Haryana Board Class 10 Physics Chapter 1 Light-Reflection And Refraction Multiple Choice Questions And Answers
Question 1. Which of the following mirrors is used by a dentist to examine a small cavity in a patient’s teeth?
- Convex Mirror
- Plane Mirror
- Concave Mirror
- Any Spherical Mirror
Answer: 3. Concave Mirror
Question 2. Which diagram shows image formation of an object on a screen by a converging lens?
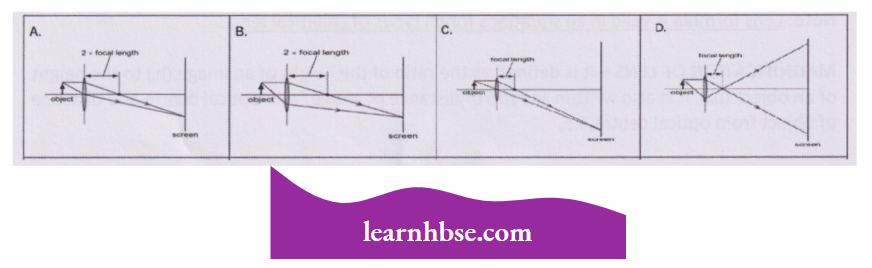
Answer: 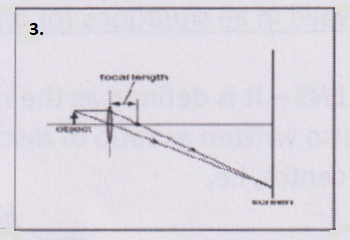
Question 3. Which of the following can make a parallel beam of light when light from a point source is incident on it?
- Concave mirror as well as convex lens;
- Convex mirror as well as concave lens.
- Two plane mirrors placed at 90° to each-other;
- Concave mirror as well as concave lens.
Answer: 1. Concave mirror as well as convex lens
Question 4. Consider these indices of refraction: glass: 1.52; air: 1.0003; water: 1.333. Based on the refractive indices of three materials, arrange the speed of light through them in decreasing order.
- The speed of light in water > the speed of light in air > the speed of light in glass.
- The speed of light in glass > the speed of light in water > the speed of light in air.
- The speed of light in air > the speed of light in water > the speed of light in glass.
- The speed of light in glass > the speed of light in air > the speed of light in water.
Answer: 3. The speed of light in air > the speed of light in water > the speed of light in glass.
Question 5. Examine the above figure and state which of the following options is correct? [One small box in the figure is equal to 1 cm]
- The mirror has a focal length of -6 cm and will produce an image of magnification +1.
- The mirror has a focal length of -3 cm and will produce an image of magnification -1.
- The mirror has a focal length of -3 cm and will produce an image of magnification +1.
- The mirror has a focal length of -6 cm and will produce an image of magnification -1.
Answer: 2. The mirror has a focal length of -3 cm and will produce an image of magnification -1.
Question 6. The angle of incidence from air to glass at the point 0 on the hemispherical glass slab is:
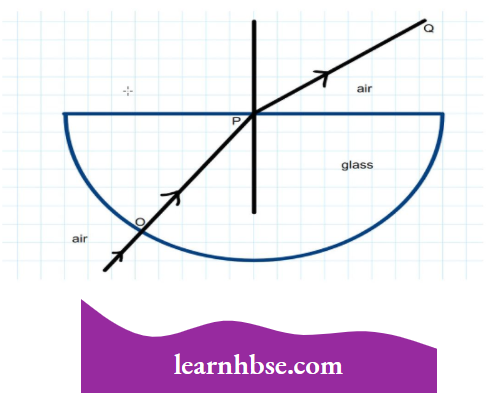
- 45°
- 0°
- 90°
- 180°
Answer: 2. 0°
Question 7. If the power of a lens is – 4.0 D, then it means that the lens is a
- Concave lens of focal length -50 m;
- Convex lens of focal length +50 cm
- Concave lens of focal length -25 cm ;
- Convex lens of focal length -25 m
Answer: 3. Concave lens of focal length -25 cm ;
Question 8. Rays from Sun converge at a point 15 cm in front of a concave mirror. Where should an object be placed so that size of its image is equal to the size of the object?
- 30 cm in front of the mirror;
- 15 cm in front of the mirror
- Between 15 cm and 30 cm in front of the mirror;
- More than 30 cm in front of the mirror
Answer: 1. 30 cm in front of the mirror
Question 9. If the real image of a candle flame formed by a lens is three times the size of the flame and the distance between lens and image is 80 cm, at what distance should the candle be placed from the lens?
- -80cm
- -40 cm
- -40/3 cm
- -80/3 cm
Answer: 4. -80/3 cm
Question 10. While looking at the above diagram, Navin concluded the following
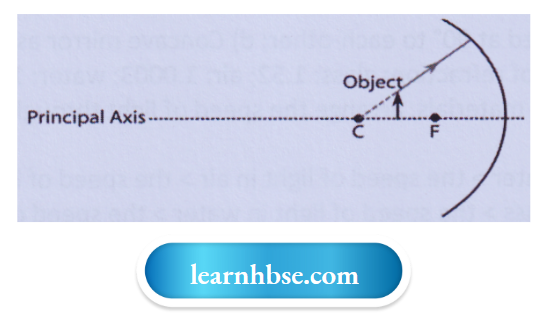
- The image of the object will be a virtual one.
- The reflected ray will travel along the same path as the incident ray but in opposite direction.
