Haryana Board Class 6 Maths Solutions For Chapter 4 Basic Geometrical Ideas
- The term ‘GEOMETRY’ is derived from the Greek word ‘GEOMETRON’.
- ‘Geo’ means earth and ‘metron’ means ‘measurement’.
- ‘Euclid’ is known as ‘Father of Geometry’. He introduced geometry in a logical order in the book ‘The Elements’..
- The ancient Indian Mathematician Aryabhata and Brahmagupta contributed their works in geometry.
- A ‘point’ determines a location. It is usually denoted by capital letters in English.
- A ‘line segment’ is formed by joining two points. It has a fixed length. A line segment has negligible thickness. It has two end points.

- A ‘line’ is obtained when a line segment extends on both sides indefinitely. It is denoted by small letters such as l, m, n etc.

- It has no end points.
- A’ray’ is a portion of a line starting at a point and goes in one direction endlessly.

- Eg: Ray \(\overrightarrow{\mathrm{AB}}\) Ray \(\overrightarrow{\mathrm{CA}}\)
- By using divider and scale, we can measure the length of line segment.
- A figure drawn without lifting a pencil is called a ‘curve’. In this sense, a line is also a curve.
- Parallel Lines: The lines in a plane that never meet even if they are extended any further are called Parallel lines. Eg: The lines in your ruled book are parallel lines.

- If line l is parallel to line ‘m’, then it is denoted by l || m. It can be read as “l is Parallel to m”.
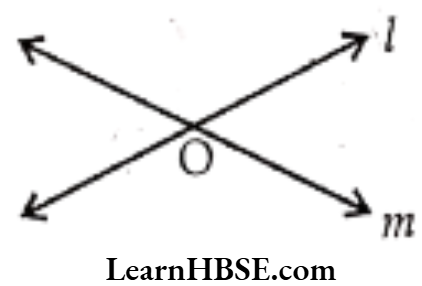
- Intersecting Lines: The lines that cross one another are called intersecting lines and the point at which they intersect is called intersecting point.
Haryana Board Class 6 Maths Basic Geometrical Ideas solutions
- Here ‘O’ is the intersecting point.
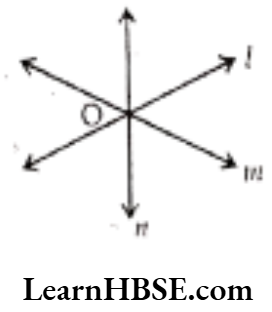
- Concurrent Lines: Three or more lines passing through the same point are called concurrent lines. The point is called point of concurrency.
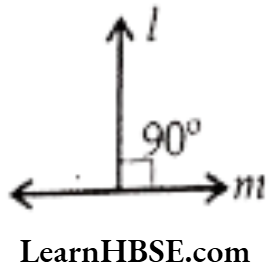
- Perpendicular Lines: The angle between any two lines is 90° are called ‘perpendicular lines’: It is denoted by ⊥ (perpendicular).
- If line l is perpendicular to the line m then it is denoted by l ⊥ m and read as ‘I is perpendicular to m’.
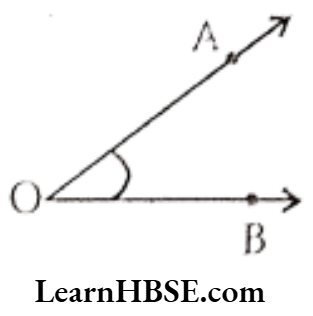
- Angle: An angle in a figure formed by two rays with a common end point. The common end point is called ‘vertex’. The rays are the ‘sides or arms’ of the angle. It is denoted by ‘∠AOB’ read as angle АОВ.
Types of angles.
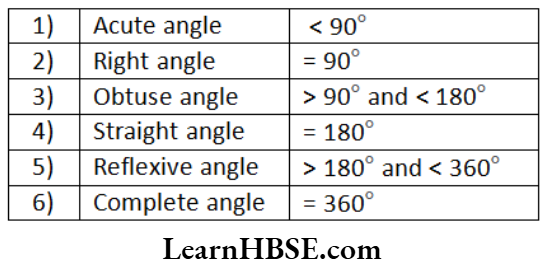
- We use a tool called “Protractor” to measure the given angle.
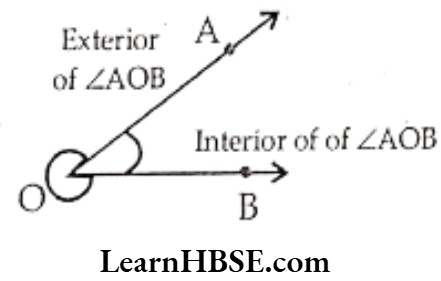
- Two rays with a common initial make two regions.
- The interior of an angle is the group of all the points between the rays of the angle.
- The exterior of an angle is the group of all points outside the rays of the angle.
- The simple closed figure formed by three line segments is called a triangle.
- The line segments are called sides.
- A triangle has three vertices, three sides and three angles.
- In triangle ABC
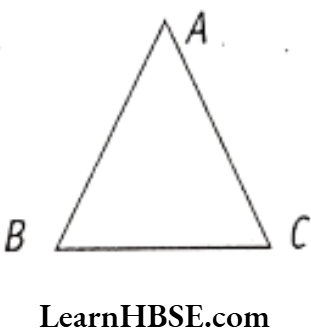
A, B, C are three vertices \(\overline{A B}, \overline{B C}, \overline{C A}\) are three sides ∠BAC, ∠ABC, ∠ACB are three angles. The triangle ABC is denoted by ΔABC.
- A triangle divides a plane into three parts
- Interior of the triangle
- Boundary of the triangle
- Exterior of the triangle
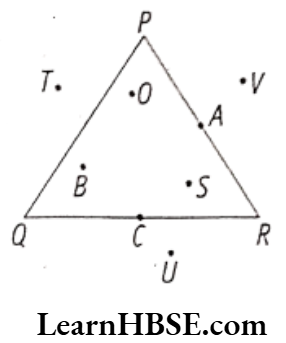
Eg. PQR is a triangle.
