Theory Of Evolution By Natural Selection
Question 1. The pioneers in the field of ‘Organic evolution’ are:
- Darwin, Hugo de Vries, Lamarck, Huxley
- Karl Landsteiner, Hugo de Vries, Malthus, Darwin
- Lamarck, Karl Landsteiner, Malthus, De Vries
- Darwin, Lamarck, Karl Landsteiner, De Vries.
Answer: 2. Karl Landsteiner, Hugo de Vries, Malthus, Darwin
Question 2. Fore-coming generations are less adaptive than these parental generations due to:
- Natural selection
- Mutation
- Genetic drift
- Adaptation
Answer: 2. Mutation
Question 3. Darwin’s theory of pangenesis shows similarity with the theory of inheritance of acquired characters, then what shall be correct according to it?
- Useful organs become strong and developed while useless organs become extinct, these organs help in the struggle for survival
- The size of organs increases with ageing
- The development of organs is due to willpower
- There should be some physical basis for inheritance.
Answer: 4. There should be some physical basis for inheritance.
evolution questions
Question 4. The frequency of an allele in an isolated population may change due to:
- Genetic drift
- Gene flow
- Mutation
- Natural selection.
Answer: 1. Genetic drift
Question 5. In Lederberg’s replica plating experiment what shall be first used to obtain streptomycin-resistant bacteria strain?
- Minimal medium and streptomycin
- Complete medium and streptomycin
- Only minimal medium
- Only a complete medium.
Answer: 2. Complete medium and streptomycin
Theory Of Evolution By Natural Selection Class 12 HBSE
Question 6. Industrial melanism is an example of:
- Defensive adaptation of skin against UV radiation
- Drug resistance
- Darkening of skin due to smoke from industries
- Protective resemblance with the surroundings.
Answer: 4. Protective resemblance with the surroundings.
Question 7. Which one of the following describes correctly the homologous structure?
- Organs appear only in the embryonic stage and disappear later in adulthood.
- Organs with anatomical similarities but performing different functions
- Organs with anatomical dissimilarities but performing the same function
- Organs that have no function now but have an important function in the ancestor.
Answer: 4. Organs that have no function now but have an important function in the ancestor.
Question 8. Darwin in his “Natural Selection Theory” did not believe in any role of which one of the following in organic evolution?
- Discontinuous variations
- Parasites and predators as natural enemies
- Survival of fittest
- Struggle for existence.
Answer: 1. Discontinuous variations
Question 9. Unit of Natural selection is:
- Individual
- Family
- Species
- Population.
Answer: 1. Individual
Darwin’S Theory Of Natural Selection Explained
Question 10. Mule is a product of:
- Breeding
- Mutation
- Intraspecific hybridisation
- Interspecific hybridisation.
Answer: 4. Interspecific hybridisation.
questions about evolution
Question 11. The natural selection really means:
- Struggle for existence
- Differential reproduction
- Survival of the fittest
- Elimination of the unfit.
Answer: 3. Survival of the fittest
Question 12. According to the modern synthetic theory of evolution, organic evolution depends upon:
- Mutation and Natural selection
- Genetic recombination and Natural selection
- Mutation, reproductive isolation and Natural selection
- All of the above factors.
Answer: 4. All of the above factors.
Question 13. The most likely reason for the development of resistance against pesticides in insects damaging a crop is:
- Directed mutation
- Acquired heritable changes
- Random mutations
- Genetic recombination.
Answer: 3. Random mutations
Industrial Melanism Example In Evolution Class 12 HBSE
Question 14. Geographic and reproductive isolation brings about:
- Over-production
- Extinction
- Speciation
- Competition.
Answer: 3. Speciation
Question 15. The term species was coined by:
- Linnaeus
- John Ray
- Aristotle
- Engler.
Answer: 4. Engler.
Question 16. Which of the following is called the Swell-Wright effect?
- Gene pool
- Gene flow
- Genetic drift
- Isolation.
Answer: 3. Genetic drift
Question 17. de Vries gave his mutation theory on organic evolution while working on:
- Althea rosea
- Drosophila melanogaster
- Oenothera lamarckiana
- Pisum sativum.
