Haryana Board Class 10 Physics Chapter 2 The Human Eye And The Colourful World Multiple Choice Questions And Answers
Question 1. In which part of the human eye the image of an object is formed?
- Iris
- Pupil
- Retina
- Cornea
Answer: 3. Retina
Question 2. A person gets out into the sunlight from a dark room. How does his pupil regulate and control the light entering the eye?
- The size of the pupil will decrease, and less light will enter the eye
- The size of the pupil will decrease, and more light will enter the eye
- The size of the pupil will remain the same, but more light will enter the eye
- The size of the pupil will remain the same, but less light will enter the eye
Answer: 1. The size of the pupil will decrease, and less light will enter the eye
Question 3. A person is seeing an object closer to his eyes. What changes in his eyes will take place?
- The pupil size will expand
- The ciliary muscles will contract
- The focal length of the eye lens will increase
- The light entering the eye will be more
Answer: 2. The ciliary muscles will contract
Question 4. A person standing at point Y is watching a car coming from point X to 0 as shown.
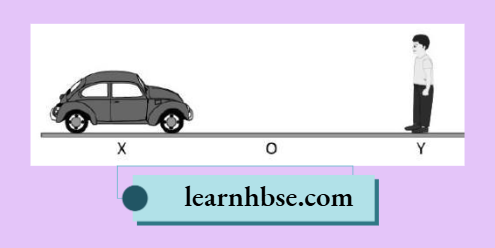
The table shows the variation in the parts of the eye while seeing the car at X and O
- At X, the focal length is higher than that at O.
- At O, the focal length is higher than that at X.
- At X, the Ciliary muscle is thicker than at O.
- At 0, the Ciliary muscle is thicker than at X.
Which change in the person’s eye would likely to occur while watching the car?
- 1 and 3
- 1 and 4
- 2 and 3
- 2 and 4
Answer: 2. 1 and 4
Question 5. A person went for a medical check-up and found that the curvature of his eye lens is increasing. Which defects is he likely to suffer from?
- Myopia
- Cataract
- Presbyopia
- Hypermetropia
Answer: 1. Myopia
Question 6. The image shows the ray diagram of a defective eye.
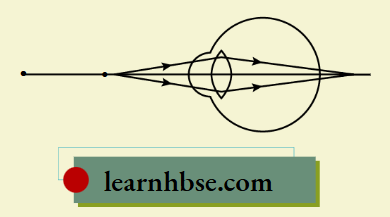
Which option shows the correction of the defect of the eye?
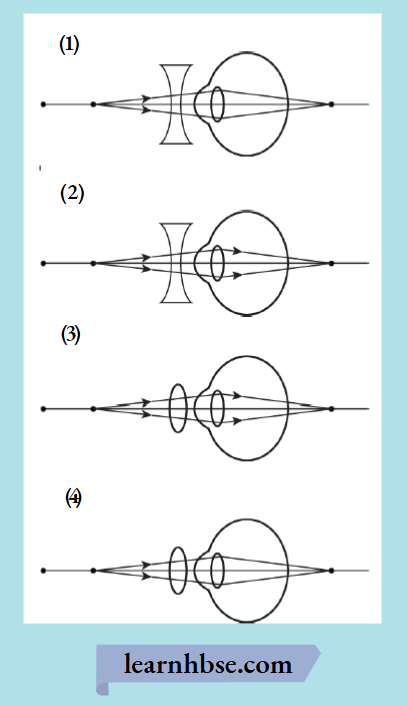
Answer: 4. 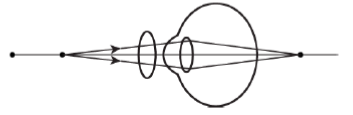
Question 7. Which image shows the deviation of light in a prism?
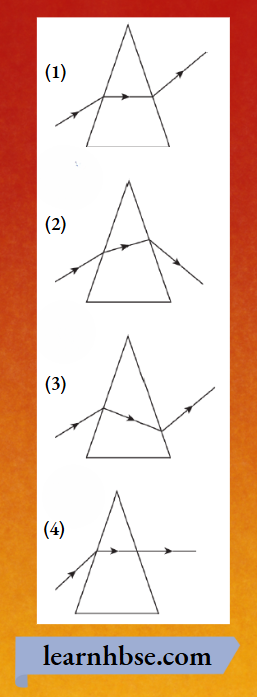
Answer: 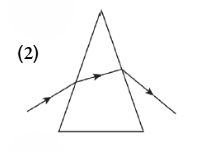
Question 8. The image shows a light ray incident on a glass prism.