The points 0, B, S are interior of the tri- angle.
The points A, C are on the Boundary of the trianlge.
The points T, U, V are exterior of the tri- angle.
- A ‘simple curve’ is one that does not cross itself.
- Curves are of 2 types – open curve; closed curve
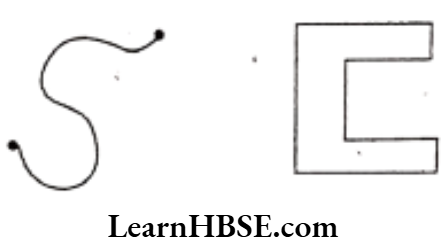
- A figure is a ‘polygon’ if it is a simple closed figure made up definite number of line segments
- A closed figure separates the plane into three parts.
- Interior (inside) of the figure.
- Boundary of the figure.
- Exterior (outside) of the figure.
- The interior of the figure together with its boundary is its ‘region’.
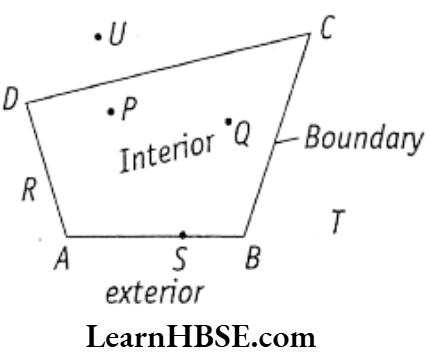
Eg. : ABCD is a closed figure formed by 4 line segments AB, BC, CD and DA.
Points P, Q are Interior of the figure, points R, S are on the Boundary line, points T, U are on the exterior of the figure.
- The interior of the figure together with its boundary is its region
Question 1. A Star in the sky also gives us an idea of a point. Identify at least five such situations in your daily life.
Solution. Five situations giving an idea of a point are:
- Sharp tip of pencil.
- Tip of a pen
- Tip of the compass
- Pointed end of the needle
- Dot on the paper
Question 2. Name the line segments in the figure 4.2. Is A, the end point of each line segment?
Solution.
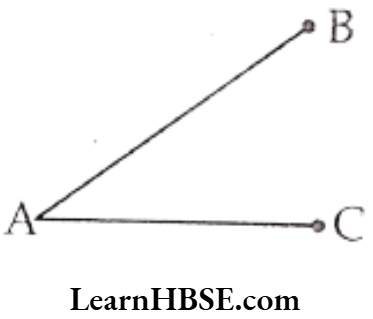
The line segments in the given figure are
\(\overline{\mathrm{AB}}\) (or \(\overline{\mathrm{BA}}\)) and \(\overline{\mathrm{AC}}\) (or \(\overline{\mathrm{CA}}\))
Yes! A is the end point of each line segment.
Points, lines, and angles Class 6 HBSE Maths
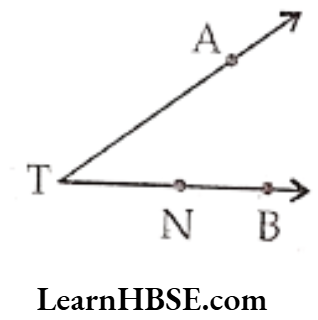
Question 3. 1. Name the rays given in this picture.
2. Is T a starting point of each of these rays?
Solution. 1) \(\overrightarrow{\mathrm{TA}}, \overrightarrow{\mathrm{TN}}, \overrightarrow{\mathrm{~TB}}, \overrightarrow{\mathrm{NB}}\)
2) No! T is not a starting point of each of these rays.
Haryana Board Class 6 Maths Solutions For Chapter 4 Basic Geometrical Ideas Exercise 4.1
Question 1. Use the figure to name :
a) Five points
b) A line
c) Four rays
d) Five line segments
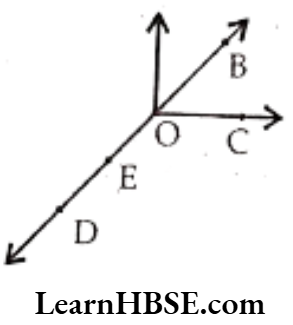
Solution. a) O, B, C, D, E
b) DB
c) \(\overrightarrow{O B}, \overrightarrow{O C}, \overrightarrow{O E}, \overrightarrow{O D}\)
d) \(\overline{O B}, \overline{O C}, \overline{O E}, \overline{O D}, \overline{E D}\)
Question 2. Name the line given in all possible (twelve) ways, choosing only two letters at a time from the four given.
Solution. Let the four points be A, B, C and D.
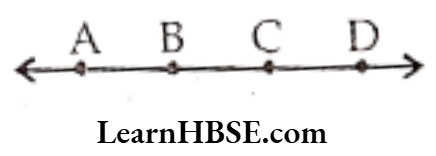
AB, AC, AD, BA, BC, BD, CA, CB, CD, DA, DB, DC.
Question 3. Use the figure to name:
a) Line containing point E.
b) Line passing through A.
c) Line on which O lies.
d) Two pairs of intersecting lines.
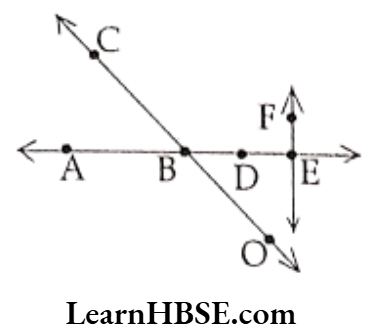
Solution.
a) EF
b) AE
c) OC
d) AE and CO; AE and EF.
Question 4. How many lines can pass through
a) one given point?
b) two given points?
Solution. a) Infinitely many lines can pass through one given point.
b) One and only one line can pass through two given points.
