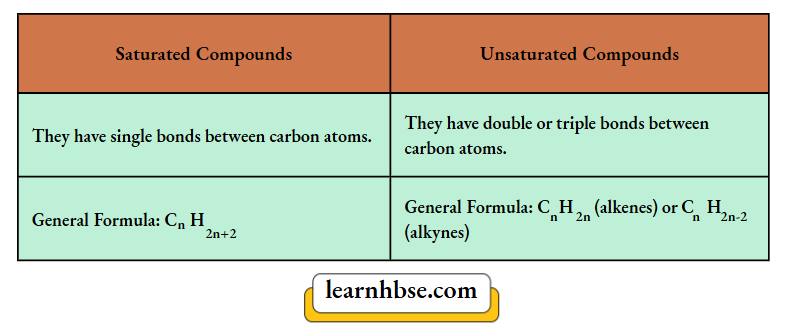
3. Differentiate between saturated and unsaturated compounds on the basis of their general formula.
OR
2. What happens when a small piece of sodium is dropped on ethanol? Write the equation for this reaction.
- Why is glacial acetic acid called so?
- What happens when ethanol is heated at 443 K in the presence of cone. H2S04? Write the role of cone. H2SO4 in this case.
- Write an equation showing saponification.
Answer:
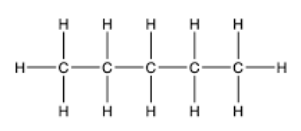
2. Structures (1) and (2) are structural isomers of each other as they have different structures but same molecular formula (C6H14). Another structural isomer is n-hexane as shown below:
3. Difference between saturated and unsaturated compounds are:
or
2. Ethanol reacts with sodium to produce hydrogen gas and sodium ethoxide.
2CH3CH2OH + 2Na -> 2CH3CH20-Na++ H2
Ethanol Sodium Ethoxide
- The freezing point of pure ethanoic acid is 290 K and hence, it freezes during winter in cold climates. That is why; it is called as glacial acetic acid.
- When ethanol is heated with concentrated sulphuric acid at 443 K, it loses one water molecule and forms ethene.
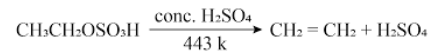
Role of H7SO4: It acts as dehydrating agent and removes water molecules from ethanol.
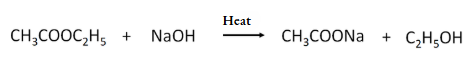
- Equation for saponification reaction:
Question 2.
- Name and explain the two modes of asexual reproduction observed in hydra.
- What is vegetative propagation? List two advantages of using this technique.
Answer:
1. The two modes of asexual reproduction observed in Hydra are : Budding and Regeneration.
Budding in Hydra: In Budding, a small part of the body of the parents grows out as a ‘bud’ which then detaches and becomes a new organism. Hydra reproduces by budding using the regenerative cells.
A bud develops as an outgrowth in Hydra due to repeated cell division at one specific site. When fully mature, the bud detaches itself from the parent body and develops into new independent individuals.
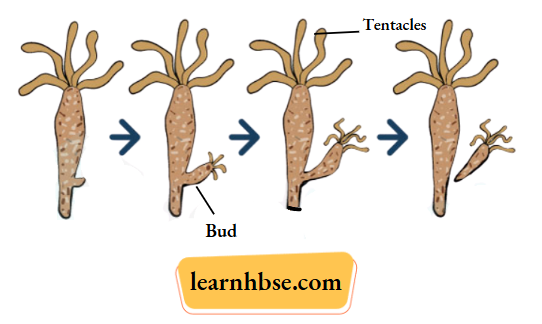
Regeneration in Hydra: In this method, small cut or broken parts of the organisms’ body grow or regenerate into separate individuals. Regeneration of Hydra from the body parts is carried out by specialized cells, which proliferate and make a large number of cells.
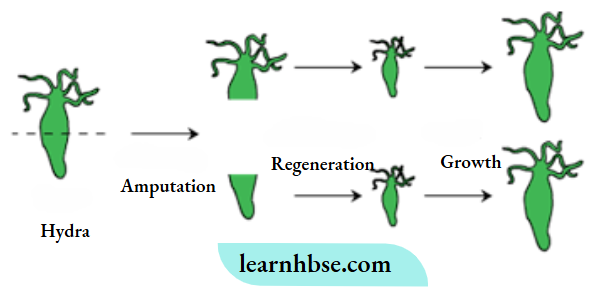
2. Vegetative propagation is the development of a new plant from the vegetative parts (roots, stem and leaves) of a plant.