Answer: 3. Oenothera lamarckiana
Question 18. One of the following phenomena supports Darwin’s concept of natural selection in organic evolution. It is:
- Development of transgenic animals
- Production of ‘dolly’ the sheep by cloning
- Prevalence of pesticide-resistant insects
- Development of organs from ‘stem cells’ for organ transplantation
Answer: 3. Prevalence of pesticide-resistant insects
Evidences Of Natural Selection Class 12 Biology
Question 19. The phenomenon of industrial melanism demonstrates:
- Natural selection
- Induced mutation
- Geographical isolation
- Reproductive isolation.
Answer: 1. Natural selection
evolution notes class 12
Question 20. Which of the following evidence does not favour the Lamarckian concept of inheritance of acquired characters?
- Absence of limbs in snakes
- Presence of webbed toes in aquatic birds
- Lack of pigment in cave-dwelling animals
- Melanization in peppered moth in industrial areas.
Answer: 4. Melanization in peppered moths in industrial areas.
Question 21. Survival of the fittest was given by:
- Darwin
- Lamarck
- Weismann
- Herbert Spencer.
Answer: 4. Herbert Spencer.
Question 22. Using imprints from a plate with a complete medium and carrying bacterial colonies, you can select streptomycin-resistant mutants and prove that such mutations do not originate as adaptation. These imprints need to be used:
- Only on plates with streptomycin
- On plates with minimal medium
- Only on plates without streptomycin
- On plates with and without streptomycin.
Answer: 1. Only on plates with streptomycin
Question 23. Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium is known to be affected by gene flow genetic drift, mutation, genetic remobination and:
- Evolution
- Limiting factors
- Natural selection
- Saltation
- Overproduction.
Answer: 3. Saltation
Survival Of The Fittest Theory Class 12 HBSE
Question 24. At a particular locus, the frequency of ‘A’ allele is 0.6 and that of ‘a’ is 0.4. What would be the frequency of heterozygotes in a random mating population at equilibrium?
- 0.16
- 0.48
- 0.36
- 0.24.
Answer: 2. 0.48
Question 25. In a random mating population in equilibrium, which of the following brings about a change in gene frequency in a non-directional manner?
- Mutations
- Random drift
- Selection
- Migration.
Answer: 2. Random drift
Question 26. The biogenetic law of Haeckel is:
- Omnis vivum e vivum
- Omnis cellula e cellula
- Ontogeny repeats phylogeny
- Phylogeny repeats ontogeny.
Answer: 3. Ontogeny repeats phylogeny
Question 27. Which of the following statements is correct?
- Genetic variability provides raw material for the operation of natural selection and reproductive isolation
- Genetic variability is produced by somatic mutation
- Somatic mutations are inherited
- None of the above.
Answer: 1. Genetic variability provides the raw material for the operation of natural selection and reproductive isolation
Question 28. The objections to Darwin’s theory of natural selection is/are:
- No differentiation between somatic and germinal variation
- It fails to explain the role of discontinuous variation
- It fails to explain the possible reason behind over-speciation
- All of the above.
Answer: 4. It fails to explain the possible reason behind over-speciation
Darwin’S Finches And Adaptive Radiation Class 12 HBSE
Question 29. Evolutionary history of an organism is known as:
- Phylogeny
- Ancestry
- Paleontology
- Ontogeny.
Answer: 1. Phylogeny
evolution short notes class 12
Question 30. Which of the following disproved experimentally the concept of inheritance of acquired characters?
- Lamarck
- Weismann
- Darwin
- Oparin.
Answer: 2. Weismann
Question 31. The Hardy-Weinberg law of equilibrium was based on the following:
- Random mating, selection, gene flow
- Random mating, genetic drift, mutation
- Non-random mating, mutation, gene flow
- Random mating, no mutation, no gene flow and no genetic drift.
Answer: 4. Random mating, no mutation, no gene flow and no genetic drift.
Question 32. Peppered moth (Biston betularia) is an example of:
- Transient Polymorphism And Disruptive Selection
- Transient Polymorphism And Directional Selection
- Balanced Polymorphism And Disruptive Selection
- Balanced Polymorphism And Directional Selection
Answer: 2. Transient Polymorphism And Directional Selection
Question 33. Darwin’s finches are a good example of:
- Convergent evolution
- Adaptive radiation
- Connecting link
- Industrial melanism.
Answer: 1. Convergent evolution
Question 34. Micro-evolution can be best defined as the evolution:
- Below species level
- Below genus level
- Above genus level
- Origin of family.
Answer: 2. Below genus level
Difference Between Lamarckism And Darwinism
Question 35. Modern synthetic theory of evolution is not based on:
- Genetic mutation
- Recombination and natural selection
- Reproductive isolation
- None of the above.
