Haryana Board Class 7 Maths Solutions For Chapter 2 Fractions and Decimals
- Fraction: The numbers of the form \(\frac{a}{b}\), where a and b are whole numbers and b #0, are called “fractions”.
- Types of fractions:
- Proper fraction: In a proper fraction, the numerator is less than the denominator
Examples: \(\frac{14}{19}, \frac{7}{9}, \frac{2}{3}, \frac{6}{13}, \frac{3}{4}\) - Improper fraction: In an improper fraction, the .numerator is bigger than or equal to the denominator.
Examples: \(\frac{9}{8}, \frac{7}{4}, \frac{21}{8}, \frac{35}{17}, \frac{43}{19}, \frac{4}{4}\) - Mixed fraction: It is a combination of a whole number and a proper fraction
Examples: \(1 \frac{3}{4}, 4 \frac{1}{9}, 5 \frac{6}{11}, 7 \frac{3}{4}, 3 \frac{4}{7}\)
An improper fraction can be converted into a mixed fraction
Examples: \(\frac{9}{8}=1 \frac{1}{8}\)
\(\frac{21}{8}=2 \frac{5}{8}\) - Fractions such as \(\frac{1}{2}, \frac{2}{4}, \frac{3}{6}\)…………. are called equivalent fractions
- ) Like fractions: Fractions with same denominators are called like fractions
Examples: \(\frac{1}{7}, \frac{2}{7} ; \frac{3}{5}, \frac{2}{5}\) - Unlike fractions: Fractions with different denominators are called unlike fractions
Examples: \( \frac{8}{9}, \frac{2}{7}, \frac{18}{17} \)……….
- Proper fraction: In a proper fraction, the numerator is less than the denominator
- Division of fractions: To divide a fraction with another fraction we multiply with its reciprocal.
- Example: \( \frac{2}{3} \div \frac{3}{4}=\frac{2}{3} \times \frac{4}{3}=\frac{8}{9} \)
- Decimal fractions or Decimal numbers:
- Fractions whose denominators are multiples of 10 only are called decimal fractions or decimal numbers.
Example: \( 2.3=\frac{23}{10}, 0.47=\frac{47}{100} \text { etc. } \)
Multiplication of decimal number by 10,100, 1000 etc.: When a decimal number is multiplied by16, 100, 1000 etc., the decimal point in the product shifts to the right as many zeros as in 10, 100, 1000 etc. - We can change an improper fraction to . a mixedfraction and vice – versa.
- Multiplying a fraction with a whole number:
To multiply a fraction with a whole number we multiply the whole number with the numerator and keeping the denominator same.
Example: \( 2 \times \frac{7}{5}=\frac{14}{5} \) - Product of two fractions \( =\frac{\text { Product of Numerators }}{\text { Product of Denominators }}\)Example: \(\frac{5}{6} \times \frac{2}{7}=\frac{5 \times 2}{6 \times 7}=\frac{10}{42}\)
- ‘of’ represents multiplication.
Example: \(\frac{1}{2} \text { of } 3=\frac{1}{2} \times 3\) - Reciprocal of a fraction: If \( \frac{a}{b} \) then \( \frac{b}{a}\) is called its reciprocal.
- A fraction means a part of a group of a region.
- Every fraction contains a numerator and a denominator
Example: In \(\frac{4}{7}\) is the numerator and 7 is the denominator.
Solutions To Try These
1. Find:
Solution: \( \frac{2}{7} \times 3=\frac{2 \times 3}{7}=\frac{6}{7}\)
2. \( \frac{9}{7} \times 6\)
Solution:
\( \frac{9}{7} \times 6=\frac{9 \times 6}{7}=\frac{54}{7}=7 \frac{5}{7}\)3. \( 3 \times \frac{1}{8}\)
Solution:
\( 3 \times \frac{1}{8}=\frac{3 \times 1}{8}=\frac{3}{8}\)HBSE Class 7 Fractions and Decimals Solutions
4. \( \frac{13}{11} \times 6\)
Solution:
\( \frac{13}{11} \times 6=\frac{13 \times 6}{11}=\frac{78}{11}\) \( =7 \frac{1}{11}\)2. Represent pictorially = \( 2 \times \frac{2}{5}=\frac{4}{5}\)
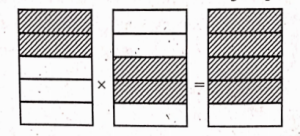
Exercise – 2.1
1) Which of the drawings (1) to (4) show:
1. \( 2 \times \frac{1}{5}\)
2. \( 2 \times \frac{1}{2}\)
3. \( 3 \times \frac{2}{3}\)
4. \( 3 \times \frac{1}{4}\)
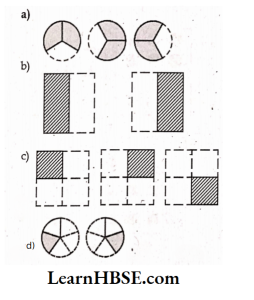
Solution:
1-d
2-b
3-a
4-c
Haryana Board Class 7 Maths Fractions and Decimals solutions
2. Some pictures (a) to (c) are given below. Tell which of them show:
1. \( 3 \times \frac{1}{5}=\frac{3}{5}\)
2. \( 2 \times \frac{1}{3}=\frac{2}{3}\)
3. \( 3 \times \frac{3}{4}=2 \frac{1}{4}\)
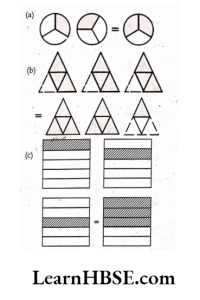
Solution:
1. \( 3 \times \frac{1}{5}=\frac{3}{5}=(\mathrm{c})\)
2. \( 2 \times \frac{1}{3}=\frac{2}{3}=(a)\)
3. \( 3 \times \frac{3}{4}=2 \frac{1}{4}=(b)\)
HBSE 7th Class Fraction and Decimal Word Problems – Focuses on word problems in this chapter.