- The image of the object will be inverted.
- This is a concave mirror and hence the focal length will be negative. Which one of the above statements are correct?
- 1 and 2;
- 1 and 3;
- 2, 3 and 4;
- 1, 2, 3 and 4
Answer: 3. 2, 3 and 4;
Question 11. In the diagram light is travelling through different media. It is noted by a scientist that ∠1= ∠3= ∠4 but ∠2 <∠l. Which of the following statement would be correct?
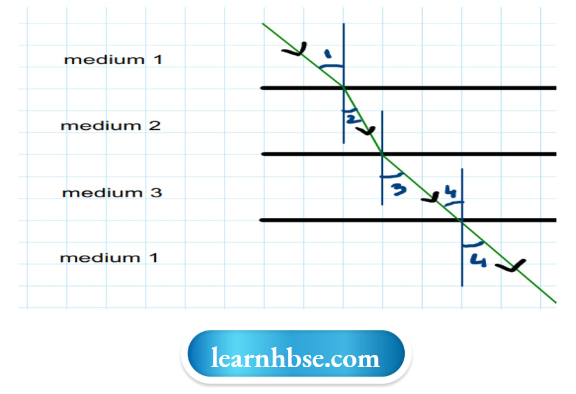
- Medium 1 is the denser than medium 3 but it’s density is equal to medium 2.
- Medium 2 is the rarest medium.
- Medium 3 is denser than medium 1.
- Medium 1 and 3 are essentially the same medium, but medium 2 is denser than 1 and 3.
Answer: 4. Medium 1 and 3 are essentially the same medium, but medium 2 is denser than 1 and 3.
Question 12. The refractive index of flint glass is 1.65 and that for alcohol is 1.36 with respect to air. What is the refractive index of the flint glass with respect to alcohol?
- 0.82
- 1.21
- 1.11
- 1.01
Answer: 2. 1.21;
Question 13. The given lens has a focal length of 10 cm. The object of height 2 mm is placed at a distance of 5 cm from the pole. Find the height of the image.
- 4 cm
- 6.67 mm
- 4 mm
- 3.33 mm
Answer: 3. 4 mm
Question 14. A ray passing through the centre of curvature of a concave mirror is inclined at an angle a to its principal axis. The angle of reflection for this ray equals:
- (∝/2)°
- 0°
- ∝°;
- 90°
Answer: 2. 0°
Question 15. Consider the situation where:
- An object is 3 cm (height)
- Mirror is concave with 6 cm focal length.
- Object is placed at the centre of curvature.
Which of the following options are correct?
- The mirror will produce an image of magnification +1.5.
- The mirror will produce an image of magnification -1.
- The mirror will produce an image of magnification +1.
- The mirror will produce an image of magnification -1.5.
Answer: 2. The mirror will produce an image of magnification -1
Question 16. If a ray passes from air to glass in a spherical glass slab and passes through the centre of the slab without deviation, then the angle of incidence from air to glass at the point on the glass slab is.
- 45°
- 0°
- 90°
- 180°
Answer: 2. 0°
Question 17. Naman draws a ray diagram for an object in front of a concave mirror. She draws a ray starting from the top of the object and falling on the mirror perpendicularly. The ray after reflection will
- Pass through focus.;
- Pass through pole.
- Pass through the centre of curvature.;
- Pass through any point on the principal axis.
Answer: 3. Pass through the centre of curvature.
Question 18. If the refractive index of water with respect to air is 1.33 and of that of glass with respect to air is 1.5 then
- Water is optically denser than glass,
- Air is optically densest of all the three media.
- Air’s optical density is between glass and air.
- Glass is optically denser than water.
Answer: 4. Glass is optically denser than water.
Question 19. A convex lens has a focal length of 10 cm. The object of height 2 mm is placed at a distance of 5 cm from the pole. Find the height of the image.
- 4 cm
- 6.67 mm
- 4 mm
- 3.33 mm
Answer: 3. 4 mm
Question 20. Magnification produced by a rear view mirror fitted in vehicles
- Is equal to one
- Can be more than or less than one depending upon the position of the object in front of it
- Is less than one
- Is more than one
Answer: 3. Is less than one
Question 21. A student has to do the experiment on finding the focal length of a given convex lens by using a distant object. She can do her experiment if she is also provided with
- A lamp and a screen
- A scale and a screen
- A lamp and a scale
- None of these
Answer: 2. A scale and a screen
Question 22. When the two opposite surfaces of the slab are not parallel, the emergent angle e and incident angle are related as
- e < i ;
- e > i;
- Does not depend on the refractive index of the medium;
- Depends on the refractive index of the medium
Answer: 4. Depends on the refractive index of the medium
Chapter 1 Light – Reflection And Refraction Very Short Questions And Answers
Question 1. If the object is placed at a distance of 15 cm in front of the concave mirror of focal length of 10 cm, then what will be the nature of the image?
Answer: The object is placed at 15 cm; this means that the object is placed between the focus and the centre of curvature of the concave mirror. When the object is placed between the focus and the centre of curvature of a concave mirror, the image formed is real, inverted and magnified.
Question 2. How is the linear magnification produced by concave mirror?
- Less than 1 or equal to 1
- Zero or 1
- More than or equal to 1
- Less than 1, more than 1 or equal to 1
Answer: 4. Less than 1, more than 1 or equal to 1
Question 3. Define power of lens.