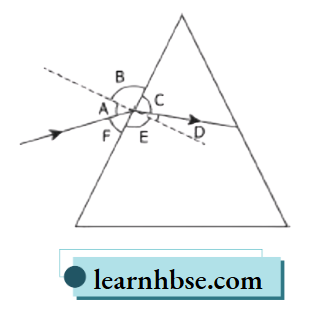
The various angles are labelled in the image. Which angle shows the angle of incidence and angle of refraction, respectively?
- A and D
- B and E
- C and F
- D and F
Answer: 1. A and D
Question 9. The image shows the dispersion of the white light in the prism.
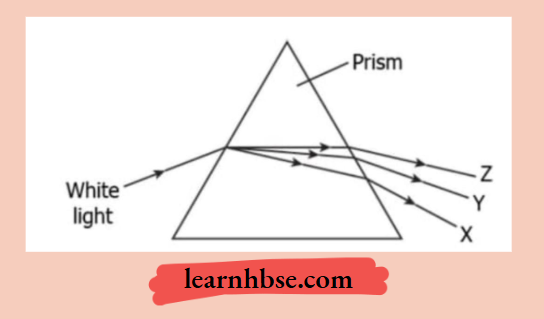
What will be the colours of the X, Y and Z?
- X: red; Y: green; Z: violet
- X: violet; Y: green; Z: red
- X: green; Y: violet; Z: red
- X: red; Y: violet; Z: green
Answer: 2. X: violet; Y: green; Z: red
Question 10. A ray of light is incident on one face of the prism, as shown.
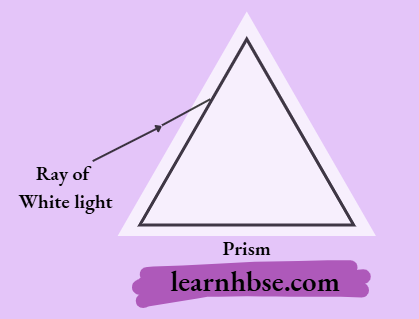
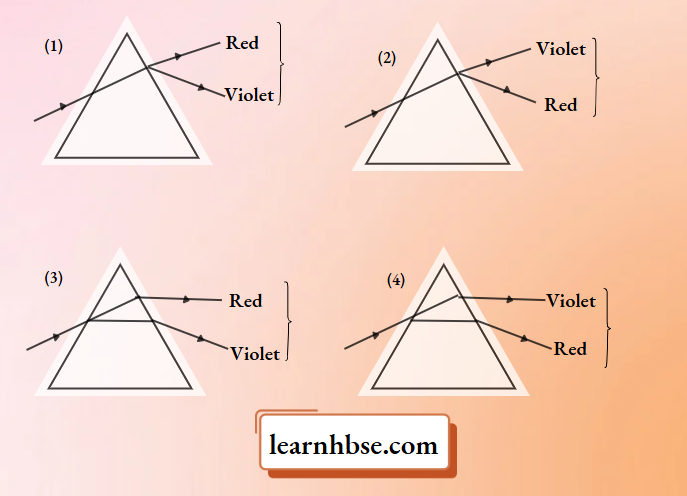
How will the ray of light disperse in the prism?
Answer: 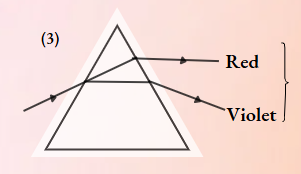
Question 11. Why do stars appear to twinkle at night?
- Because the light of stars travels in a different medium
- Because the distance of the star varies when Earth rotates
- Because the star changes its position relative to Earth
- Because the atmosphere reflects the light at different angles
Answer: 1. Because the light of stars travels in a different medium
Question 12. A student learns that the scattering of sunlight depends on the wavelength of the light and the size of particles present in the atmosphere. The student collects the data about the wavelength of the visible lights and the size of the particle, as shown.