3. Multiply and reduce to lowest form and convert into a mixed fraction:
1. \( 7 \times \frac{3}{5}\)
Solution: \( 7 \times \frac{3}{5}=\frac{7 \times 3}{5}=\frac{21}{5}=4 \frac{1}{5}\)
2. \( 4 \times \frac{1}{3}\)
Solution: \( 4 \times \frac{1}{3}=\frac{4 \times 1}{3}=\frac{4}{3}=1 \frac{1}{3}\)
3. \( 2 \times \frac{6}{7}\)
Solution:\( 2 \times \frac{6}{7}=\frac{2 \times 6}{7}=\frac{12}{7}=1 \frac{5}{7}\)
4.\( 5 \times \frac{2}{9}\)
Solution:\( 5 \times \frac{2}{9}=\frac{5 \times 2}{9}=\frac{10}{9}=1 \frac{1}{9}\)
5. \( \frac{2}{3} \times 4\)
Solution:\( \frac{2}{3} \times 4=\frac{2 \times 4}{3}=\frac{8}{3}=2 \frac{2}{3}\)
6.\( \frac{5}{2} \times 6\)
Solution:\( \frac{5}{2} \times 6=\frac{5 \times 6}{2}=\frac{30}{2}=15\)
7. \( 11 \times \frac{4}{7}\)
Solution:\( 11 \times \frac{4}{7}=\frac{11 \times 4}{7}=\frac{44}{7}=6 \frac{2}{7}\)
8. \( 20 \times \frac{4}{5}\)
Solution:\( 20 \times \frac{4}{5}=\frac{20 \times 4}{5}=\frac{80}{5}=16\)
9.\( 13 \times \frac{1}{3}\)
Solution: \( 13 \times \frac{1}{3}=\frac{13 \times 1}{3}=\frac{13}{3}=4 \frac{1}{3}\)
10.\( 15 \times \frac{3}{5}\)
Solution:\( 15 \times \frac{3}{5}=\frac{15 \times 3}{5}=\frac{45}{5}=9\)
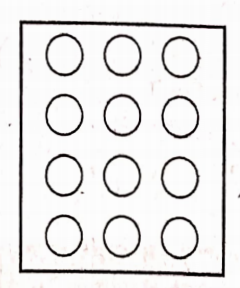
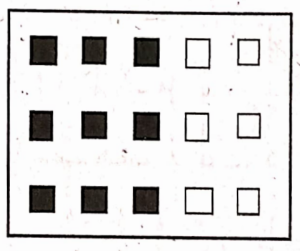
4. Shade:
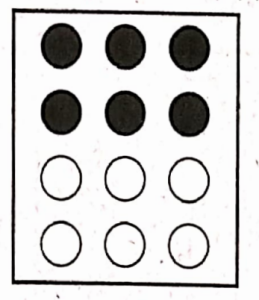
1. \( \frac{1}{2}\) of the circles in box (1)
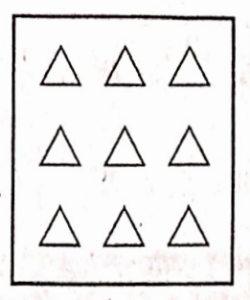
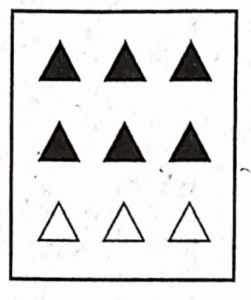
2. \( \frac{2}{3}\) of the trianglesin box (2)
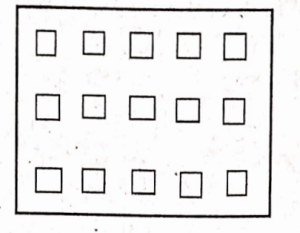
3. \( \frac{3}{5}\) of the squares in box (3)
1)
2)
Sample Problems Fractions and Decimals Haryana Board Class 7
3) 
Addition and subtraction of fractions Class 7 HBSE
Solution:
1)
2)
3) 
5. Find:
1) \( \frac{1}{2}\) of (1) 24 (2) 46
Solution: (1) \( \frac{1}{2}\) of 24 =\( \frac{1}{2} \times 24\)\( =\frac{1 \times 24}{2}=\frac{24}{2}=12\)
(2)\( \frac{1}{2} \text { of } 46=\frac{1}{2} \times 46\)
\( =\frac{1 \times 46}{2}=\frac{46}{2}=23\)
2)\( \frac{2}{3}\) of (1) 18 (2) 27
Solution:
1)\( \frac{2}{3}\) of 18 \( =\frac{2}{3} \times 18=\frac{2 \times 18}{3}=\frac{36}{3}=12 \)
(2)\( \frac{2}{3} \text { of } 27=\frac{2}{3} \times 27\)
\( =\frac{2 \times 27}{3}=\frac{54}{3}=18\)3) \( \frac{3}{4}\) of (1) 16 (2) 36
Solution:
(1)\( \frac{3}{4} \text { of } 16=\frac{3}{4} \times 16=\frac{3 \times 16}{4}=\frac{48}{4}=12\)
(2)\( \frac{3}{4} \text { of } 36=\frac{3}{4} \times 36\)
\( =\frac{3 \times 36}{4}=\frac{108}{4}=27\)4. \( \frac{4}{5} \) of (1) 20 (2) 35
Solution:
(1)\( \frac{4}{5} \text { of } 20=\frac{4}{5} \times 20=\frac{4 \times 20}{5}=\frac{80}{5}=16 \)
(2) \( \frac{4}{5} \text { of } 35=\frac{4}{5} \times 35 \)
\( =\frac{4 \times 35}{5}=\frac{140}{5}=28 \)6. Multiply and express as a mixed fraction:
1) \( 3 \times 5 \frac{1}{5} \)
Solution:
\( 3 \times 5 \frac{1}{5}=3 \times\left(\frac{5 \times 5+1}{5}\right)=3 \times\left(\frac{25+1}{5}\right) \) \( =3 \times \frac{26}{5}=\frac{78}{5}=15 \frac{3}{5} \)2) \( 5 \times 6 \frac{3}{4} \)
Solution:
\( 5 \times 6 \frac{3}{4}=5 \times\left(\frac{6 \times 4+3}{4}\right) \) \( =5 \times\left(\frac{24+3}{4}\right)=5 \times \frac{27}{4} \) \( =\frac{135}{4}=33 \frac{3}{4} \)3) \( 7 \times 2 \frac{1}{4} \)
Solution: \( 7 \times 2 \frac{1}{4}=7 \times\left(\frac{2 \times 4+1}{4}\right) \)
\( =7 \times\left(\frac{8+1}{4}\right)=\frac{7 \times 9}{4}=\frac{63}{4}=15 \frac{3}{4} \)4) \( 4 \times 6 \frac{1}{3} \)
Solution: \( 4 \times 6 \frac{1}{3}=4 \times\left(\frac{6 \times 3+1}{3}\right) \)
\( =4 \times\left(\frac{18+1}{3}\right)=\frac{4 \times 19}{3}=\frac{76}{3} \) \( =25 \frac{1}{3} \)5) \( 3 \frac{1}{4} \times 6 \)
Solution: \( \left(\frac{3 \times 4+1}{4}\right) \times 6=\left(\frac{12+1}{4}\right) \times 6 \)
\( =\frac{13}{4} \times 6=\frac{13 \times 6}{4}=\frac{78}{4} \) \( =\frac{78 \div 2}{4 \div 2}=\frac{39}{2}=19 \frac{1}{2} \)Multiplying and Dividing Fractions Class 7 Haryana Board
6) \( 3 \frac{2}{5} \times 8 \)
Solution: \( \left(\frac{3 \times 5+2}{5}\right) \times 8=\left(\frac{15+2}{5}\right) \times 8 \)
\( =\frac{17 \times 8}{5}=\frac{136}{5}=27 \frac{1}{5} \)7) Find:
1) \( \frac{1}{2} of \) (1) \( 2 \frac{3}{4} \) (2)\( 4 \frac{2}{9} \)
Solution:
(1) \( \frac{1}{2} \text { of } 2 \frac{3}{4}=\frac{1}{2} \times\left(\frac{2 \times 4+3}{4}\right) \)
\( =\frac{1}{2} \times\left(\frac{8+3}{4}\right)=\frac{1}{2} \times \frac{11}{4} \) \( =\frac{1 \times 11}{2 \times 4}=\frac{11}{8}=1 \frac{3}{8}\)(2) \( \frac{1}{2} \text { of } 4 \frac{2}{9}=\frac{1}{2} \times\left(\frac{4 \times 9+2}{9}\right) \)
\( =\frac{1}{2} \times\left(\frac{36+2}{9}\right)=\frac{1}{2} \times \frac{38}{9} \) \( =\frac{1 \times 38}{2 \times 9}=\frac{38}{18}=\frac{38 \div 2}{18 \div 2}=\frac{19}{9}=2 \frac{1}{9} \)Multiplication and division of decimals Class 7 HBSE
2) \( \frac{5}{8} \) of (1) \( 3 \frac{5}{6} \) (2) \( 9 \frac{2}{3} \)
Solution:
(1) \( \frac{5}{8} \text { of } 3 \frac{5}{6} \)
\( =\frac{5}{8} \times\left(\frac{3 \times 6+5}{6}\right)=\frac{5}{8} \times\left(\frac{18+5}{6}\right) \) \( =\frac{5}{8} \times \frac{23}{6}=\frac{115}{48}=2 \frac{19}{48} \)(2) \( \frac{5}{8} \text { of } 9 \frac{2}{3} \)
\( =\frac{5}{8} \times\left(\frac{9 \times 3+2}{3}\right)=\frac{5}{8} \times\left(\frac{27+2}{3}\right) \) \( =\frac{5}{8} \times \frac{29}{3}=\frac{5 \times 29}{8 \times 3}=\frac{145}{24}=6 \frac{1}{24} \)
8) Vidya and Pratap went for a picnic. Their mother gave them a water bottle that contained 5 litres of water. Vidya consumed \( \frac{2}{5} \) of the water. Pratap consumed the remaining water
(1) How much water did Vidya drink?