Advantages:
- Such plants can bear flowers and fruits earlier than those produced from seeds.
- Allows propagation of plants (banana, orange etc) that have lost capacity to produce seeds.
- All plants produced are genetically similar to the parent plant and hence have all its characters.
Question 3.
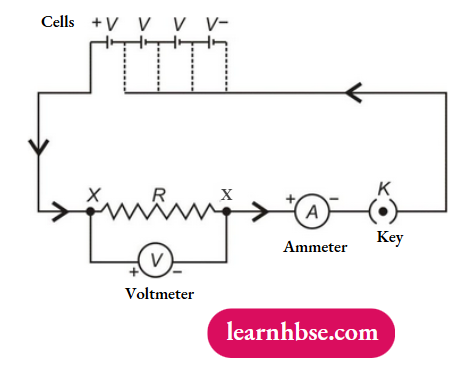
- How is electric current related to the potential difference across the terminals of a conductor? Draw a labelled circuit diagram to verify this relationship.
- Why should an ammeter have low resistance?
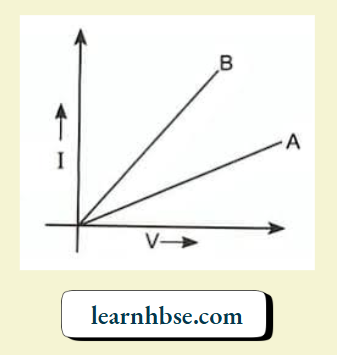
- Two V – 1 graphs A and B for series and parallel combinations of two resistors are as shown. Giving reason state which graph shows (a) series, (b) parallel combination of the resistors.
Answer:
1. The ratio of potential difference to the flow of current in conductor is constant which is called the resistance of the conductor provided the physical conditions of the conductor remains constant. This is called Ohm’s Law. Mathematically, V/l = R (constant)
Circuit Diagram:
2. An ammeter is a device used to measure the amount of current flowing in a circuit. The resistance of an ideal ammeter should be zero as it is always connected in series in a circuit.
Hence, its resistance adds to the total resistance of the circuit. If the resistance of the ammeter would be high, then the total resistance would be too high. This in turn would decrease the amount of current flowing through the circuit.
3. The slope of l-V graph gives the reciprocal of resistance. So, the graph with a lesser slope will indicate a larger resistance.
The series combination of resistances has a large net resistance than the corresponding parallel combination. So, Graph A indicates series combination and graph B indicates parallel combination.
Source Based Or Case Based Questions And Answers
Question 1. The melting points and boiling points of some ionic compounds are given below:
![]()
These compounds are termed ionic because they are formed by the transfer of electrons from a metal to a non-metal. The electron transfer in such compounds is controlled by the electronic configuration of the elements involved. Every element tends to attain a completely filled valence shell of its nearest noble gas or a stable octet.
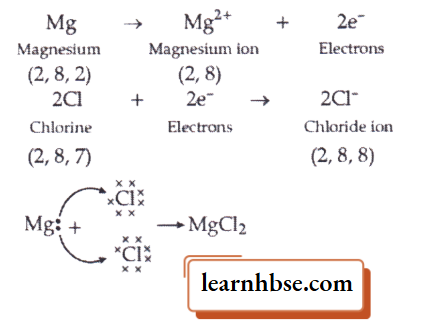
- Show the electron transfer in the formation of magnesium chloride.
- List two properties of ionic compounds other than their high melting and boiling points.
- While forming an ionic compound say sodium chloride how does sodium atom attain its stable configuration ?
OR
2. Give reasons:
- Why do ionic compounds in the solid state not conduct electricity?
- What happens at the cathode when electricity is passed through an aqueous solution of sodium chloride ?
Answer:
1. Electron transfer in the formation of magnesium chloride:
2. Two properties of ionic compounds are:
- They conduct electricity in solution or molten state.
- They are hard and brittle crystalline solids. ‘A + ‘A
3. Sodium chloride is formed by the combination of sodium and chloride ions. Sodium loses one electron from valence shell to attain stable noble gas configuration.
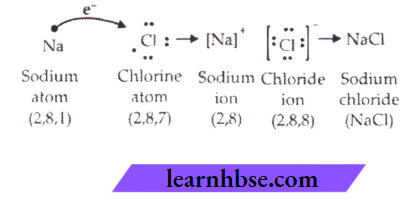
or
- Ionic compounds do not conduct electricity in solid state due to the absence of free ions but they conduct electricity in molten and aqueous state due to presence of free ions.