Answer: 4. None of the above.
Question 36. The tendency of the population to remain in genetic equilibrium may be disturbed by:
- Lack of migration
- Lack of mutations
- Lack of random mating
- Random mating
Answer: 3. Lack of random mating
Question 37. Industrial melanism as observed in peppered moths proves that:
- The melanic form of the moth has no selective advantage over the lighter form in an industrial area
- The lighter-form moth has no selective advantage either in polluted industrial areas or non-polluted area
- Melanism is a pollution-generated feature
- The true black melanic forms arise by a recurring random mutation.
Answer: 4. The true black melanic forms arise by a recurring random mutation.
Question 38. A high density of elephant population in an area can result in:
- Intraspecific competition
- Interspecific competition
- Predation on one another
- Mutualism.
Answer: 1. Intraspecific competition
Question 39. Adaptive radiation refers to
- Evolution of different species from a common ancestor
- Migration of members of a species to different geographical areas
- Power of adaptation in an individual to a variety of environments
- Adaptations due to Geographical isolation.
Answer: 4. Adaptations due to Geographical isolation.
Question 40. Select the correct statement from the following:
- Fitness is the end result of the ability to adapt and gets selected by nature
- All mammals except whales and camels have seven cervical vertebrae
- Mutations are random and directional
- Darwinian variations are small and directionless.
Answer: 1. Fitness is the end result of the ability to adapt and gets selected by nature
Natural Selection Vs Artificial Selection Class 12 HBSE
Question 41. One of the important consequences of geographical isolation is:
- Preventing Speciation
- Speciation through reproductive isolation
- Random creation of new species
- No change in the isolated fauna.
Answer: 2. Speciation through reproductive isolation
Question 42. Match the following:
The correct match is:
- a = 3, b = 2, c = 5, d = 4, e = 1
- a = 3, b = 4, c = 2, d = 5, e = 1
- a = 3, b = 4, c = 5, d = 2, e = 1
- a = 3. b = 5, c = 4, d = 1, e = 2.
Answer: 3. a = 3, b = 4, c = 5, d = 2, e = 1
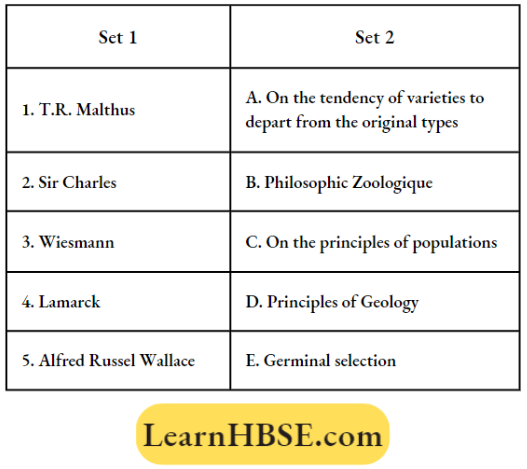
Question 43. Match the scientists and their contributions to the field of evolution.

- 1—D, 2—C, 3—A, 4—E, 5—B
- 1—D, 2—C, 3—E, 4—A, 5—F
- 1—D, 2—C, 3—E, 4—C, 5—A
- 1—B, 2—C, 3—A, 4—E, 5—B
- 1—C, 2—D, 3—A, 4—E, 5—B.
Answer: 1. 1—D, 2—C, 3—A, 4—E, 5—B
Natural Selection In Human Evolution Class 12 Biology
Question 44. Which one of the following scientist’s name is correctly matched with the theory put forth by him:
Answer: 4
Question 45. The process by which organisms with different evolutionary histories evolve similar phenotypic adaptations in response to a common environmental challenge is called:
- Convergent evolution
- Non-random evolution
- Adaptive radiation
- Natural selection
Answer: 1. Convergent evolution
Question 46. Variation in gene frequencies within populations can occur by chance rather than by natural selection. This is referred to as:
- Genetic drift
- Random mating
- Genetic load
- Genetic flow
Answer: 1. Genetic drift
Genetic Variation And Natural Selection Class 12 HBSE
Question 47. According to Darwin. The organic evolution is due to:
- Interspecific competition
- Competition within closely related species
- Reduced feeding efficiency in one species due to the presence of interfering species
- Intraspecific competition
Answer: 4. Intraspecific competition