(2) What fraction of the total quantity of water did Pratap drink?
Solution:
Quantity of water in the bottle = 5 litres
(1) Water consumed by Vidya = \( \frac{2}{5} \) of 5 litres
\( =\frac{2}{5} \times 5=\frac{2 \times 5}{5}=\frac{10}{5}=2 \text { litres } \)(2) Water consumed by Pratap = \( \frac{1}{1}-\frac{2}{5} \)
\( =\frac{5-2}{5}=\frac{3}{5} \text { litres } \)
Solutions To Try These
Find:
1. \( 7 \div \frac{2}{5} \)
Solution: \( 7 \div \frac{2}{5}=7 \times \frac{5}{2}=\frac{7 \times 5}{2}=\frac{35}{2}=17 \frac{1}{2} \)
2. \( 6 \div \frac{4}{7} \)
Solution: \( \begin{aligned}
6 \div \frac{4}{7} & =6 \times \frac{7}{4}=\frac{6 \times 7}{4} \\
& =\frac{42}{4}=\frac{42 \div 2}{4 \div 2}=\frac{21}{2}=10 \frac{1}{2}
\end{aligned} \)
3. \( 2 \div \frac{8}{9} \)
Solution: \( \begin{aligned}
2 \div \frac{8}{9}=2 \times \frac{9}{8} & =\frac{2 \times 9}{8}=\frac{18}{8}=\frac{18 \div 2}{8 \div 2} \\
& =\frac{9}{4}=2 \frac{1}{4}
\end{aligned} \)
Solutions To Try These
Find:
1. \( 6 \div 5 \frac{1}{3} \)
Solution: \( \begin{aligned}
6 \div 5 \frac{1}{3} & =6 \div \frac{16}{3}=6 \times \frac{3}{16}=\frac{6 \times 3}{16} \\
& =\frac{18}{16}=\frac{18 \div 2}{16 \div 2}=\frac{9}{8}=1 \frac{1}{8}
\end{aligned} \)
2. \( 7 \div 2 \frac{4}{7} \)
Solution:
\( \begin{aligned}7 \div 2 \frac{4}{7} & =7 \div \frac{18}{7} \\
& =7 \times \frac{7}{18}=\frac{49}{18}=2 \frac{13}{18}
\end{aligned} \)
HBSE Class 7 Maths Chapter 2 Guide
Solutions To Try These
Find:
1. \( \frac{3}{5} \div \frac{1}{2} \)
Solution: \( \frac{3}{5} \div \frac{1}{2}=\frac{3}{5} \times \frac{2}{1}=\frac{3 \times 2}{5 \times 1}=\frac{6}{5}=1 \frac{1}{5} \)
2. \( \frac{1}{2} \div \frac{3}{5} \)
Solution:
\( \frac{1}{2} \div \frac{3}{5}=\frac{1}{2} \times \frac{5}{3}=\frac{1 \times 5}{2 \times 3}=\frac{5}{6} \)3. \( 2 \frac{1}{2} \div \frac{3}{5} \)
Solution:
\( \begin{gathered}2 \frac{1}{2} \div \frac{3}{5}=\frac{5}{2} \div \frac{3}{5}=\frac{5}{2} \times \frac{5}{3}=\frac{5 \times 5}{2 \times 3} \\
=\frac{25}{6}=4 \frac{1}{6}
\end{gathered} \)
4. \( 5 \frac{1}{6} \div \frac{9}{2} \)
Solution:
\( \begin{aligned}5 \frac{1}{6} \div \frac{9}{2} & =\frac{31}{6} \div \frac{9}{2}=\frac{31}{6} \times \frac{2}{9} \\
& =\frac{31 \times 2}{6 \times 9}=\frac{62}{54}=\frac{62 \div 2}{54 \div 2} \\
& =\frac{31}{27}=1 \frac{4}{27}
\end{aligned} \)
Exercise 2.3
1. Find:
1. \( 12 \div \frac{3}{4} \)
Solution:
\( 12 \div \frac{3}{4}=\frac{12}{1} \times \frac{4}{3}=\frac{12 \times 4}{1 \times 3}=\frac{48}{3}=16 \)2. \( 14 \div \frac{5}{6} \)
Solution:
\( 14 \div \frac{5}{6}=\frac{14}{1} \times \frac{6}{5}=\frac{14 \times 6}{1 \times 5}=\frac{84}{5}=16 \frac{4}{5} \)3. \( 8 \div \frac{7}{3} \)
Solution:
\( 8 \div \frac{7}{3}=\frac{8}{1} \times \frac{3}{7}=\frac{8 \times 3}{1 \times 7}=\frac{24}{7}=3 \frac{3}{7} \)4. \( 4 \div \frac{8}{3} \)
Solution:
\( \begin{aligned}4 \div \frac{8}{3} & =\frac{4}{1} \times \frac{3}{8}=\frac{4 \times 3}{1 \times 8}=\frac{12}{8}=\frac{12 \div 4}{8 \div 4} \\
& =\frac{3}{2}=1 \frac{1}{2}
\end{aligned} \)
5. \( 3 \div 2 \frac{1}{3} \)
Solution:
\( \begin{aligned}3 \div 2 \frac{1}{3}=3 \div \frac{7}{3}=\frac{3}{1} \times \frac{3}{7} & =\frac{3 \times 3}{1 \times 7} \\
& =\frac{9}{7}=1 \frac{2}{7}
\end{aligned} \)
Important Concepts Fractions and Decimals Class 7 HBSE
6. \( 5 \div 3 \frac{4}{7} \)
Solution:
\( \begin{aligned}5 \div 3 \frac{4}{7} & =5 \div \frac{25}{7}=\frac{5}{1} \times \frac{7}{25}=\frac{5 \times 7}{1 \times 25} \\
& =\frac{35}{25}=\frac{35 \div 5}{25 \div 5}=\frac{7}{5}=1 \frac{2}{5}
\end{aligned} \)
2. Find the reciprocal of each of the following fractions. Classify the reciprocal as proper fraction,improper fraction and whole numbers.