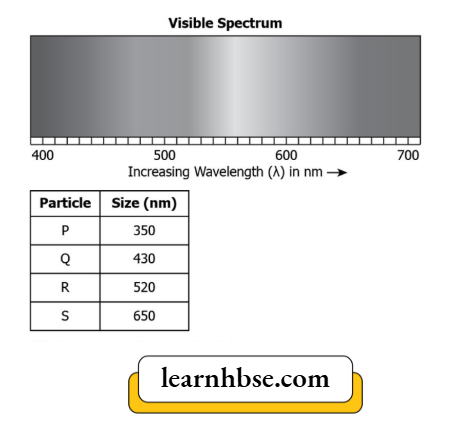
Which particles will scatter blue light?
- P and R
- R and S
- P and Q
- Q and S
Answer: 3. P and Q
Question 13. A got his eye tested. The optician’s prescription for the spectacles was:
Left eye: -3 D
Right eye: -3.50 D
The person is having a defect of vision called:
- Presbyopia
- Myopia
- Astigmatism
- Hypermetropia
Answer: 3. Astigmatism
Question 14. A man finds it difficult to read the odometer on the dashboard of the car but is able to clearly read a distant road sign. Which of the following statements is correct about this man?
- The near point of his eyes has receded away.
- The near point of his eyes has come closer to him.
- The far point of his eyes has receded away.
- The far point of his eyes has come closer to him.
Answer: 1. The near point of his eyes has receded away.
Question 15. Figures a, b, c, respectively, indicate the point in case of:
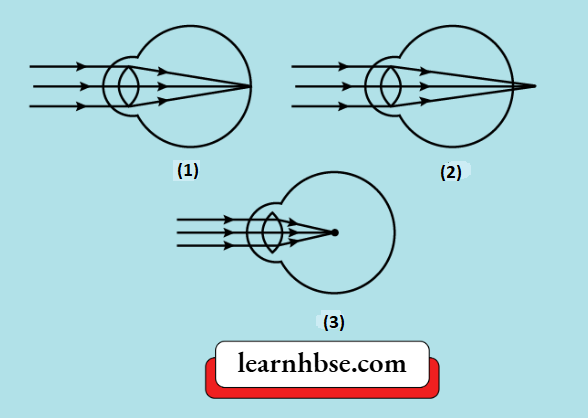
- The Hypermetropia eye, the myopic eye and the normal eye
- The normal eye, the myopic eye and hypermetropic eye
- The normal eye, the Hypermetropia eye and the myopic eye
- The myopic eye, the normal eye and hypermetropic eye
Answer: 3. The normal eye, the Hypermetropia eye and the myopic eye
Question 16. In which of the following cases will no dispersion take place when sunlight passes through it?
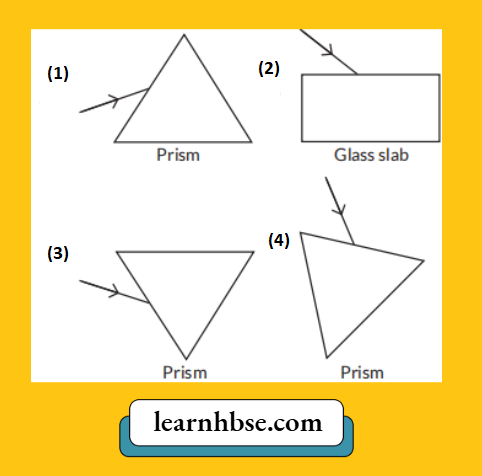
Answer: 
Chapter 2 The Human Eye And The Colourful World Very Short Questions And Answers
Question 1. By how much time the day would have been shorter if the Earth had no atmosphere?
Answer: 4 minutes
Question 2. What colour does the sky appear to an astronaut?
Answer: The Sky appears dark to astronauts.
Question 3. Which colour of light has the shorter wavelength- red or violet?
Answer: Violet
Question 4. Name the phenomenon due to which a swimming pool appears less deep than it really is.
Answer: Refraction of light
Question 5. Name the phenomenon due to which the stars seem higher in the sky than they actually are.
Answer: Atmospheric refraction of light.