Answer:
The ability of a lens to converge or diverge the rays of light is called power of a lens. It is equal to the reciprocal of the focal length. P = l/f (in metre)
Question 4. Which type of reflection of light leads to the formation of images?
Answer: Regular reflection
Question 5. What kind of mirror can have a focal length of, -10 cm?
Answer: Concave mirror (since focal length is negative)
Question 6. Refractive indices of carbon disulphide and ethyl alcohol are 1.63 and 1.36 respectively. Which is optically denser?
Answer: Carbon disulphide is denser than the ethyl alcohol.
Question 7. If an object is at an infinity in front of a convex lens, where is the image formed?
Answer: At focus F
Question 8. What is the nature of the image formed by a convex lens if the magnification produced by the lens is +3?
Answer: Since the magnification has positive value, the image will be virtual and erect
Question 9. Why convex mirror is preferred as rear-view mirror in vehicles?
Answer: Convex mirror is preferred as rear-view mirror in vehicles because it gives virtual, erect image when object is beyond focus and gives wide field of view.
Question 10. Define principal focus for spherical mirrors.
Answer: It is the point on principal axis at which the incident rays parallel to principal axis, after reflection either meet or appear to meet.
Question 11. In torches, search lights and headlights of vehicles, the bulb is placed:
- Between the pole and the focus of the reflector
- Very near to the focus of the reflector
- Between the focus and centre of curvature of reflector
- At the centre of curvature
Answer: 2. Very near to the focus of the reflector
Explanation: The rays of light passing through the principal focus will go parallel to principal axis after reflection thus, forming a concentrated beam of light. Thus, in torches, headlights the bulb is placed very near to focus of the reflector.
Question 12. Light travels more quickly through water than through glass. What is optically denser among the medium mentioned in the statement?
Answer: Glass is optically denser than water.
Question 13. When does the light bend away from the normal during refraction?
Answer: When lights rays pass from optically denser to optically rarer medium.
Question 14. Which type of mirror could be used as a dentist’s mirror?
Answer: Concave mirror
Question 15. What is the full form of MRI?
Answer: Magnetic Resonance Imaging.
Question 16. A converging lens has a focal length of 20 cm. What is the power of the lens?
Answer: As the lens is converging, the focal length is positive. We know that Power = 1/ focal length (in m) = 1/0.2 m = + 5D
Question 17. For what position of an object, a concave mirror forms a real image equal in size to the object?
Answer: At the centre of curvature.
Question 18. A man stands 10 m away in front of a large plane mirror. How far must he walk before he is 5 m away from his image?
- 2.5 m
- 4.5 m
- 7.5 m
- 5 m
Answer: 3. 7.5 m;
Explanation: To be 5 m away from his image, the man must be standing 2.5 m away from the mirror. Thus, image distance + object distance = 2.5 m + 2.5 m = 5 m; Initially, he is 10 m away from the mirror. So, the man must walk a distance of 10 m- 2.5 m = 7.5 m.
Question 19. The incident ray makes an angle of 30° with a plane mirror. What is the total angle between the incident ray and the reflected ray?
- 60°
- 30°
- 120°
- 80°
Answer: 3. 120°
Explanation: ∠i = 90° – 30° = 60°; Since ∠i = ∠r, therefore ∠r = 60°; Angle between incident ray and reflected ray = ∠i + ∠r = 60° + 60° = 120°.
Chapter 1 Light-Reflection And Refraction Short Questions And Answers
Question 1. The image of an object placed at 40 cm in front of a lens is obtained on a screen at a distance of 100 cm from it. Find the focal length of the lens.
Answer:
f = 28.57 cm
Question 2. A concave mirror produces two times magnified real image of an object placed at 20 cm in front of it. What is the position of the image?
Answer:
v = —20 cm; the image is located at a distance of 20 cm in front of the mirror.
Question 3. An object is placed between infinity and the pole of a convex mirror. Draw a ray diagram and also state the position, the relative size and the nature of the image formed.
Answer:
When an object is placed between infinity and the pole of a convex mirror, the image formed is
- Behind the mirror at the focus (F)
- Virtual and erect
- Highly diminished.
Question 4. An object 20 cm from a spherical mirror gives rise to a virtual image 15 cm behind the mirror. Determine the magnification of the image and the type of the mirror used.
Answer:
m = 0.75; The magnification sign is positive while the value 0.75 is less than 1. This indicates that the mirror is convex mirror.
Question 5. What is the nature of the image formed by a convex lens if the magnification produced by the lens is +3?
Answer:
The image will be virtual and erect, since the magnification has positive value.
Question 6.
What type of lens is shown in the diagram on the right? What will happen to the parallel rays of light? Show by completing the ray diagram.
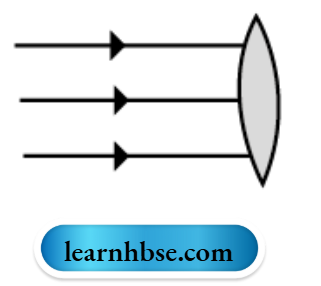
Your eye contains a convex lens. Why is it unwise to look at the sun?
Answer:
The lens shown in convex. The parallel rays will converge to a point called focus (F).
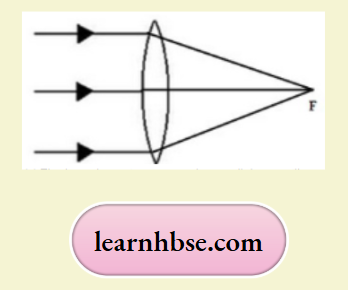
It is unwise to look at the sun because the convex lens focuses a lot of sun rays into our eyes and this may damage them.