1) \( \frac{3}{7} \)
Solution: \( \text { Reciprocal of } \frac{3}{7} \text { is } \frac{7}{3} \)
\( \frac{7}{3} \text { is an improper fraction. } \)Word problems on fractions and decimals Class 7 HBSE
2) \( \frac{5}{8} \)
Solution: \( \text { Reciprocal of } \frac{5}{8} \text { is } \frac{8}{5} \)
\( \frac{8}{5} \text { is an improper fraction. } \)3) \( \frac{9}{7} \)
Solution: \( \text { Reciprocal of } \frac{9}{7} \text { is } \frac{7}{9} \)
\( \frac{7}{9} \text { is a proper fraction. } \)4) \( \frac{6}{5} \)
Solution: \( \frac{12}{7} \)
\( \text { Reciprocal of } \frac{6}{5} \text { is } \frac{5}{6} \) \( \frac{5}{6} \text { is a proper fraction. } \)5) \( \frac{12}{7} \)
Solution:
\( \text { Reciprocal of } \frac{12}{7} \text { is } \frac{1}{12} \) \( \frac{7}{12} \text { is a proper fraction. } \)6) \( \frac{1}{8} \)
Solution: \( \text { Reciprocal of } \frac{1}{8} \text { is } \frac{8}{1}=8 \)
∴ 8 is a whole number
7) \( \frac{1}{11} \)
Solution:
\( \text { Reciprocal of } \frac{1}{11} \text { is } \frac{11}{1}=11 \)∴ 11 is a whole number.
3. Find:
1) \( \frac{7}{3} \div 2 \)
Solution:
\( \frac{7}{3} \div \frac{2}{1}=\frac{7}{3} \times \frac{1}{2}=\frac{7 \times 1}{3 \times 2}=\frac{7}{6}=1 \frac{1}{6} \)2) \( \frac{4}{9} \div 5 \)
Solution:
\( \frac{4}{9} \div \frac{5}{1}=\frac{4}{9} \times \frac{1}{5}=\frac{4 \times 1}{9 \times 5}=\frac{4}{45} \)3) \( \frac{6}{13} \div 7 \)
Solution:
\( \frac{6}{13} \div \frac{7}{1}=\frac{6}{13} \times \frac{1}{7}=\frac{6 \times 1}{13 \times 7}=\frac{6}{91}\)4) \( 4 \frac{1}{3} \div 3 \)
Solution:
\( \begin{aligned}4 \frac{1}{3} \div 3=\frac{13}{3} \div \frac{3}{1} & =\frac{13}{3} \times \frac{1}{3} \\
& =\frac{13 \times 1}{3 \times 3}=\frac{13}{9}=1 \frac{4}{9}
\end{aligned} \)
5) \( 3 \frac{1}{2} \div 4 \)
Solution:
\( 3 \frac{1}{2} \div 4=\frac{7}{2} \div \frac{4}{1}=\frac{7}{2} \times \frac{1}{4}=\frac{7 \times 1}{2 \times 4}=\frac{7}{8} \)6) \( 4 \frac{3}{7} \div 7 \)
Solution:
\( \begin{aligned}4 \frac{3}{7} \div 7=\frac{31}{7} \div \frac{7}{1} & =\frac{31}{7} \times \frac{1}{7} \\
& =\frac{31 \times 1}{7 \times 7}=\frac{31}{49}
\end{aligned} \)
4. Find:
1) \( \frac{2}{5} \div \frac{1}{2} \)
Solution:
\( \frac{2}{5} \div \frac{1}{2}=\frac{2}{5} \times \frac{2}{1}=\frac{2 \times 2}{5 \times 1}=\frac{4}{5} \)2) \( \frac{4}{9}+\frac{2}{3} \)
Solution:
\( \begin{aligned}\frac{4}{9} \div \frac{2}{3}=\frac{4}{9} \times \frac{3}{2} & =\frac{4 \times 3}{9 \times 2} \\
& =\frac{12}{18}=\frac{12 \div 6}{18 \div 6}=\frac{2}{3}
\end{aligned} \)
3) \( \frac{3}{7} \div \frac{8}{7} \)
Solution:
\( \frac{3}{7} \div \frac{8}{7}=\frac{3}{7} \times \frac{7}{8}=\frac{3 \times 7}{7 \times 8}=\frac{21}{56}=\frac{21 \div 7}{56 \div 7}=\frac{3}{8} \)4) \( 2 \frac{1}{3} \div \frac{3}{5} \)
Solution:
\( \begin{aligned}2 \frac{1}{3} \div \frac{3}{5}=\frac{7}{3} \div \frac{3}{5} & =\frac{7}{3} \times \frac{5}{3} \\
& =\frac{7 \times 5}{3 \times 3}=\frac{35}{9}=3 \frac{8}{9}
\end{aligned} \)
5) \( 3 \frac{1}{2} \div \frac{8}{3} \)
Solution:
\( \begin{aligned}3 \frac{1}{2} \div \frac{8}{3}=\frac{7}{2} \div \frac{8}{3} & =\frac{7}{2} \times \frac{3}{8} \\
& =\frac{7 \times 3}{2 \times 8}=\frac{21}{16}=1 \frac{5}{16}
\end{aligned} \)
6) \( \frac{2}{5} \div 1 \frac{1}{2} \)
Solution:
\( \frac{2}{5} \div 1 \frac{1}{2}=\frac{2}{5} \div \frac{3}{2}=\frac{2}{5} \times \frac{2}{3}=\frac{2 \times 2}{5 \times 3}=\frac{4}{15} \)7) \( 3 \frac{1}{5} \div 1 \frac{2}{3} \)
Solution:
\( \begin{aligned}3 \frac{1}{5} \div 1 \frac{2}{3}=\frac{16}{5} \div \frac{5}{3} & =\frac{16}{5} \times \frac{3}{5} \\
& =\frac{16 \times 3}{5 \times 5}=\frac{48}{25}=1 \frac{23}{25}
\end{aligned} \)
8) \( 2 \frac{1}{5} \div 1 \frac{1}{5} \)
Solution:
\( \begin{aligned}2 \frac{1}{5} \div 1 \frac{1}{5} & =\frac{11}{5} \div \frac{6}{5}=\frac{11}{5} \times \frac{5}{6}=\frac{11 \times 5}{5 \times 6}=\frac{55}{30} \\
& =\frac{55 \div 5}{30 \div 5}=\frac{11}{6}=1 \frac{5}{6}
\end{aligned} \)
1. Find:
1) 2.7×4
Solution: 2.7×4 = 10.8
2) 1.8 x 1.2
Solution: 1.8 x 1.2 = 2.16
3) 2.3 x 4.35
Solution: 2.3 x 4.35 = 10.005
2. Arrange the products obtained in (1) in descending order.
Solution:
The three products obtained in (1) are
10.8, 2.16,10.005. Their descending order is 10.8,10.005,2.16.