Question 5. Draw a rough figure and label suitably in each of the following cases:
a) Point Plies on \(\overleftrightarrow{\mathrm{AB}}\)
b) \(\overleftrightarrow{\mathrm{XY}}\) and \(\overleftrightarrow{\mathrm{PQ}}\) intersect at M.
c) Line I contains É and F but not D.
d) \(\overleftrightarrow{\mathrm{OP}}\) and \(\overleftrightarrow{\mathrm{OQ}}\) meet at O.
Solution.
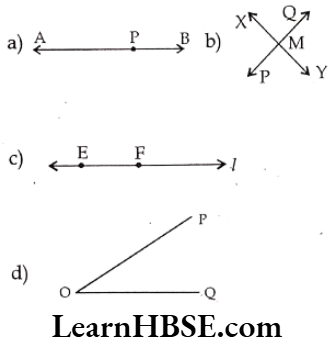
Question 6. Consider the following figure of line \(\overline{\mathbf{M N}}\). Say whether following statements are true or false in context of the given figure.
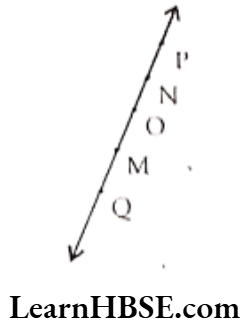
a. Q, M, O, N, P are points on the line \(\overline{\mathbf{M N}}\)
Solution. True.
b. M, O, N are points on a line segment \(\overline{\mathbf{M N}}\)
Solution. True
c. M and N are end points of line segment \(\overline{\mathbf{M N}}\)
Solution. True
d. O and N are end points of line segment \(\overrightarrow{\mathrm{OP}}\)
Solution. False.
e. M is one of the end points of the line segment \(\overline{\mathbf{Q O}}\)
Solution. False.
f. M is point on ray \(\overrightarrow{\mathrm{OP}}\).
Solution. False.
g. Ray \(\overrightarrow{\mathrm{OP}}\) is different from ray \(\overrightarrow{\mathrm{QP}}\).
Solution. True.
h. Ray \(\overrightarrow{\mathrm{OP}}\) is same as ray \(\overrightarrow{\mathrm{OM}}\).
Solution. False.
i. Ray \(\overrightarrow{\mathrm{OM}}\) is not opposite to ray \(\overrightarrow{\mathrm{OP}}\).
Solution. False.
j. ‘O’ is not an initial point of ray \(\overrightarrow{\mathrm{OP}}\).
Solution. False.
k. N is the initial point of \(\overrightarrow{\mathrm{NP}} \text { and } \overrightarrow{\mathrm{NM}}\).
Solution. True
Haryana Board Class 6 Maths Solutions For Chapter 4 Basic Geometrical Ideas Exercise – 4.2
Question 1. Classify the following curves as
(1) Open or
(2) Closed.
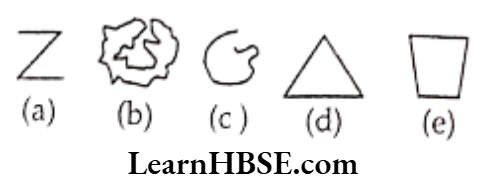
Solution. (1) a, c – open curves
(2) b, d, e – closed curves.
Question 2. Draw rough diagrams to illustrate the following:
(a) Open curve
(b) Closed curve
Solution.
Types of angles in geometry Class 6 Haryana Board
Question 3. Draw any polygon and shade its interior.
Solution.
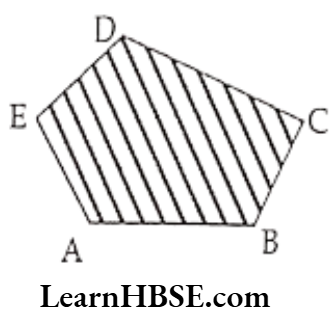
Question 4. Consider the given figure and answer the questions:
a) Is it a curve?
b) Is it closed?
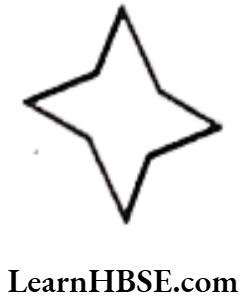
Solution. a) Yes! it is a curve.
b) Yes! it is closed.
Question 5. Illustrate, if possible, each one of the following with a rough diagram:
Solution. a) A closed curve that is not a polygon.

b) An open curve made up entirely of line segments.
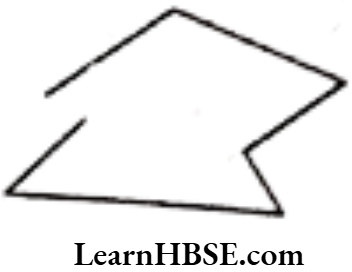
c) A polygon with two sides.
Not Possible.
A: A polygon is a closed plane figure with three or more sides that are all straight. Therefore, A polygon with two side cannot be drawn.
Haryana Board Class 6 Maths Solutions For Chapter 4 Basic Geometrical Ideas Exercise – 4.3
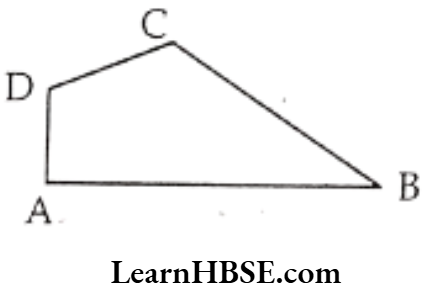
Question 1. Name the angles in the given figure.
Solution. ∠ABC, ∠BCD, ∠CDA, ∠DAB
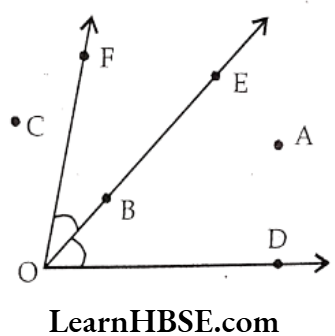
Question 2. In the given diagram, name the point(s)
a) In the interior of DOE
b) In the exterior of ZEOF
c) On ∠EOF
Answer. a) A
b) C, A, D
c) O, B, E, F
Polygons and their properties Class 6 HBSE Maths
Question 3. Draw rough diagrams of two angles such that they have
a. One point in common
Solution.