Question 7. The diagrams show the appearance of a fork when placed in front of and close to two mirrors A and B, turn by turn.
- Which mirror is convex?
- Which mirror is concave? Give reasons for your choice.
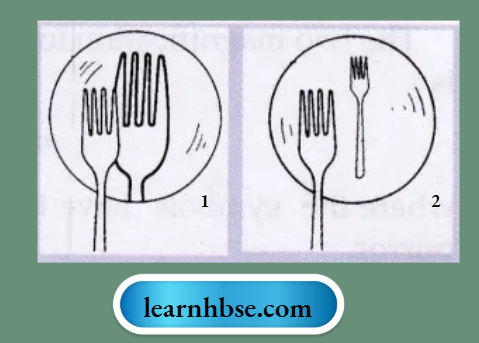
Answer:
- Mirror B is convex since it forms a smaller image of fork,
- Mirror A is concave since it forms a larger image of fork.
Question 8. Observe the diagram and answer the questions based on the studied concepts.
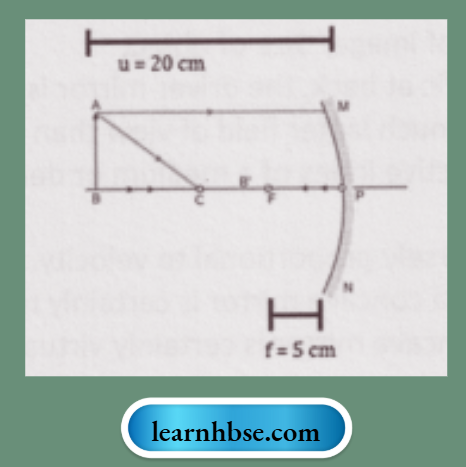
- Complete the given ray diagram.
- Calculate the position of the image formed.
Answer:
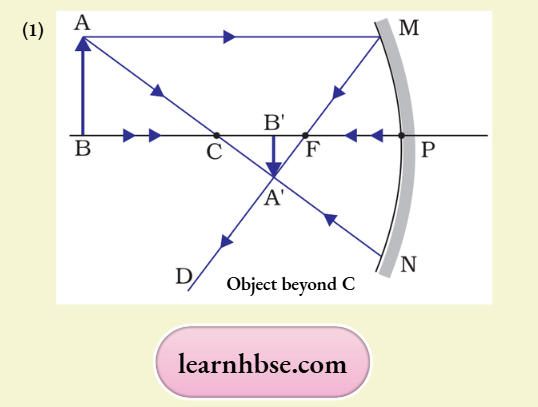
2. v = —6.67 cm; Thus, the image is formed at a distance of 6.67 cm between the centre of curvature and the focus.
Question 9. In which of the following media: glass, water and diamond
- Light travels slowest,
- Light travels fastest. Justify your answer
Answer:
Refractive index of glass: 1.52 to 1.9; Refractive index of water: 1.33; Refractive index of diamond: 2.42 – A substance having higher refractive index is optically denser then the substance of lower refractive index and light will travel slowest in the most optically dense substance highest refractive index.
Question 10.
- A wall reflects light and a mirror also reflects light. What difference is there in the way they reflect light?
- Which type of reflection of light leads to the formation of images?
Answer:
- A wall has a rough surface, so the reflection by a wall is a diffuse reflection. On the other hand, a mirror surface is smooth, so the reflection by a mirror is a regular reflection,
- Regular reflection
Question 11. Which type of mirror has:
- Positive focal length?
- Negative focal length?
Answer:
- Convex mirror
- Concave mirror
Question 12. Between which two points of concave mirror should an object be placed to obtain a magnification of:
- -3
- + 2.5
Answer:
- Between focus and centre of curvature
- Between pole and focus.
Question 13. If the focal length of a convex mirror is 15 cm, what is its radius of curvature?
Answer:
R = 30 cm
Question 14. The characteristics of image formed for an optical device are as follows:
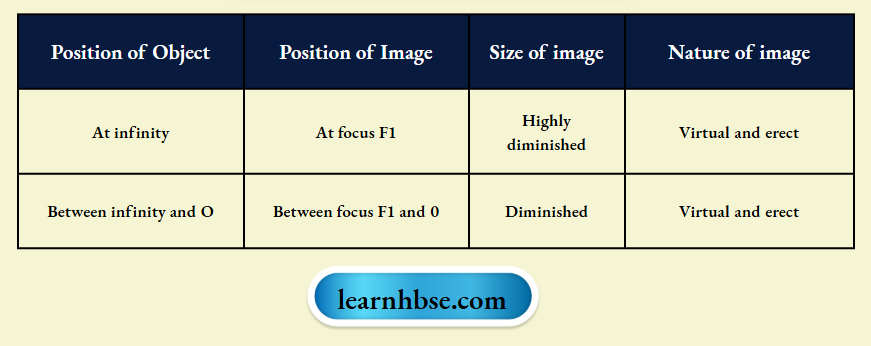
- To which spherical lens or mirror do the characteristics mentioned in the table belongs to?
- What sign is assigned to the value of focal length of this lens or mirror according to New Cartesian sign convention?
Answer:
- The characteristics mentioned in the given below belongs to the images formed by concave lens,
- The diverging les or concave lens has negative focal length according to the New Cartesian sign convention.