Question 6. Why does the Sun appear white at noon?
Answer: The Sun is nearly overhead at noon. The sunlight has to pass through a much smaller portion of the Earth’s atmosphere. The scattering is much less, and thus, the Sun looks white.
Question 7. An object is moved closer to an eye. What changes must take place in the eye in order to keep the image in Sharp focus?
Answer: The shape of the eye-lens should must be changed by the ciliary muscles to make it thicker and increase its converging power in order to keep the image sharp and in focus.
Question 8. Name the part of our eyes that helps us to focus on near and distant objects in quick succession.
Answer: Ciliary muscles
Question 9. A person is advised to wear spectacles with concave lenses. What type of defect of vision is he suffering from?
Answer: Myopia or short-sightedness.
Question 10. A person can comfortably read a book but finds it difficult to read the number on a bus parked 5 m away from him. Name the type of defect of vision he is suffering from. Which type of lens should he use in his spectacles to correct his vision?
Answer: Myopia or short-sightedness. A concave lens should be used to correct his vision.
Question 11. Name the type of particles which act as a prism in the formation of the rainbow in the sky.
Answer: Water droplets present in the atmosphere.
Question 12. Give the condition required to achieve a larger magnification of a small object by a compound microscope?
Answer: To achieve a larger magnification of a small object, both the objective and the eyepiece of a compound microscope should have smaller focal lengths.
Chapter 2 The Human Eye And The Colourful World Short Questions And Answers
Question 1. A student observes the following phenomenon in the lab as a white light passes through a prism. Among many other colours, he observed the position of the two colours, Red and Violet.
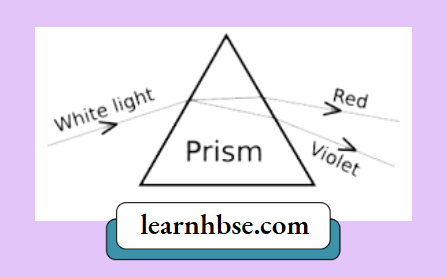
What is the phenomenon called? What is the reason for the violet light to bend more than the red light?
Answer:
Dispersion. The speed of violet light inside the prism is the slowest, and that of red is the highest. Hence, the deviation of violet light is maximum and that of red is minimum.
Question 2.
- Name the colour of light which undergoes
- More scattering and
- Less scattering while passing through the atmosphere.
- Draw a ray diagram to show the formation of a rainbow.
Answer:
While passing through the atmosphere
- Blue light undergoes more scattering, while
- Red light undergoes less scattering.
Question 3. Observe the experimental setup given below and answer the following questions:
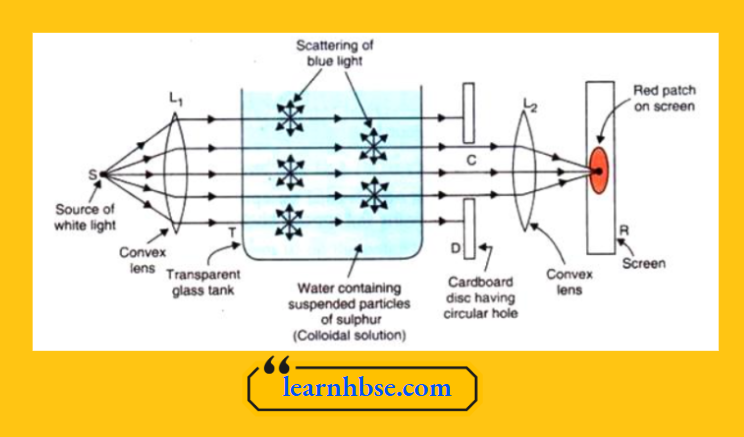
- Out of blue light and red light, which one is scattered more easily?
- What causes the scattering of the blue component of sunlight in the atmosphere?
Answer:
- Blue light scatters more easily due to its smaller wavelength
- Gas molecules are present in the air.
Question 4. Give reasons:
- The extent of deviation of a ray of light on passing through a glass prism depends on its colour.
- Lights of red colour are used for danger signals.
Answer:
- The refractive index of a medium is different for different colours of light,
- Due to a large wavelength, red colour is the least scattered and travels to longest distance.