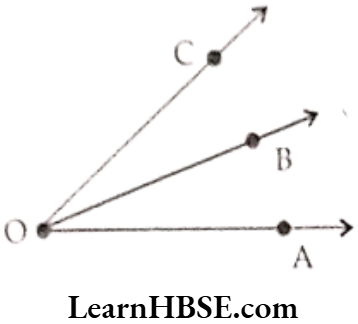
∠AOB and ∠BOC have one point ‘O’ in common.
b. Two points in common.
Solution. ∠AOB and ∠OBC have two points O and B in common.
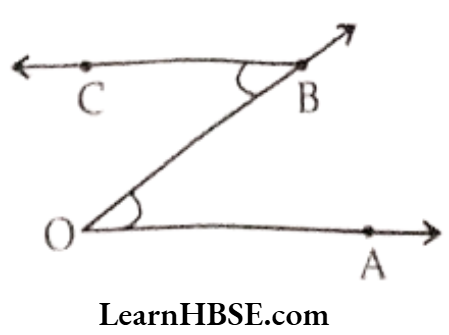
c. Three points in common.
Solution. Not possible
d. Four points in common.
Solution. Not possible
e. One ray in common.
Solution. ∠AOB and ∠BOC have one ray OB in common.
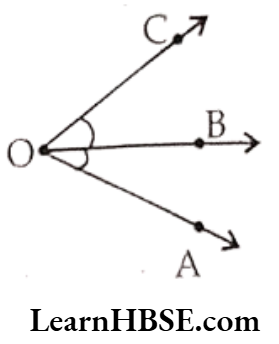
Chapter 4 Basic Geometrical Ideas Very Short Answer Questions
Question 1. Draw a line, ray and a line segment.
Solution.

Question 2. Mark two points X and Y. Also mark three more points between them and another three points that are not in between those two points.
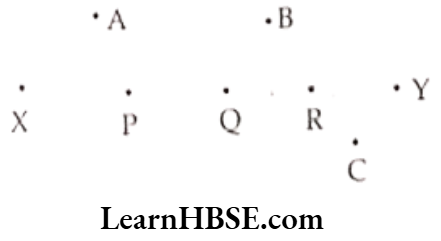
Solution. X, Y are any two points.
P, Q, R are three points between X and Y.
A, B, C are three points not between X and Y.
Question 3. Define a triangle. Write the parts in it.
Solution. A simple colsed figure formed by three line segments is called a triangle. It has 3 sides, 3 vertices and 3 angles.
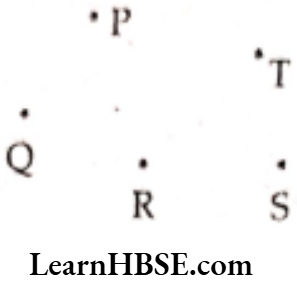
Question 4. Join the points given below. Name the line segments so formed in the figure.
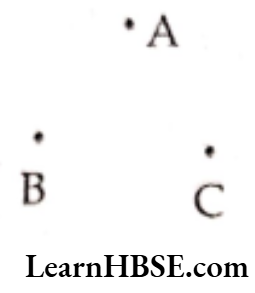
Solution. 1)
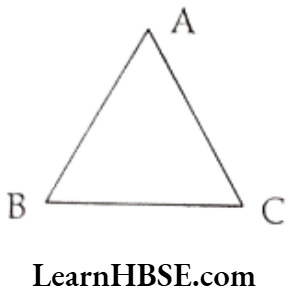
Line segments so formed are: \(\overline{\mathrm{AB}}, \overline{\mathrm{BC}}, \overline{\mathrm{CA}}\)
2)
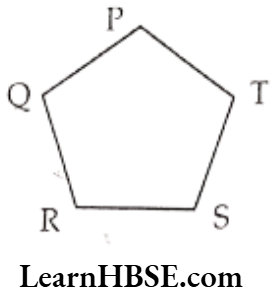
Line segments so formed are: \(\overline{\mathrm{PQ}}, \overline{\mathrm{QR}}, \overline{\mathrm{RS}}, \overline{\mathrm{ST}}, \overline{\mathrm{TP}}\)
Parts of a circle Class 6 HBSE Maths
Question 5. Which of the following has a definite length?
1) Line
2) Point
3) Line segment
4) Ray
Solution. Line segment. Because it has two end points.We can measure it.
Question 6. Tell which letter is an example of simple curve.
Solution. The letter O is an example of simple curve.
Question 7. What is the least no. of sticks needed to form a closed figure?
Solution. Three sticks are needed to form a closed figure.
Haryana Board Class 6 Maths Solutions For Chapter 4 Basic Geometrical Ideas Short Answer Questions
Question 1. From the adjacent figure, write down
1) The sides of the triangle
2) The angles of the triangle
3) The vertices of the triangle.
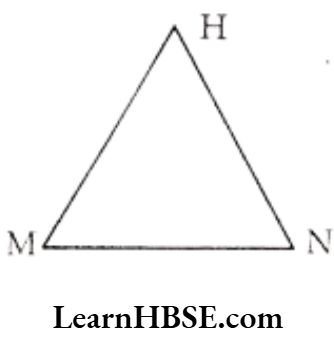
Solution. 1) The sides of the triangle – \(\overline{\mathrm{MN}}, \overline{\mathrm{NH}}, \overline{\mathrm{HM}}\)
2) The angles of the triangle – ∠HMN, ∠MNH, ∠NHM
3) The vertices of the triangle – H, M, N
Question 2. Write the set of parallel lines and perpendicular lines in the given figure by using symbols.