Solutions To Try These
Find:
1) 0.3 x 10
Solution: 0.3 x l0 = 3
2) 1.2×100
Solution: 1.2 x100 = 1.20 x100 = 120
3) 56.3 x1000
Solution: 56.3 x1000 = 56.300 x1000 = 56300
Exercise -2.4
1. Find:
1) 0.2 x 6
Solution: 0.2 x 6 = 1.2
2) 8 x 4.6
Solution: 8×4.6 = 36.8
3) 2.71 x 5
Solution: 2.71 x 5 = 13.55
4) 20.1 x 4
Solution: 20.1 x 4 = 80.4
5) 0.05 x 7
Solution: 0.05×7 = 0.35
6) 211.02×4
Solution: 211.02 x4 = 844.08
7) 2x 0.86
Solution: 2×0.86 = 1.72
2. Find the area of rectangle whose length is 5.7 cm and breadth is 3 cm.
Solution:
Length of the rectangle = 5.7 cm
Breadth of the rectangle = 3 cm
Area of the rectangle = Length x Breadth
= 5.7 cm x 3 cm = 17.1 cm2
3. Find:
1) 1.3 x 10
Solution: 1.3 x 10 = 13.0 or 13
2) 36.8 x 10
Solution: 36.8 x10 = 368.0 or 368
3) 153.7 x 10
Solution: 153.7 x 10 = 1537.0 or 1537
4) 168.07 x 10
Solution: 168.07 x 10 = 1680.7
5) 31.1 x 100
Solution: 31.1 x100 = 3110
6) 156.1 xl00
Solution: 156.1 x100 = 15610
7) 3.62 x 100
Solution: 3.62 x 100 = 362
8) 43.07 x100
Solution: 43.07 x 100 = 4307
9) 0.5 x 10
Solution: 0.5 x10 = 5
10) 0.08 x 10
Solution: 0.08 x 10 = 0.80 or 0.8
11) 0.9 x 100
Solution: 0.9 x 100 = 90.0 or 90
12) 0.03 x 1000
Solution: 0.03 x 1000 = 30.0 or 30
How to convert fractions to decimals Class 7
4. A two-wheeler covers a distance of 55.3 km with one litre of petrol. How much distance will it cover in 10 litres of petrol ?
Solution:
Distance covered with one litre of petrol = 55.3 km
Distance covered with10litres of petrol = 55.3 x10 = 553 km
5. Find:
1) 2.5 x 0.3
Solution: 2.5 x 0.3 = 0.75
2) 0.1 x 51.7
Solution: 0.1 x 51.7 = 5.17
3) 0.2 x 316.8
Solution: 0.2 x 316.8 = 63.36
4) 1.3 x 3.1
Solution: 1.3×3.1=4.03
5) 0.5 x 0.05
Solution: 0.5 x 0.05 = 0.025
6) 11.2 x 0.15
Solution: 11.2 x 0.15 =1.680
7) 1.07 x. 0.02
Solution: 1.07 X 0.02 = 0.0214 .
8) 10.05 x 1.05
Solution: 10.05 x 1.05 = 10.5525
9) 101.01 x 0.01
Solution: 101.01 x 0.01 = 1.0101
10) 100.01 x 1.1
Solution: 00.01 x 1.1 = 110.011
Solutions To Try These
1. Find:
1) 235.4 – 10
Solution: 235.4 + 10 = 23.54
2) 235.4 +100
Solution: 235.4 = 2.354
3) 235.4 +1000
Solution: 235.4 +1000 = 0.2354
2. Find:
1) 35.7 +3 = ?
Solution: 35.7+3 = 11.9
2) 25.5 +3 =?
Solution: 25.5 +3 = 8.5
Practice Problems Fractions and Decimals Class 7 Haryana Board
3. Find:
1) 43.15+5 = ?
Solution: 43.15 +5 = 4315 +5 = 863
43.15 +5 = 8.63
2) 82.44 +6 =?
Solution: 8244 + 6 = 1374
82.44 + 6 = 13.74
Solutions To Try These
1. Find:
1) 15.5+5
Solution: 155 +5=31
15.5 +5 = 3.1
2) 126.35 +7
Solution: 12635 + 7 = 1805
126.35 +7 = 18.05
2. Find:
1. \( \frac{7.75}{0.25} \)
Solution:
\( \frac{7.75}{0.25}=\frac{7.75 \times 100}{0.25 \times 100}=\frac{775}{25}=31 \)2. \( \frac{42.8}{0.02} \)
Solution:
\( \frac{42.8}{0.02}=\frac{42.8 \times 100}{0.02 \times 100}=\frac{4280}{2}=2140 \)3) \( \frac{5.6}{1.4} \)
Solution: \( \frac{5.6}{1.4}=\frac{5.6 \times 10}{1.4 \times 10}=\frac{56}{14}=4 \)
Exercise – 2.5
1. Find:
1. 0.4 ÷ 2
Solution:
\( 0.4 \div 2=0.4 \times \frac{1}{2}=\frac{4}{10} \times \frac{1}{2}=\frac{2}{10}=0.2 \)2) 0.35 ÷ 5
Solution:
\( \begin{gathered}0.35 \div 5=0.35 \times \frac{1}{5}=\frac{35}{100} \times \frac{1}{5} \\
\quad=\frac{5 \times 7}{100 \times 5}=\frac{7}{100}=0.07
\end{gathered} \)
3) 2.48 ÷ 4
Solution:
\( \begin{gathered}2.48 \div 4=2.48 \times \frac{1}{4}=\frac{248}{100} \times \frac{1}{4} \\
=\frac{62}{100}=0.62
\end{gathered} \)
4) 65.4 ÷ 6
Solution:
\( \begin{aligned}65.4 \div 6=65.4 \times \frac{1}{6}=\frac{654}{10} & \times \frac{1}{6} \\
& =\frac{109}{10}=10.9
\end{aligned} \)
5) 651.2 ÷ 4
Solution:
\( \begin{aligned}651.2 \div 4=651.2 \times \frac{1}{4} & =\frac{6512}{10} \times \frac{1}{4} \\
& =\frac{1628}{10}=162.8
\end{aligned} \)
6) 14.49 ÷ 7
Solution:
\( \begin{aligned}14.49 \div 7=14.49 \times \frac{1}{7} & =\frac{1449}{100} \times \frac{1}{7} \\
& =\frac{207}{100}=2.07
\end{aligned} \)
7) 3.96 ÷ 4
Solution:
\( \begin{aligned}3.96 \div 4=3.96 \times \frac{1}{4}=\frac{396}{100} \times \frac{1}{4}= & \frac{99}{100} \\
& =0.99
\end{aligned} \)
8) 0.80 ÷ 5
Solution:
\( \begin{aligned}0.80 \div 5=0.80 \times \frac{1}{5} & =\frac{80}{100} \times \frac{1}{5} \\
& =\frac{16}{100}=0.16
\end{aligned} \)
2. Find:
1) 4.8 ÷ 10
Solution:
\( \begin{aligned}& 4.8 \div 10=4.8 \times \frac{1}{10} \\
& =\frac{48}{10} \times \frac{1}{10}=\frac{48}{100}=0.48