Question 15. A 4 cm tall object is placed perpendicular to the principal axis of a convex lens of focal length 24 cm. The distance of the object from the lens is 16 cm. Find the position, size and nature of the image formed, using the lens formula.
Answer:
Position of image: Image is formed at a distance of 48 cm from the optical centre of the lens on the same side of the object. It is indicated by the negative sign.
Size of image: It is three times the size of object, i.e. 12 cm.
Nature of image: Positive sign in the image height indicates that image is virtual and erect.
Question 16.
- Under what condition will a glass lens placed in a transparent liquid become invisible?
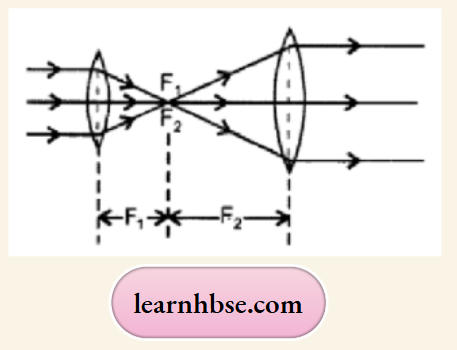
- Describe and illustrate with a diagram, how we should arrange two converging lenses so that a parallel beam of light entering one lens emerges as a parallel beam after passing through the second lens.
Answer:
- When the refractive index of glass lens becomes equal to the refractive index of transparent liquid, the glass lens will become invisible,
- Parallel beam converges at focus of the first lens and emerges parallel as it is at the focus of second lens, as shown in figure.
Question 17.
- If the image formed by a lens is diminished in size and erect, for all positions of the object, what type of lens is it?
- Name the point on the lens through which a ray of light passes undeviated.
Answer:
- Concave lens
- Optical centre
Question 18. The outer surface of a hollow sphere of aluminium of radius 50 cm is to be used as a mirror. What will be the focal length of this mirror? Which type of spherical mirror will it provide?
Answer:
f = R/2 = 25 cm. It will form a convex mirror.
Question 19. What is the nature of the image formed by a convex mirror when the object is placed between the pole and infinity?
- What is diffused reflection of light?
- Which mirror is used as a rear-view mirror? Why?
Answer:
- When an object is placed between the pole and infinity, the image formed is virtual, erect and diminished,
- When light rays are incident on the rough surface, they are reflected in different directions. This type of reflection is called diffused reflection or irregular reflection,
- A convex mirror always produces an erect, virtual and diminished image. This enables a driver to view a much larger area behind him. Hence, a convex mirror is suitable as a rear-view mirror.
Question 20. State the signs (positive or negative) and give reasons which can be given to the following:
- Object distance (u) for a concave mirror or convex mirror
- Image distances (v) for a concave mirror
- Image distances (v) for a convex mirror
Answer:
- Object distance (u) for a concave mirror or convex mirror is always negative because an object is always placed to the left side of the mirror and the distances towards the left of the mirror are always negative,
- In case of a concave mirror, if the image is formed on the left side of the mirror, then the image distance (v) will be negative and if the image is formed on the right side of the mirror, then the image distance (v) will be positive. This is because distances measured to the left of the mirror are negative and to the right of the mirror is positive,
- Image distances (v) for a convex mirror is always positive because the image is always formed behind the mirror.
Question 21. A person got his eyes tested by an optician. The prescription for the spectacle lenses to be made reads:
Left eye: + 2.50 D; Right eye: + 2.00 D
- State whether these lenses are thicker in the middle or at the edges.
- Which lens bends the light rays more strongly?
- State whether these spectacles lenses will converge light rays or diverge light rays.
Answer:
- These lenses have positive powers and hence positive focal lengths, so they are convex lenses. Convex lenses are thicker in the middle,
- Lens of greater power bends light rays more quickly. So, +2.50 D lens bends light rays more quickly,
- These spectacle lenses will converge the light rays because these are convex lenses.
Question 22. The image of an object placed at 30 cm in front of a lens is obtained on a screen at a distance of 60 cm from it. Find the focal length of the lens. What would be the height of the image if the object is 2 cm high?
Answer:
Object distance, u = – 30 cm
Image distance, v = 60 cm
From the lens formula,
⇒ \(\frac{1}{f}=\frac{1}{v}-\frac{1}{u}=\frac{1}{60}-\frac{1}{-30}=\frac{1}{60}+\frac{1}{30}=0.05\)
Therefore, f = 20 cm
Height of the object, h = 2 cm
From the magnification formula,
⇒ \(\mathrm{m}=\frac{\mathrm{v}}{\mathrm{u}}=\frac{\mathrm{h}^{\prime}}{\mathrm{h}}\)
Therefore, \(\mathrm{h}^{\prime}=\frac{\mathrm{v}}{\mathrm{u}} \mathrm{~h}=\frac{60}{-30} \times 2\)
h’ = -4 cm
Question 23. Refractive index of water with respect to air is 1.33 and that of diamond is 2.42.
- In which medium does the light move faster, water or diamond?
- What is the refractive index of diamond with respect to water?
Answer:
- Refractive index = speed of light in vacuum / speed of light in medium.
The refractive index of diamond is more.
Thus, the speed of light is lesser in diamond. Hence, the light moves faster in water than in diamond.
2. Let speed of light in water be vw and that in diamond be vd.
Let refractive index of diamond w.r.t water = μ
Therefore, p = Speed of light in water / speed of light in diamond
P = Vw/Vd
P = (Vw/c) ÷ (vd/c)μ = 2.42/1.33 = 1.82
Question 24. A 2 cm high object is placed at a distance of 20 cm from a concave mirror. A real image is formed at 40 cm from the mirror. Calculate the focal length of the mirror. Also, find the height of the image formed.