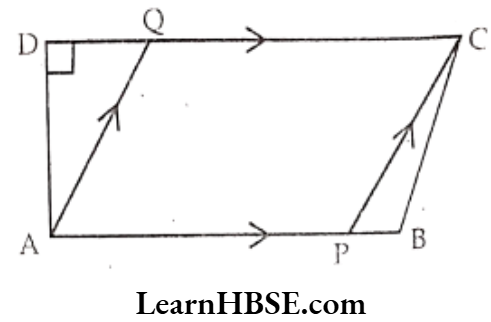
Solution. Parallel lines: \(\overline{\mathrm{AB}} \text { and } \overline{\mathrm{DC}} ; \overline{\mathrm{AB}} \| \overline{\mathrm{DC}} ; \overline{\mathrm{AQ}} \text { and } \overline{\mathrm{PC}} ; \overline{\mathrm{AQ}} \| \overline{\mathrm{PC}}\)
Perpendicular lines: \(\overline{\mathrm{AD}} \perp \mathrm{AB} \text { and } \overline{\mathrm{AD}} \perp \mathrm{DC}\)
Question 3. Draw
1) Intersecting lines
2) Parallel lines
3) Perpendicular lines.
Solution.
1) Intersecting lines
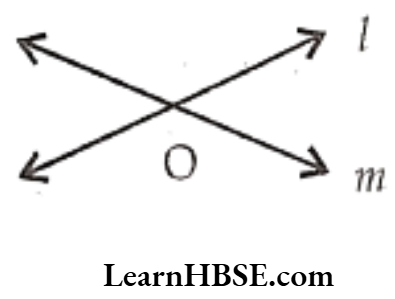
2) Parallel lines
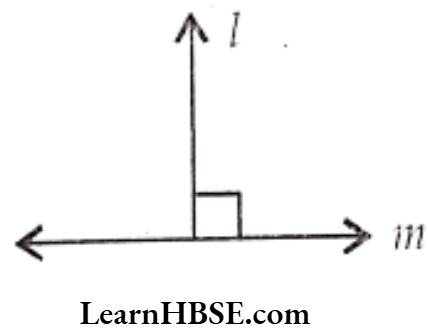
3) Perpendicular lines
Question 4. Name the following from the figure.
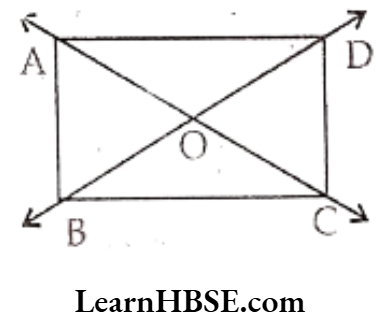
1) Any five points : A, B, C, D, O
2) Any five line segments : \(\overline{\mathrm{AB}}, \overline{\mathrm{BC}}, \overline{\mathrm{CD}}, \overline{\mathrm{DA}}\)
3) Any three rays : \(\overrightarrow{\mathrm{OA}}, \overrightarrow{\mathrm{OB}}, \overrightarrow{\mathrm{OC}}\)
4) Any two lines : \(\overrightarrow{\mathrm{AC}}, \overrightarrow{\mathrm{BD}}\)
Question 5. Move your pencil along the following english letters and state which are open and which are closed.
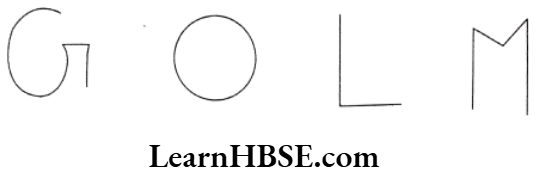
Solution. (i), (iii), (iv) are open, (ii) is closed.
Question 6. Tick the figures which are simple curves.
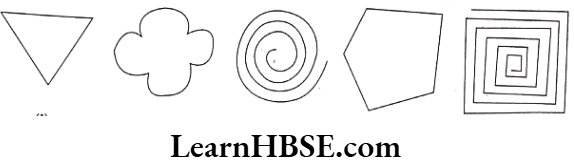
Solution. Simple curves: (i), (ii), (iv)
Question 7. State which curves are open and which are closed.

Solution. Open curves: (i), (v)
Closed curves: (ii), (iii), (iv)
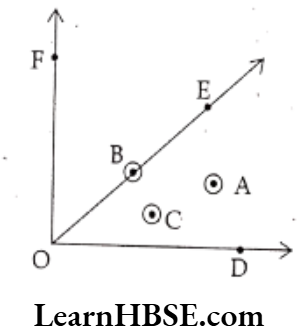
Question 8. Mark the points in the figure which satisfy all the three conditions.
1) A, B in the interior of ∠DOF
2) A, C in the exterior of ∠EOF
3) B is on ∠DOE
Solution.
Question 9. Identify simple closed and open figures from the figures given here under.
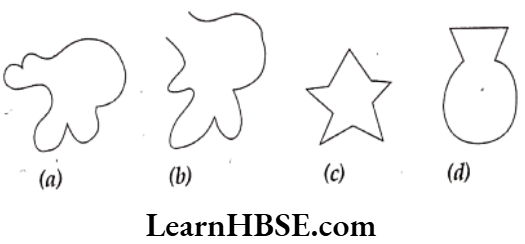
Solution. Simple closed figures – a, c, d;
Simple open figure – b
Question 10. Identify simple curved figures.
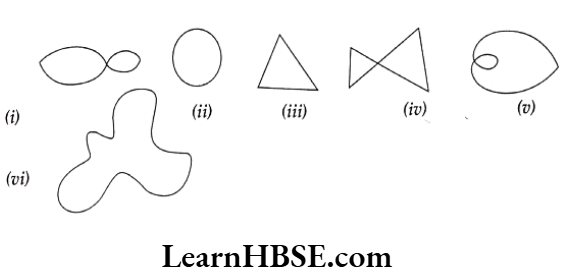
Solution. (ii), (iii), (vi) are simple curved figures.
Haryana Board Class 6 Maths Solutions For Chapter 4 Basic Geometrical Ideas Long Answer Questions
Question 1. Write the names of the angles, their vertices and arms.