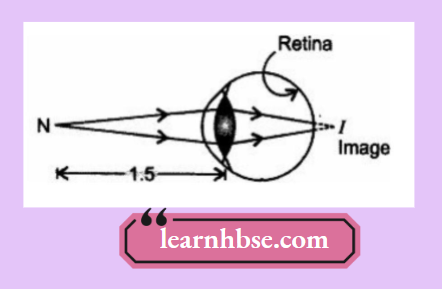
Question 5. A student sitting at the back bench in a class is not able to see what is written on the blackboard. He, however, sees it clearly when sitting on the front seat at an approximate distance of 1.5 m from the blackboard. Draw ray diagrams to illustrate the image formation of the blackboard when he is seated at the
- Back seat
- Front seat.
Answer:
1. When a student is seated in the back seat
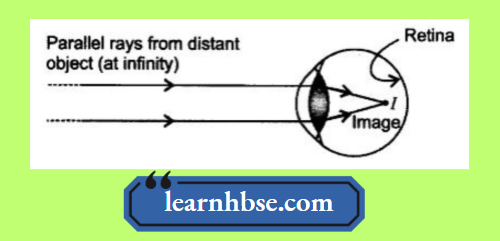
2. When a student is seated in the front seat
Question 6. How does the eye adjust itself to deal with light of varying intensity?
Answer:
The amount of light entering the eye is controlled by the pupil. If the intensity of the outside light is low, then the pupil expands to allow more light to enter the eye. If the outside intensity is high, then the pupil contracts so that less light enters the eye.
Question 7. How do we see colours?
Answer:
- The retina of our eyes has a large number of light-sensitive cells. The cells on the retina are of two shapes:
- Rod-shaped and cone-shaped. The rod-shaped cells of our retina respond to the intensity of light. The cone-shaped cells of our retina respond to colours. These cells make us see colours and distinguish between them. Thus cones make colour perception possible.
Question 8. When is a person said to have developed cataract in their eye? How is the vision of a person having cataracts restored?
Answer:
Cataract develops when the lens of a person becomes unclear due to the formation of a membrane over it. The vision of a person having cataract can be restored after getting cataract surgery done on the eye-lens having cataract. This defect cannot be corrected by any type of spectacle lenses.
Question 9. Why do we have two eyes? Binocular (or two-eyed) vision has several advantages, one of which is the ability to see the world in three dimensions.
Answer:
Binocular (or two-eyed) vision has several advantages, one of which is the ability to see the world in three dimensions.
Question 10.
- Which property of light is rainbow formation based on?
- Why is the rainbow not visible on polluted skies?
Answer:
- Refraction, Dispersion and Total Internal Reflection of Light;
- Pollution particles change how the air scatters and absorbs different colours of light.
Question 11. What material is the human lens made up of? How is that different from the artificial lenses which are installed in the eye during an eye surgery?
The human eye lens is made up of proteins. The main difference between an artificial eye and lens is that a human eye lens provides sight, whereas an artificial eye does not.
Answer:
The human eye lens is made up of proteins. The main difference between an artificial eye and lens is that a human eye lens provides sight, whereas an artificial eye does not.
Question 12. An old person is unable to see clearly nearby objects as well as distant objects. To correct the vision, what kind of lens will he require?
Answer:
The upper portion (concave lens) facilitates the distant vision, and the lower portion (convex lens) facilitates near vision. Hence, a bifocal lens should be used, whose upper portion is a concave lens and lower portion is a convex lens.
Question 13. Why are danger signal lights red in colour?
Answer:
Danger signal lights are red in colour because red colour is the least scattered by fog or smoke.
Question 14. How will you use two identical prisms so that a narrow beam of white light incident on one prism emerges out of the second prism as white light? Draw the diagram.
Answer:
When an inverted prism is kept a little distance away from the prism causing dispersion or basically in the path of the split beam, the spectrum recombines to form white light.
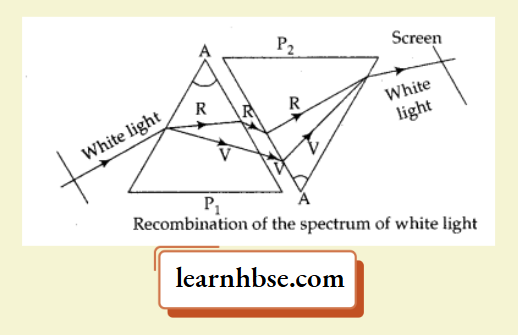
Question 15. Which part of human eye helps in the perception of colours?