Answer:
Object distance, u = -20 cm
Image distance, v = -40 cm
Height of object (h0) = 2 cm
According to the mirror formula,
⇒ \(\frac{1}{v}+\frac{1}{u}=\frac{1}{f}\)
⇒ \(\frac{1}{-40}+\frac{1}{-20}=\frac{1}{f}\)
∴ \(\mathrm{f}=-\frac{4 0}{3}=-13.33 \mathrm{~cm}\)
Magnification, m = -v/u = himage/hobject
-40/-20 = himage/2
himage= – 4 Cm
Question 25. The face of a person is 24 cm long and 20 cm wide. What is the minimum size of the mirror required to see the full face?
Answer:
The size of the mirror required to see the full face should be half the size of the face.
Hence, the mirror should be 24/2 = 12 cm long and 20/2 = 10 cm wide. Also, the mirror should be placed with the longer side vertical and the eyes kept at proper height.
Question 26. The image of an object placed at 25 cm in front of a concave mirror is obtained on a screen at a distance of 50 cm from it. Find the focal length of the lens. What would be the height of the image if the object is 2 cm high?
Answer:
Object distance, u = -25 cm
Image distance, v = -50 cm
From the mirror formula,
⇒ \(\frac{1}{\mathrm{f}}=\frac{1}{v}+\frac{1}{u}=\frac{1}{-50}+\frac{1}{-25}=-0.06\)
Therefore, f (focal length of mirror) = -16.66 cm
Height of the object, h = 2 cm
From the magnification formula,
⇒ \(m=-\frac{v}{u}=\frac{h 2}{h 1}\)
∴ \(\mathrm{h} 2=-\frac{\mathrm{v}}{\mathrm{u}} h 1=-\left(-\frac{50}{-25}\right) \times 2=-4 \mathrm{~cm}\)
Height of the image is 4 cm.
Question 27. An object 4 cm in size is placed at a distance of 8 cm from a convex mirror of radius of curvature 20 cm. Find the nature, position and size of the image.
Answer:
Object distance, u = 8 cm
Image distance (v) = ?
Focal length = f = R/2 = 10 cm
⇒ \(\frac{1}{10}=\frac{1}{v}+\frac{1}{-8}\)
⇒ \(\frac{1}{v}=\frac{1}{10}+\frac{1}{8}=\frac{18}{80}=0.225\)
v = +4.4 cm
Thus, the position of the image is 4.4 cm behind the convex mirror. As the image is formed behind the convex mirror, its nature will be virtual and erect.
Magnification of the convex mirror is
m =-v/u = -4.4/-8 = 0.55
Also, m = h2/h1
0.55 = h2/4
h2 = 2.2 cm; Thus, the size of the image is 2.2 cm.
Question 28. A concave mirror produces a three times larger real image of an object placed at a distance of 20 cm in front of it. Find the position of the image and the nature of the image. Also, find the focal length of the mirror.
Answer:
m = -3; u = -20 cm
m = -v/u
-3 = -v/ (-20)
v = -60 cm
The image is located at a distance of 60 cm, and the nature of the image is enlarged, real and inverted.
∴ \(\frac{1}{f}=\frac{1}{v}+\frac{1}{u}=\frac{1}{-60}+\frac{1}{-20}=-\frac{80}{1200}\)
f = -15 cm
Thus, the focal length of a concave mirror is 15 cm.
Question 29.
- For what position of the object does a convex lens form an erect and virtual image?
- What is regular reflection of light?
- What type of mirror is used as a shaving mirror? Support your answer with a reason.
Answer:
- When the object lies between the optical centre and the focus of the lens, a convex lens forms an erect and virtual image.
- When a parallel beam of light falls on a smooth and highly polished surface, the reflected beam is also parallel and directed in a fixed direction. Such reflection of light is called regular reflection.
- Concave mirrors are used as shaving mirrors to see a large image of the face. This is because when the face is held within the focus of a concave mirror, an enlarged image of the face is seen in the concave mirror. This helps in getting a smooth shave.
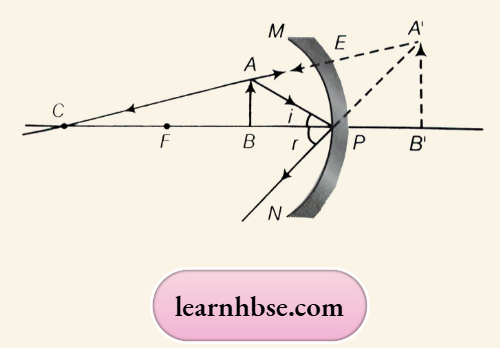
Question 30. What is the focal length of a concave mirror if the radius of curvature is 12 cm? What is the nature of the image formed by a concave mirror when an object is placed between its focus and pole? Draw the diagram for the same.
Answer:
R = -12 cm (Radius of curvature of a concave mirror)
We know that, f = R/2 = -12/2 =- 6 cm.
The image formed by a concave mirror when an object is placed between the focus and pole is virtual, erect and magnified.
Question 31. A ray of light is incident at an angle of 45° at the interface of medium (1) and medium (2) as shown in the above diagram. Redraw this diagram in the answer book and complete it. If the angle of refraction is 30°, find the refractive index of medium (2) with respect to medium (1).