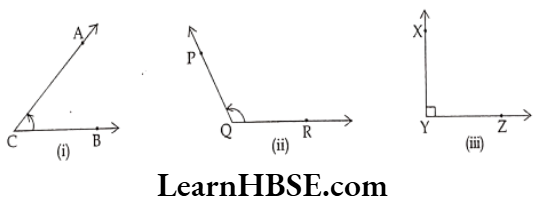
Solution.
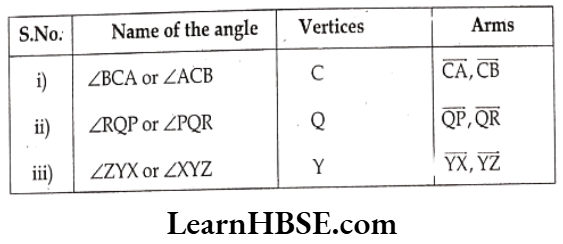
Question 2. From the adjacent figure write the points that belongs to
1) the angle
2) the interior of the angle
3) the exterior of the angle
Solution. The points that belongs to
1) The angle – B, R, E, O, C, A
2) The interior of the angle – D, F, Q
3) The exterior of the angle – M,L, N
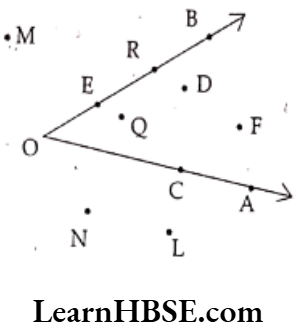
Question 3. From the adjacent figure write
1) Interior points of the triangle.
2) Exterior points of the triangle.
3) Points on the boundary of the triangle.
4) Vertices of the triangle.
Solution. 1) Interior points of the triangle – B, M
2) Exterior points of the triangle – A, C, N
3) Points on the boundary of the triangle – P, Q, R, D, L
4) Vertices of the triangle-P, Q, R
Question 4. Write ‘True’ or ‘False”.
1) A line has no end points.
True
2) Ray is a part of a line.
True
3) A line segment has no definite length.
False
4) A line segment has only one end point.
False
5) We can draw many lines through a point.
True
Question 5. Identify which are simple curves and which are not?
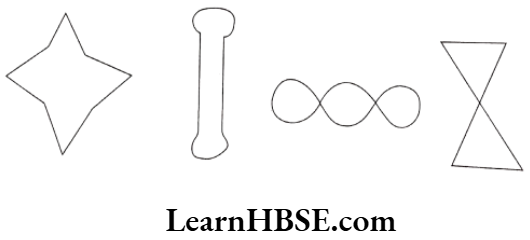
Solution. If a curve does not cross itself then it is a simple curve.
(i), (ii), (iv) are simple curves.
(iii) The curve crosses it self so it is not a simple curve.
Question 6. Name the points that lie in the interior, on boundary and in the exterior of the figure.
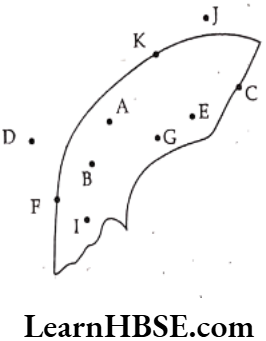
Solution. The points that lie
1) Interior – A, B, E, G, I;
2) Boundary – K, F, C;
3) Exterior – J, D
Question 7. Draw three simple closed figures:
1) By straight lines only.
Solution.
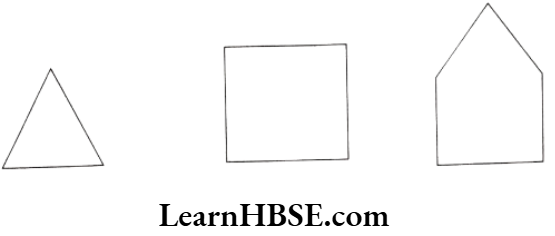
2) By straight lines and curved lines both.
Solution.

Question 8. Name the angles, vertex and arms of the angles from the figure.
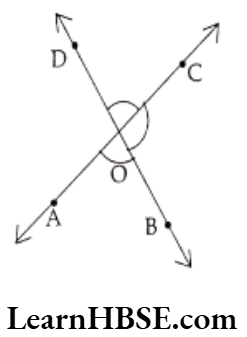
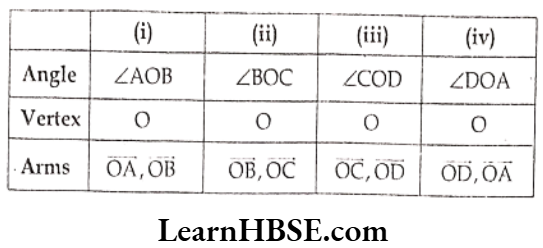
Difference between line and line segment Class 6
Question 9. In the figure given below, Identify which points lie
1) in the interior,
2) in the exterior,
3) on the boundary.
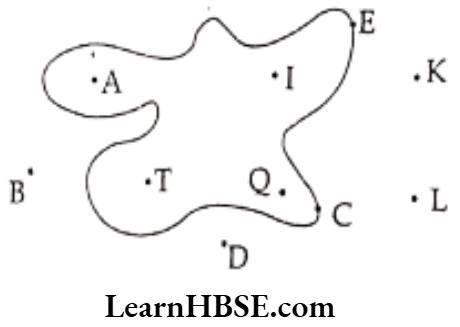
Solution. 1) Interior points – A, T, Q, I
2) Exterior points – B, D, L, K
3) On the boundary-C, E
Question 10. Observe the adjacent figure. Write answers for the following.