- Reduction takes place at cathode. Therefore, during electrolysis of aqueous solution of sodium chloride, hydrogen gas is evolved at cathode due to reduction of H+ ions.
Question 2. The most obvious outcome of the reproductive process is the generation of individuals of similar design, but in sexual reproduction they may not be exactly alike. The resemblances as well as differences are marked. The rules of heredity determine the process by which traits and characteristics are reliably inherited. Many experiments have been done to study the rules of inheritance.
- Why an offspring of human being is not a true copy of his parents in sexual reproduction?
- While performing experiments on inheritance in plants, what is the difference between FI and F2 generation?
- Why do we say that variations are useful for the survival of a species over time ?
OR
Study Mendel’s cross between two plants with a pair of contrasting characters.
RRYY X rrYY
Round Yellow Wrinkiled Green
He observed 4 types of combinations in F2 generation. Which of these were new combinations? Why do new features which are not present in the parents, appear in F2 generation?
Answer:
- An offspring is not a true copy of his parents in sexual reproduction because of variations due to recombination of genetic material from two different parents.
- All the FI offspring are genetically identical and exhibit the dominant trait. F2 offspring can exhibit a range of dominant to recessive traits.
- Variations help the organism to become more adapted to the changing environmental conditions. This helps the organisms to overcome the adverse conditions.
or
Round Green and Wrinkled Yellow are the new combinations in F2 generation. New features which are not present in parents appear in F2 generation due to the segregation of different combinations of alleles of different characters independently during gamete formation and fertilisation.
Question 3. The ability of a medium to refract light is expressed in terms of its optical density. Optical density has a definite connotation. It is not the same as mass density. On comparing two media, the one with the large refractive index is optically denser medium than the other. The other medium with a lower refractive index is optically rarer. Also the speed of light through a given medium is inversely proportional to its optical density.
Determine the speed of light in diamond if the refractive index of diamond with respect to vacuum is 2.42. Speed of light in vacuum is 3 x 108 m/s.
Refractive indices of glass, water and carbon disulphide are 1.5, 1.33 and 1.62 respectively. If a ray of light is incident in these media at the same angle (say q), then write the increasing order of the angle of refraction in these media.
The speed of light in glass is 2 x 108 m/s and in water is 2.25 x 108 m/s.
Which one of the two is optically denser and why ?
A ray of light is incident normally at the water-glass interface when it enters a thick glass container filled with water. What will happen to the path of the ray after entering the glass? Give reason.
OR
The absolute refractive indices of water and glass are 4/3 and 3/2 respectively. If the speed of light in glass is 2 x 108 m/s, find the speed of light in (i) vacuum and (ii) water.
Answer:
1. \(\mu=\frac{\text { Speed of light in vacuum (c) }}{\text { Speed of light in any medium (v) }}\)
Given, p = 2.42, c = 3 x 108 m/s
Therefore, speed of light in medium (diamond) = \(\frac{3 \times 10^8}{2.42}=1.24 \times 10^8 \mathrm{~m} / \mathrm{s}\)
2. Carbon disulphide is most dense and water is least dense.
From Snell’s Law, \(\mu=\frac{\sin i}{\sin r}\)
So, \(\frac{\sin i}{1.33}>\frac{\sin i}{1.5}>\frac{\sin i}{1.62}\)
Hence, for angle of refraction, increasing order will be rcs > rg > rw
3. Speed of light is more in rarer medium than denser medium. So, glass is denser.
When light is incident normally at waterglass interface, it goes straight through the medium with no bending. It is because, by bending light prefers to go shortest path. In case when normally incident, it is already along shortest path.
Or
3. \(\mu=\frac{\text { Speed of light in vacuum (c) }}{\text { Speed of light in any medium (v) }}\)
Given, \(\mu_w=\frac{4}{3} ; \mu_{\mathrm{g}}=\frac{3}{2}\)
Speed of light in glass, vg= 2 x 108 m/s
\(\mu_{\mathrm{g}}=\frac{\mathrm{c}}{v_g}\)or, \(\mathrm{c}=\frac{3}{2} \times 2 \times 10^8=3 \times 10^8 \mathrm{~m} / \mathrm{s}\)
\(\mu_w=\frac{c}{v_w}\)or, \(\frac{c}{v_w}=\frac{3 \times 10^8}{4 / 3}=2.25 \times 10^8 \mathrm{~m} / \mathrm{s}\).