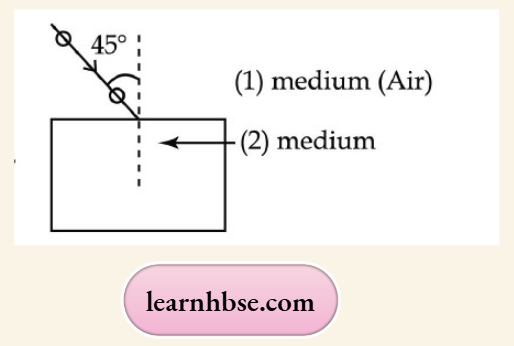
(Given that sin 450 =1/ V2 sin and sin 30° =1/2)
If the second medium is water in place of medium (2), will the angle of refraction increase or decrease? Why? (Refractive index of water = 4/3)
Answer:
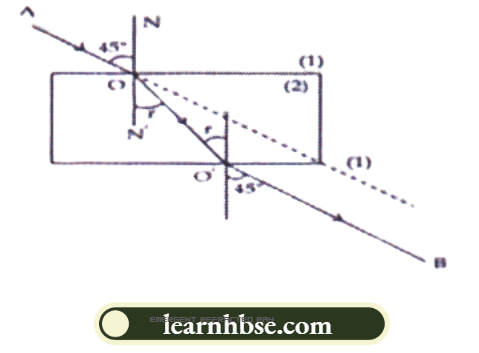
Using Snell’s law, the refractive index of medium (2) with respect to medium (1) is given as
∴ \(n 21=\frac{\sin i}{\sin r}=\sin 45^{\circ} / \sin 30^{\circ}=1.414\)
If the second medium is water in place of medium (2), the angle of refraction will decrease because water is rarer than medium (2).
Question 32.
- What is meant by refraction of light?
- One student measures the angle of refraction as 25° in medium A, and the other student measures the angle of refraction as 23° in the other medium B for the same angle of incidence 40°. Find the refractive index of both media. In which medium does light travel faster?
Answer:
- When light travels from one transparent medium to another transparent medium, deviation of its path takes place at the boundary. When light rays enter from a rarer medium to a denser medium (For Example. air to glass), they deviate towards the normal drawn at the point of incidence on the boundary. When light rays emerge out of a denser medium to a rarer medium (For Example. glass to air), they deviate away from the normal drawn at the point of incidence on the boundary. This is known as refraction of light.
- In medium A: Refractive index μA = sin (40°)/sin (25°) = 1.521.
In medium B: Refractive index μB = sin (40°)/sin (23°) = 1.645.
Refractive index (μ) of medium = c/v = velocity in air/ velocity in medium.
Hence, velocity in a medium is inversely proportional to the refractive index. So, light travels faster in medium A compared to medium B.
Question 33.
- A girl was playing with a thin beam of light from her laser torch by directing it from different directions on a convex lens held vertically. She was surprised to see that in a particular direction the beam of light continues to move along the same direction after passing through the lens. State the reason for this observation.
- Explain why a ray of light passing through the centre of curvature of a concave mirror, gets reflected along the same path.
Answer:
- A ray of light passing through the optical centre of the convex lens will continue to move along the same direction after refracting through the lens.
- The ray passing through the centre of curvature incident to the mirror along its normal so ∠i = ∠r = 0. Therefore, the ray retraces its path.
Question 34. Define refractive index. If light enters from air to glass having a refractive index 1.5, then calculate the speed of light in glass.
Answer:
The ratio of the speed of light in vacuum to the speed of light in a medium is called the refractive index of the medium.
n = Speed of light in air/ Speed of light in glass
1.5 = 3 x108/ Speed of light in glass
Speed of light in glass = 3 x 108/1.5 = 2.5 x 108 ms-1
Chapter 1 Light-Reflection And Refraction Long Questions And Answers
Question 1.
1. Name the type of mirrors used in
- A search light and
- Rear-view mirror. Draw labelled diagrams to show the formation of an image in each of these two cases.
2. Which of these mirrors could also form a magnified and virtual image of an object? Illustrate with the help of a ray diagram.
Answer:
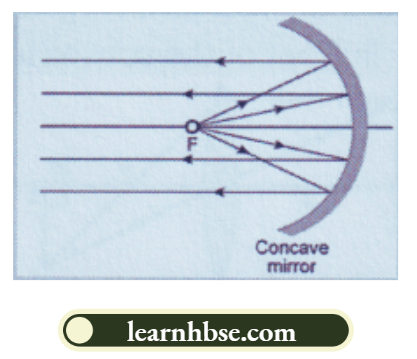
1. The mirror used in a searchlight is a concave mirror. A light source is placed at the focal point of the mirror. Light rays from the source are reflected by the mirror and all the reflected rays are parallel so that they travel a long distance to help in search operations.
The mirror used as a rear-view mirror is a convex mirror. Image formed by a convex mirror is as follows:
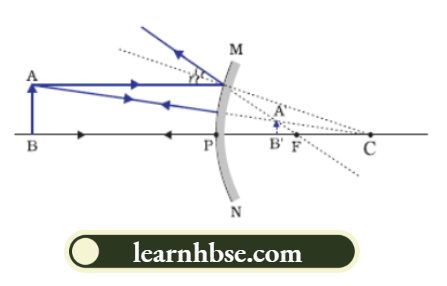
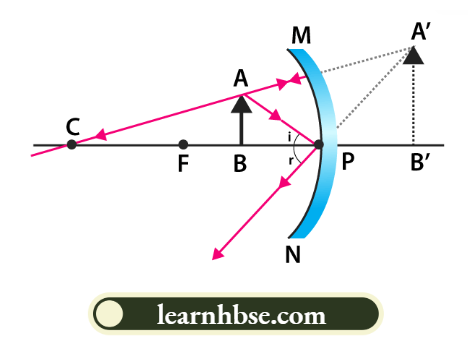
2. A concave mirror can form a magnified and virtual image. A convex mirror cannot form an enlarged image. When the object is placed between the pole and the focus of the mirror, the image formed is virtual, enlarged and erect.