\end{aligned} \)
2) 52.5 ÷ 10
Solution:
\( \begin{aligned}& 52.5 \div 10=52.5 \times \frac{1}{10}=\frac{525}{10} \times \frac{1}{10} \\
& =\frac{525}{100}=5.25
\end{aligned} \)
3) 0.7 ÷ 10
Solution:
\(\begin{aligned}
& 0.7 \div 10=0.7 \times \frac{1}{10}=\frac{7}{10} \times \frac{1}{10} \\
& =\frac{7}{100}=0.07
\end{aligned} \)
4) 33.1 ÷ 10
Solution:
\( \begin{aligned}33.1 & \div 10=33.1 \times \frac{1}{10}=\frac{331}{10} \times \frac{1}{10} \\
& =\frac{331}{100}=3.31
\end{aligned} \)
5) 272.23 ÷ 10
Solution: 272.23 ÷10 = 27.223
6) 0.56 ÷ 10
Solution: 0.56 ÷ 10 = 0.056
7) 3.97 ÷ 10
Solution: 3.97 ÷10 = 0.397
Key Questions in Fractions and Decimals for Class 7 HBSE
3. Find:
1) 2.7 ÷100
Solution: 2.7 ÷100 = 0.027
2) 0.3 ÷ 100
Solution: 0.3 ÷100 = 0.003
3) 0.78 ÷100
Solution: 0.78 ÷100 = 0.0078
4) 432.6 ÷100
Solution: 432.6÷100 = 4.326
5) 23.6 ÷100
Solution: 23.6 ÷100 = 0.236
6) 98.53 ÷100
Solution: 98.53 ÷100 = 0.9853
4. Find:
1) 7.9 ÷1000
Solution: 7.9 ÷1000 = 0.0079
2) 26.3 ÷1000
Solution: 26.3÷1000 = 0.0263
3) 38.53÷1000
Solution: 38.53÷1000 = 0.03853
4) 128.9÷1000
Solution: 128.9÷1000 = 0.1289
5) 0.5 ÷1000
Solution: 0.5 ÷1000 = 0.0005
5. Find:
1) 7 ÷ 3.5
Solution: \( 7 \div 3.5=\frac{7.0}{3.5}=\frac{70}{35}=2 \)
2) 36 ÷ 0.2
Solution: \( 36 \div 0.2=\frac{36.0}{0.2}=\frac{360}{2}=180 \)
3) 3.25 ÷ 0.5
Solution: \( 3.25 \div 0.5=\frac{3.25}{0.50}=\frac{325}{50}=6.5\)
4)30.94 ÷ 0.7
Solution: \( 30.94 \div 0.7=\frac{30.94}{0.70}=\frac{3094}{70}=44.2 \)
5) 0.5 ÷0.25
Solution: \( 0.5 \div 0.25=\frac{0.50}{0.25}=\frac{50}{25}=2 \)
6) 7.75 0.25
Solution: \( 7.75 \div 0.25=\frac{7.75}{0.25}=\frac{775}{25}=31 \)
7) 76.5 -0.15
Solution: \( 76.5 \div 0.15=\frac{76.50}{0.15}=\frac{7650}{15}=510 \)
8) 37.8 -1.4
Solution: \( 37.8 \div 1.4=\frac{37.8}{1.4}=\frac{378}{14}=27 \)
9) 2.73 -1.3
Solution: 2.73 -1.3
\( =\frac{2.73}{1.3}=\frac{2.73}{1.30}=\frac{273}{130}=\frac{21}{10}=2.1 \)
6. A vehicle covers a distance of 43.2 km in 2.4 litres of petrol. How much distance will it cover with one litre of petrol?
Solution: Distance covered with 2.4 litres of petrol = 43.2 km
Distance covered with1 litre ofpetrol = 43.2 4- 2.4
\( =\frac{43.2}{2.4}=\frac{432}{24}=18 \mathrm{~km} \)Additional Questions
Very Short Answer Questions
1. Surya can walk \( \frac{18}{5} \) kmin an hour. How much distance can he walk in \( 2 \frac{1}{2} \) hours?
Solution:
The distance walked by Suryain an hour \( =\frac{18}{5} \mathrm{~km} \)
The distance walked by
\( \text { Surya in } 2 \frac{1}{2} \text { hours }=2 \frac{1}{2} \times \frac{18}{5} \)\(\frac{5}{2}\) x \(\frac{18}{5}\)
= 9 km
2. If 24 students share \( 4 \frac{4}{5} \) kg of cake, then how much cake does each one get?
Solution:
Total number of students = 24
Total weight of cake \( =4 \frac{4}{5} \mathrm{~kg} \)
\( =\frac{24}{5} \mathrm{~kg} \)The share of a cake that each one get
\( \begin{aligned}& =\frac{24}{5} \div 24 \\
& =\frac{24}{5} \times \frac{1}{24}=\frac{1}{5} \mathrm{~kg}(200 \mathrm{~g})
\end{aligned} \)
3. If the cost of each cement bagis 326.50,then find the cost of 24 bags of cement.
Solution:
The cost of each cement bag = 326.50
The cost of 24 bags of cement = 24 x 326.50
= 7836
= 7836
4. Dharmika purchased chudidhar material of 1.40m at the rate of 152.5 per metre. Find the amount to be paid.
Solution:
The length of chudidhar material purchased by Dharmika = 1.40 m
The cost of material per meter = 152.5
The total amount to be paid = 1.40 x 152.5
= 213.5
= 213.50
5. If a picture chart costs 4.25. Amrutha wants to buy 16 charts to make an album. How much money does she have; to pay?
Solution:
The cost of picture chart = 4.25
Number of charts that she want to buy = 16
The amount of money she has to pay
= 4.25×16
= 68.00 = 68
6. Which is bigger \( \frac{5}{8} \text { or } \frac{3}{5} ? \)
Solution:
\( \begin{gathered}\frac{5}{8}=\frac{5 \times 5}{8 \times 5}=\frac{25}{40}, \frac{3}{5}=\frac{3 \times 8}{5 \times 8}=\frac{24}{40} \\
\frac{25}{40}>\frac{24}{40} \text { and So, } \frac{5}{8}>\frac{3}{5}
\end{gathered} \)
[Hint: To compare, convert the fractions into like fractions]
Short Answer Questions
7. In Jagananna Gorumudda (MDM) scheme each student got \( \frac{3}{20} \) kg. rice per day, find the weight of the rice required for 60 students in a class per day.