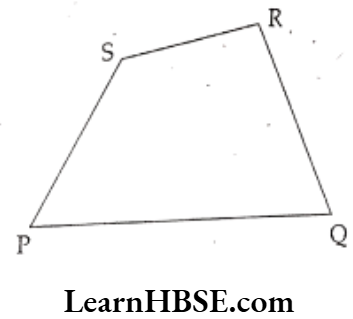
Solution. 1) Name : PQRS Quadrilateral
2) Vertices : P, Q, R, S
3) Sides : \(\overline{\mathrm{PQ}}, \overline{\mathrm{QR}}, \overline{\mathrm{RS}}, \overline{\mathrm{SP}}\)
4) Angles : ∠SPQ, ∠PQR, ∠QRS, ∠RSP
5) Opposite sides : \(\overline{\mathrm{PQ}}, \overline{\mathrm{RS}} ; \overline{\mathrm{QR}}, \overline{\mathrm{PS}}\)
6)Opposite angles : ∠SPQ, ∠QRS; ∠PQR, ∠RSP
7) Adjacent angles : ∠SPQ, ∠PQR, ∠QRS, ∠RSP, ∠SPQ
Haryana Board Class 6 Maths Solutions For Chapter 4 Basic Geometrical Ideas Objective Type Questions
Choose the correct answer:
Question 1. How many end points does a line have?
- Infinite
- 2
- 0
- 1
Answer. 4. 1
Question 2. How many end points does a line have?
- No end points
- 2
- Infinite
- 1
Answer. 1. No end points
Question 3. The closed figure formed by more line segments is called
- square
- polygon
- triangle
- circle
Answer. 2. polygon
Question 4. We denote line AB as
- \(\overrightarrow{\mathrm{AB}}\)
- \(\overline{\mathrm{AB}}\)
- \(\overleftrightarrow{\mathrm{AB}}\)
- \(\widehat{\mathrm{AB}}\)
Answer. 3. \(\overleftrightarrow{\mathrm{AB}}\)
Question 5. Number of points on a line
- 3
- 2
- 4
- Infinite
Answer. 4. Infinite
Question 6. There are …… vertices in a triangle.
- 4
- 3
- 2
- 8
Answer. 2. 3
Question 7. In the figure vertex of the angle is …..
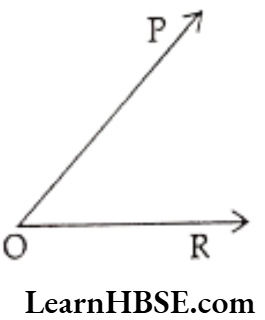
- P
- O
- R
- \(\overrightarrow{\mathrm{OP}}\)
Answer. 2. O
Observe the following figure and answer the following questions from 8 to 10.
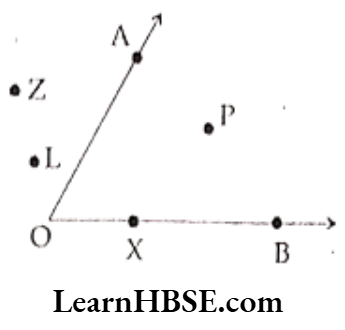
Word problems on basic geometrical ideas for Class 6 HBSE
Question 8. Interior point
- X
- L
- P
- Z
Answer. 3. P
Question 9. Exterior points
- X,L
- Z,L
- O,P
- X,Z
Answer. 2. Z,L
Question 10. Points on the ray \(\overrightarrow{\mathrm{OB}}\)
- X
- Z
- P
- O
Answer. 1. X
Question 11. Number of vertices of a square is ……..
- 3
- 4
- 8
- 13
Answer. 2. 4
Question 12. Triangle PQR can be denoted by …….
- PΔQR
- ΔPQR
- QRPΔ
- PQR
Answer. 2. ΔPQR
Question 13. How many lines can be drawn through a point in a plane?
- 16
- 12
- 3
- Infinite
Answer. 4. Infinite
Question 14. The symbol of perpendicular is
- |
- X
- ⊥
- T
Answer. 3. ⊥
Question 15. The symbol of parallel is
- X
- ∥
- ⊥
- T
Answer. 2. ∥
Question 16. Which of the following are intersecting lines?
- ∥
- X
- *
- ⊥
Answer. 2. X
Question 17. Two adjacent edges of blackboard are example for …… lines.
- parallel
- concurrent
- perpendicular
- all above
Answer. 3. perpendicular
Question 18. Two opposite edges of a paper is example for …….. lines.
- intersecting
- perpendicular
- parallel
- concurrent
Answer. 3. parallel
Question 19. To measure the angle we use
- divider
- ruler
- setsquare
- protractor
Answer. 4. protractor
Question 20. How many right angles can make a complete angle?
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
Answer. 4. 4
Question 21. End points of a line segment are
- 0
- 1
- 2
- Infinite
Answer. 3. 2
Question 22. How many lines can be drawn through two points?
- 0
- 1
- 2
- Infinite
Answer. 2. 1
Question 23. How many line segments lie in the given line?
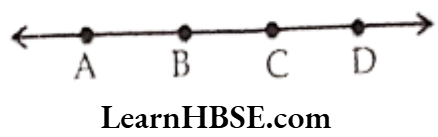
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
Answer. 3. 6
Question 24. Father of Geometry
- Phythagoras
- Ramanujan
- Euclid
- Thales
Answer. 3. Euclid
Question 25. The word Geometry is derived from ……. language.
- Greek
- Latin
- Italian
- Indian
Answer. 1. Greek
Question 26. If two lines cross one another that lines are called
- Parallel lines
- Intersecting lines
- Concurrent lines
- Perpendicular lines
Answer. 2. Intersecting lines
Question 27. If three or more lines passing through the same point are …….. lines.
- parallel
- intersecting
- concurrent
- perpendicular
Answer. 3. concurrent
Question 28. The angle between two lines are 90° then they are …… lines.
- parallel
- intersecting
- concurrent
- perpendicular
Answer. 4. perpendicular
Question 29. If two lines does not meet at any where are ….. lines.
- parallel
- intersecting
- concurrent
- perpendicular
Answer. 1. intersecting
Question 30. The lines in your ruled book are example of …… lines.