Question 2.
1. Define:
- Principal focus of a convex lens
- Optical centre
2. State the lens formula.
3. Magnification produced by a spherical lens is -1. What is the nature of the image and lens?
Answer:
- The principal focus of a convex lens is a point on its principal axis to which light rays parallel to the principal axis converge after passing through the lens.
- The centre point of the lens is known as the optical centre.
2. Lens Formula is \(\frac{1}{f}=\frac{1}{v}-\frac{1}{u}\)
where”f is the focal length of the lens, “v” is the image distance and “u” is the object distance
3. Magnification of the lens = -1
Since magnification is negative, the image formed is real and inverted. Value 1 indicates that the size of the image is equal to the size of the object. Such an image can be formed by a convex lens. Hence, it is a convex lens.
Question 3.
- What do you mean by linear magnification produced by mirrors?
- The power of a lens is +1.5 D. What kind of lens is it and what is its focal length?
- Draw a ray diagram of an image when an object is placed on the principal axis of a convex lens between the focus and the optical centre.
Answer:
1. The linear magnification produced by a mirror is defined as the ratio of the height of the image to the height of the object.
2. The power of the lens has a positive sign; so, it is a convex lens.
Power, \(P=\frac{1}{f}\)
∴ \(\mathrm{f}=\frac{1}{\mathrm{p}}=\frac{1}{2.5}\)
f = 0.4 m = 40 cm
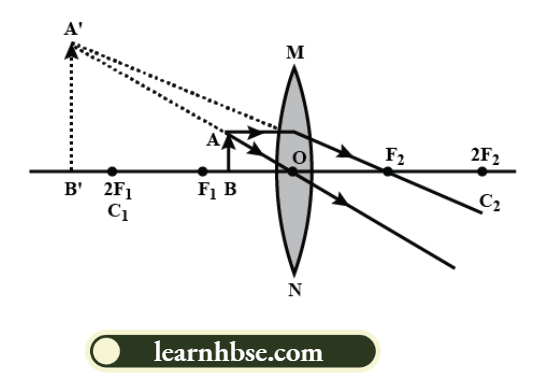
3. When the object is between the focus and the optical centre of a convex lens, the image formed is
- Beyond the focus
- Virtual and erect
- Enlarged.
Question 4. Draw the ray diagram and state the nature and position of the image formed when the object is placed at
- 2F in front of a convex lens
- Anywhere between the optical centre and infinity of the concave lens
Answer:
1. When an object is placed at 2F in front of the convex lens:
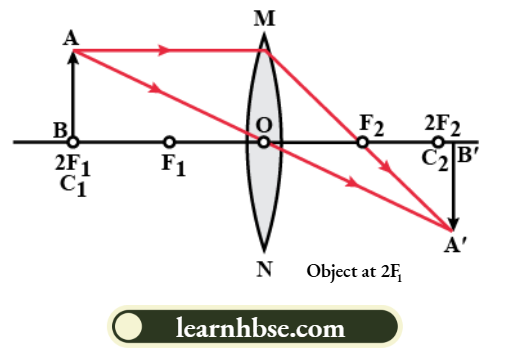
Nature of the image is real, inverted and is of the same size as that of the object. Position of the image formed is at a distance of 2f on the other side of the image.
2. When an object is placed anywhere between the optical centre and infinity of the concave lens:
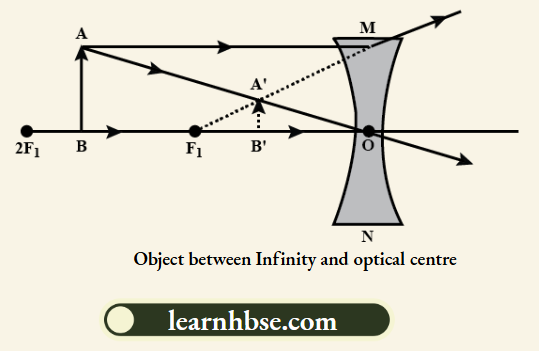
Nature of the image is virtual, erect and diminished. Position of the image is between the optical centre and the focus.
Question 5.
- What is the mirror formula? Give an expression for the mirror formula.
- Define the following terms related to spherical mirrors:
- Pole
- Centre of curvature
- Principal axis
Answer:
1. The relation between the object distance (u), image distance (v) and focal length (f) of a spherical mirror is given by the mirror formula. The object distance (u), image distance (v) and focal length (f) of a spherical mirror are related as \(\frac{1}{u}+\frac{1}{v}=\frac{1}{f}\)
2.
- The pole (P) of a spherical mirror is the centre of the mirror.
- The centre of curvature (C) of a spherical mirror is the centre of the hollow sphere of glass, of which the spherical mirror is a part.
- The principal axis of a spherical mirror is a straight line passing through the centre of curvature C and pole P of the spherical mirror.