Solution: The weight of rice for each student per day = \( \frac{3}{20} \) kg
Number of students in a class = 60
Total weight of rice required for 60 students in a class per day
\( =\frac{3}{20} \times 60 \)\( \frac{3}{20} \times \frac{60}{1} \) = 3 x 3 = 9 kg
8. Find the product:
1. 32.5 x 8
Solution: 1) 32.5 x 8
\( \begin{aligned}& =\frac{325}{10} \times 8 \\
& =\frac{2600}{10}
\end{aligned} \)
= 260.0
= 260
2. 94.62 x7
Solution: 94.62 x7
\( \begin{aligned}& =\frac{9462}{100} \times 7 \\
& =\frac{66234}{100}
\end{aligned} \)
= 662.34
3.109.761 x 3
Solution: 109.761 x 3
\( \begin{aligned}& =\frac{109761}{1000} \times 31 \\
& =\frac{3402591}{1000}
\end{aligned} \)
= 3402.591
4. 61 x 2.39
Solution: 61 x 2.39
\( \begin{aligned}& =61 \times \frac{239}{100} \\
& =\frac{14579}{100}
\end{aligned} \)
= 145.79
9. Find the product of the following
1. 23.4×6
2. 681.25×9
3. 53.29×14
4. 8 x 2.52
5. 25 x 2.013
Solution:
1. 23.4 x 6
23.4 x 6 = 140.4
(or)
\( \begin{aligned}23.4 \times 6 & =\frac{234}{10} \times 6 \\
& =\frac{1404}{10}=140.4
\end{aligned} \)
2. 681.25 x 9
681.25 x 9 = 6131.25
(or)
\( 681.25 \times 9=\frac{68125}{100} \times 9=\frac{613125}{100}=6131.25 \)3. 53.29 x 14
53.29 x 14 – 746.06
or
\( \begin{aligned}53.29 \times 14=\frac{5329}{100} \times 14 & =\frac{74606}{100} \\
& =746.06
\end{aligned} \)
4. 8 x-2.52
8 x 2.52 = 20.16
or
\( 8 \times 2.52=8 \times \frac{252}{100}=\frac{2016}{100}=20.16 \)5. 25 x 2.013
25 x 2.013 = 50.325
or
\( 25 \times 2.013=25 \times \frac{2013}{1000}=\frac{50325}{1000}=50.325 \)10. Represent \( 2 \frac{1}{4} \) pictorially. How many units are needed for this?
Solution:
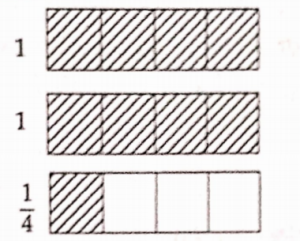
The shaded region in the above figure represents the fraction \( 2 \frac{1}{4} \).
Three units are needed for this.
11. Arrange the following in ascending order.
1. \( \frac{5}{8}, \frac{5}{6}, \frac{1}{2} \)
2. \( \frac{2}{5}, \frac{1}{3}, \frac{3}{10} \)
Solution:
1. Given fractious are \( \frac{5}{8}, \frac{5}{6}, \frac{1}{2} \)
L.C.M. of the denominators 8, 6 and 2 = 24
Now \( \frac{5}{8}=\frac{5 \times 3}{8 \times 3}=\frac{15}{24} \)
\( \begin{aligned}& \frac{5}{6}=\frac{5 \times 4}{6 \times 4}=\frac{20}{24} \\
& \frac{1}{2}=\frac{1 \times 12}{2 \times 12}=\frac{12}{24}
\end{aligned} \)
Clearly
\( \begin{aligned}& \frac{12}{24}<\frac{15}{24}<\frac{20}{24} \\
& \frac{1}{2}<\frac{5}{8}<\frac{5}{6}
\end{aligned}\)
Second method
\( \frac{1}{2}=\frac{1 \times 5}{2 \times 5}=\frac{5}{10} \)clearly 10 > 8 > 6
\( \begin{aligned}& \frac{5}{10}<\frac{5}{8}<\frac{5}{6} \\
& \frac{1}{2}<\frac{5}{8}<\frac{5}{6}
\end{aligned} \)
2. Given fractions are \( \frac{2}{5}, \frac{1}{3}, \frac{3}{10} \)
LCM of the denominators 5, 3, 10 = 30
Now \( \begin{aligned}
& \frac{2}{5}=\frac{2 \times 6}{5 \times 6}=\frac{12}{30} \\
& \frac{1}{3}=\frac{1 \times 10}{3 \times 10}=\frac{10}{30} \\
& \frac{3}{10}=\frac{3 \times 3}{10 \times 3}=\frac{9}{30}
\end{aligned} \)
Clearly
\( \begin{aligned}& \frac{9}{30}<\frac{10}{30}<\frac{12}{30} \\
& \frac{3}{10}<\frac{1}{3}<\frac{2}{5}
\end{aligned} \)
12. Write the following fractions in ascending order.
1. \( \frac{3}{2}, \frac{5}{2}, \frac{1}{2}, \frac{17}{2}, \frac{9}{2} \)
2. \( \frac{6}{5}, \frac{11}{10}, \frac{19}{5}, \frac{7}{10}, \frac{5}{10} \)
3. \( \frac{8}{3}, \frac{7}{6}, 3 \frac{1}{4}, \frac{5}{3}, \frac{11}{4} \)
Solution:
1. Ascending order :
\( \frac{1}{2}<\frac{3}{2}<\frac{5}{2}<\frac{9}{2}<\frac{17}{2} \)2. \( \frac{6}{5}, \frac{11}{10}, \frac{19}{5}, \frac{7}{10}, \frac{5}{10} \)
LCM of denominators = 10
\( \frac{6}{5}=\frac{6}{5} \times \frac{2}{2}=\frac{12}{10} ; \frac{19}{5}=\frac{19}{5} \times \frac{2}{2}=\frac{38}{10} \)Ascending order:
\( \begin{aligned}& =\frac{5}{10}<\frac{7}{10}<\frac{11}{10}<\frac{12}{10}<\frac{38}{10} \\
& =\frac{5}{10}<\frac{7}{10}<\frac{11}{10}<\frac{6}{5}<\frac{19}{5}
\end{aligned} \)
3. \( \frac{8}{3}, \frac{7}{6}, 3 \frac{1}{4}, \frac{5}{3}, \frac{11}{4} \)
LCM of denominators = 12
\( \begin{aligned}& \frac{8}{3}=\frac{8}{3} \times \frac{4}{4}=\frac{32}{12} ; \frac{7}{6}=\frac{7}{6} \times \frac{2}{2}=\frac{14}{12} \\
& 3 \frac{1}{4}=\frac{13}{4} \times \frac{3}{3}=\frac{39}{12} \\
& \frac{5}{3}=\frac{5}{3} \times \frac{4}{4}=\frac{20}{12} ; \frac{11}{4}=\frac{11}{4} \times \frac{3}{3}=\frac{33}{12}
\end{aligned} \)
Ascending order:
\( \begin{aligned}& \frac{14}{12}<\frac{20}{12}<\frac{32}{12}<\frac{33}{12}<\frac{39}{12} \\
& =\frac{7}{6}<\frac{5}{3}<\frac{8}{3}<\frac{11}{4}<3 \frac{1}{4}
\end{aligned} \)