Answer:
The retina of the human eye has a large number of cone-shaped and rod-shaped cells. The rods respond to the intensity of light and the cones to the colours. These help us to perceive colours.
Question 16.
- A person having a myopic eye used the concave lens of focal length 50cm. What is the power of the lens?
- What property of the eye is the principle of motion, pictures
Answer:
- The formula for the power of a lens is Power (P) = 1/f. P = 1/50 = 0.02 dioptre.
- Refraction of light through the eye lens is the basic principle for the visualization of pictures and motion.
Question 17. What happens when ciliary muscles get relaxed and then get contracted?
Answer:
When ciliary muscles get relaxed then the lens becomes thin, due to which the focal length increases and we can easily see distant objects clearly. When we see the objects which are near to our eyes, then the ciliary muscles get contracted, due to which the curvature of the eye lens increases and the eye lens becomes thicker. Hence, focal length decreases, which enables us to see objects which are placed near our eyes.
Question 18. A child, while playing with his father, threw the spectacles of his father. Now, father is not able to read the newspaper. Identify the defect of vision and how it was corrected. Draw a ray diagram of the defect and also a correcting diagram of the defect.
Answer:
As the father of the child is not able to read the newspaper means he can’t see the nearby objects clearly. This means that the father is suffering from the defect of hypermetropia. In this defect, the near point becomes farther away from the normal near point. His spectacles were made up of a convex lens of proper focal length to correct his defect.
Question 19. Give reason:
- Why do stars twinkle?
- Why do the planets not twinkle?
- Why does the sun appear reddish early in the morning?
- Why does the sky appear dark instead of blue to an astronaut?
- Why does the Sun appear white at noon?
Answer:
- Stars appear to twinkle due to atmospheric refraction. The light of a star after the entry of light into Earth’s atmosphere undergoes refraction continuously (due to the different density of the layers of the atmosphere) till it reaches the surface of the Earth. As the path of light coming from stars keeps on changing, the apparent position of stars keeps changing, and the amount of light from stars entering the eye keeps twinkling. Due to this, a star sometimes appears bright and
sometimes dim (called the twinkling effect), - The planets are much nearer to the Earth than stars, and because of this they can be considered as a large source of light. If a planet is considered to be a collection of a very large number of point sources of light, then the average value of change in the amount of light entering the eye from all point-sized light sources is zero. Due to this, the effect of twinkling is nullified.
- The light coming from the sun passes through various denser layers of air in the Earth’s atmosphere before reaching our eyes near the horizon. Most of the part of blue light and light of small wavelengths gets scattered by dust particles near the horizon. So, the light reaching our eyes is of a large wavelength. Due to this, the sun appears reddish at the time of sunrise and sunset.
- As an astronaut moves away from the atmosphere of Earth, the atmosphere becomes thin. Due to the absence of molecules (or dust particles) in the air, the scattering of light does not take place. Thus, the sky appears dark in the absence of scattering.
- At noon, the Sun appears white because the light from the Sun is directly overhead and travels a relatively shorter distance. Thus, only blue and violet colours are scattered.
Question 20. On a rainy day, Ram reached his grandfather’s place in the village. On the way to the house, he saw a beautiful rainbow in the sky. In the night, he saw lots of twinkling stars in the clear sky. He was very excited to see this beautiful natural phenomenon, which he was not able to see in the city, where he lived with his father. Explain the phenomenon on the basis of science. Do you think that pollution in the atmosphere affects the formation of rainbows and the twinkling of stars? Do you agree with the fact that a pollution-free environment will strengthen such natural phenomena in the cities as well. Elaborate.
Answer:
The twinkling of stars is due to atmospheric refraction. The formation of a rainbow is due to dispersion, refraction and internal reflection. Yes, pollution in the atmosphere affects the formation of rainbows and the twinkling of stars, and a pollution-free environment will strengthen such natural phenomena in the cities as well.