- intersecting
- parallel
- perpendicular
- concurrent
Answer. 2. parallel
Question 31. Straight angle =
- 0°
- 90°
- 180°
- 360°
Answer. 3. 180°
Question 32. Complete angle =
- 0°
- 90°
- 180°
- 360°
Answer. 4. 360°
Question 33. Reflexive angle =
- 190°
- 210°
- 315°
- all the above
Answer. 4. 315°
Question 34. Flag pole on the earth is an example for …… lines.
- perpendicular
- parallel
- concurrent
- intersecting
Answer. 1. perpendicular
Question 35. How many common points that parallel lines have
- 0
- 1
- 2
- Infinite
Answer. 1. 0
Observe the following figure and answer the questions (36 – 37)
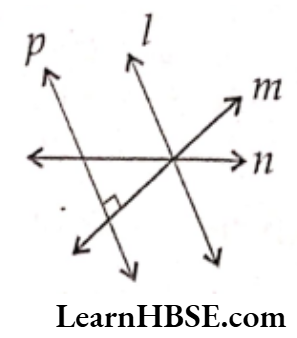
Question 36. Identify the perpendicular lines.
- l, m, n
- p, m
- p, n
- l, m
Answer. 2. p, m
Question 37. Identify the intersecting lines
- p, l
- l, m, n
- p, n and p, m
- None
Answer. 3. p, l
Question 38. The closed figure formed by more line segments is called …..
- square
- polygon
- triangle
- circle
Answer. 2. polygon
Question 39. We denote line AB as
- \(\overrightarrow{\mathrm{AB}}\)
- \(\overline{\mathrm{AB}}\)
- \(\overleftrightarrow{\mathrm{AB}}\)
- \(\overparen{\mathrm{AB}}\)
Answer. 3. \(\overleftrightarrow{\mathrm{AB}}\)
Question 40. The word ‘Geo means ……
- Geometry
- Geogre
- Earth
- Metron
Answer. 3. Earth
Question 41. A point determines a ……….
- location
- line
- object
- none
Answer. 1. location
Question 42. Two points determine a …..
- circle
- line
- triangle
- sector
Answer. 2. line
Question 43. If two lines l1 and l2 are parallel, then we represent this with …..
- l1,l2
- l1 ∥ l2
- l1/l2
- l2 ∥ l1
Answer. 2. l1 ∥ l2
Question 44. A …… is a portion of line.
- circle
- point
- triangle
- ray
Answer. 4. ray
Question 45. The line segments forming a polygon are called its …….
- vertex
- circle
- interior
- side
Answer. 1. vertex
Question 46. The two rays forming the angle are called ………. of the angle.
- segment
- common
- vertex
- arms
Answer. 4. arms
Question 47. The three sided polygon is called …..
- quadrilateral
- line segment
- side
- triangle
Answer. 4. triangle
Haryana Board Class 6 Maths Solutions For Chapter 4 Basic Geometrical Angles Fill in the blanks:
Question 48. 72° is a measure of ……….. angle
Answer. acute
Question 49. A straight angle measures……….
Answer. 180°
Question 50. Your 6th class mathematics text book corner will be taken as a measure of ………
Answer. 90°
Question 51. Half of complete angle. ……………
Answer. 180°
Question 52. Symbolic form of “The line I is parallel to the line m”……….
Answer. 1 || m
Question 53. The angle shown in the figure represents …… angle

Answer. reflex
Question 54. In the figure x° = …………
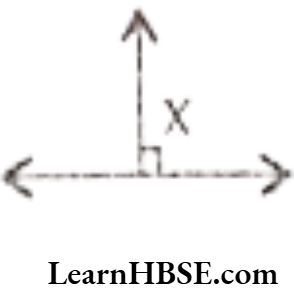
Answer. 90°
Question 55. The union of two rays having same initial point is called …………..
Answer. angle
Question 56. Ray is a part of line (T/F)
Answer. True
Question 57. In the figure p || q, r is a transversal then x° = …………
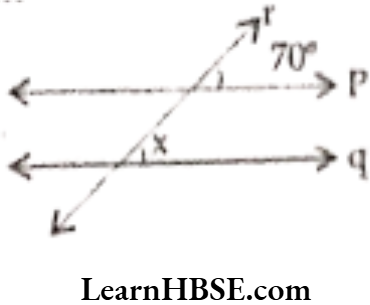
Answer. 70°
Question 58………………………… is one that does not cross itself.
Answer. simple curve
Question 59. ……….is the union of two rays with a common point.
Answer. Angle
Question 60. A triangle with its boundary and its interior is called the ………..
Answer. Triangle region
Question 61. Number of end points of a line segment ……….
Answer. 2
Question 62.
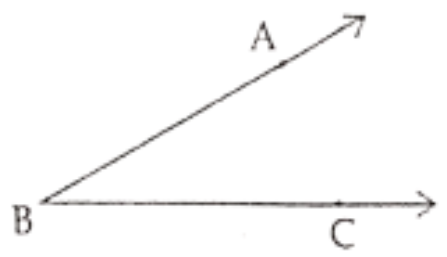
Vertex of this angle ………….
Answer. B
Question 63.
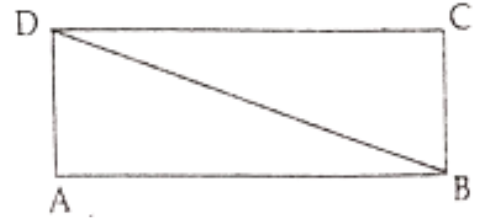
Number of closed figures in the adjoining diagram……
Answer. 3
Question 64. Mathematical form of a line segment PQ is.
Answer. PQ
Question 65. How we denote triangle ABC?..
Answer. ΔΑΒC
Question 66. Parallel lines never
Answer. Intersect
Question 67. If two lines \(\overleftrightarrow{\mathrm{AB}}\) and \(\overleftrightarrow{\mathrm{CD}}\) are parallel, we write.
Answer. AB ||CD
Question 68. In a closed curve there are……………………… disjoint parts.
Answer. 3
Question 69. The interior of a curve together with its boundary is called …..
Answer. region
Question 70. A polygon with least number of sides is ……..
Answer. triangle