13. Determine if the following pairs are equal by writing each in their simplest form.
1. \( \frac{3}{8} \text { and } \frac{375}{1000} \)
2. \( \frac{18}{54} \text { and } \frac{23}{69} \)
3. \( \frac{6}{10} \text { and } \frac{600}{1000} \)
4. \( \frac{17}{27} \cdot \text { and } \frac{25}{45} \)
Solution:
\( \begin{aligned}&\frac{3}{8} \text { is in the simplest form. }\\
&\frac{375}{1000}=\frac{25 \times 15}{25 \times 40}=\frac{15}{40}=\frac{5 \times 3}{5 \times 8}=\frac{3}{8}
\end{aligned} \)
Shortly, \( \frac{375}{1000}\) = \( \frac{3}{8} \)
2. \( \frac{18}{54} \) = \( \frac{1}{3} \) and \( \frac{23}{69} \) = \( \frac{1}{3} \)
\( \text { So, } \frac{18}{54}=\frac{23}{69}\)3. \( \frac{6}{10} \) = \( \frac{3}{5} \) and \( \frac{600}{1000}\) = \( \frac{3}{5} \)
\( \text { So, } \frac{6}{10}=\frac{600}{100}\)4. \( \frac{17}{27} \text { is in the simplest form. } \)
\( \frac{25}{45} \) = \( \frac{5}{9} \)
But \( \frac{17}{27} \neq \frac{5}{9}\)
So, they are not equivalent
14; Compute the following and express the result as a mixed fraction
1. \( 2+\frac{3}{4} \)
2. \( \frac{7}{9}+\frac{1}{3} \)
3. \( 1-\frac{4}{7} \)
4. \( 2 \frac{2}{3}+\frac{1}{2} \)
5. \( \frac{5}{8}-\frac{1}{6} \)
6. \( 2 \frac{2}{3}+3 \frac{1}{2} \)
Solution:
1) \( \begin{aligned}
& \begin{aligned}
2+\frac{3}{4}=\frac{2 \times 4+3}{4} & =\frac{11}{4}=2 \frac{3}{4} \\
\text { Alter }: 2+\frac{3}{4} & =\frac{2}{1}+\frac{3}{4}=\frac{8}{4}+\frac{3}{4} \\
& =\frac{8+3}{4}=\frac{11}{4}=2 \frac{3}{4}
\end{aligned}
\end{aligned} \)
2. \( \frac{7}{9}+\frac{1}{3}=\frac{7}{9}+\frac{3}{9}=\frac{7+3}{9}=\frac{10}{9}=1 \frac{1}{9} \)
3. \( 1-\frac{4}{7}=\frac{7}{7}-\frac{4}{7}=\frac{7-4}{7}=\frac{3}{7} \)
4. \( \begin{aligned}
2 \frac{2}{3}+\frac{1}{2}=\frac{8}{3}+\frac{1}{2}= & \frac{16}{6}+\frac{3}{6} \\
& =\frac{16+3}{6}=\frac{19}{6}=3 \frac{1}{6}
\end{aligned} \)
5. \( \frac{5}{8}-\frac{1}{6}=\frac{15}{24}-\frac{4}{24}=\frac{15-4}{24}=\frac{11}{24} \)
6. \( \begin{aligned}
2 \frac{2}{3} & +3 \frac{1}{2}=\frac{8}{3}+\frac{7}{2} \\
& =\frac{16}{6}+\frac{21}{6}=\frac{16+21}{6}=\frac{37}{6}=6 \frac{1}{6}
\end{aligned} \)
15. Check whether in this square the sum of the numbers in each row and in each column and along the diagonals is the same
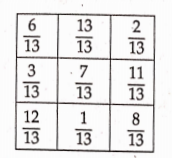
Solution: Sum of the fractions of first row
\( =\frac{6}{13}+\frac{13}{13}+\frac{2}{13}=\frac{6+13+2}{13}=\frac{21}{13} \)Sum of the fractions of second row
\( =\frac{3}{13}+\frac{7}{13}+\frac{11}{13}=\frac{3+7+11}{13}=\frac{21}{13} \)Sum of the fractions of third row
\( =\frac{12}{13}+\frac{1}{13}+\frac{8}{13}=\frac{12+1+8}{13}=\frac{21}{13} \)Sum of the fractions of first column
\( =\frac{6}{13}+\frac{3}{13}+\frac{12}{13}=\frac{6+3+12}{13}=\frac{21}{13} \)Sum of the fractions of second column
\( =\frac{13}{13}+\frac{7}{13}+\frac{1}{13}=\frac{13+7+1}{13}=\frac{21}{13} \)Sum of the fractions of third column
\( =\frac{2}{13}+\frac{11}{13}+\frac{8}{13}=\frac{2+11+8}{13}=\frac{21}{13} \)Sum of die fractions of the first diagonal
\( =\frac{6}{13}+\frac{7}{13}+\frac{8}{13}=\frac{6+7+8}{13}=\frac{21}{13} \)Sum of the fractions of the second diagonal
\( =\frac{2}{13}+\frac{7}{13}+\frac{12}{13}=\frac{21}{13} \)Thus, the sum of the numbers in each row and in each column and along the diagonals is \( \frac{21}{13} \) which is sam.
Hint: Such type of squares are called magic squares. You can try some more also.
Fill in the blanks:
101. Fractions with same denominators are called ………………
Answer: like fractions
102. The product of two improper fractions is………. the two fractions
Answer: greater than
103. A ……of a fraction is obtained by inverting it upside down.
Answer: reciprocal
104. \(\frac{2}{7}\) x …… = 1
Answer:
\(\left(\frac{7}{2}\right)\)105.\(10 \frac{3}{7}=\)…….
Answer:
\(\left(\frac{73}{7}\right)\)106. Simplest form of
\(\frac{16}{40}\) is………
Answer:
\(\left(\frac{2}{5}\right)\)107. \(\frac{8}{15}\)…….\(\frac{2}{3}\) (Use > or <)
Answer: (<)
108. \(\frac{1}{4} \text { of } \frac{4}{3}=\) = …………
Answer:
\(\left(\frac{1}{3}\right)\)109. 21.36 + 37.3 =………
Answer: (58.66)
110. How much less is 28 km than 42.6 km ?………..
Answer: (14.6 km)
111. Match the following:
1. \( \frac{1}{2}, \frac{2}{4}, \frac{3}{6} \text { are } \) ( ) A) Like fractions
2. \( \frac{1}{7}, \frac{2}{7}, \frac{5}{7} \text { are }\) ( ) B) Improper fractions
3. \( 1 \frac{3}{4}, 2 \frac{2}{3}, 3 \frac{5}{8} \text { are }\) ( ) C) Decimal fractions
4. \( \frac{7}{4}, \frac{8}{5}, \frac{9}{7} \text { are }\) ( ) D) Equivalent fractions
5. \( \frac{5}{10}, \frac{7}{100}, \frac{9}{1000} \text { are }\) ( ) E) Mixed fractions
Answer:
1. D 2. A 3. E 4. B 5. C
