Question 1. Two non-allelic genes produce the new phenotype when present together but fail to do so independently, then it is called:
- Epistasis
- Polygene
- Non-complementary gene
- Complementary gene.
Answer: 4. Complementary gene
Question 2. Two individuals with similar external appearance but different genetic make up have the similar:
- Genotype
- Phenotype
- Hctcrozygotc
- Homozygote.
Answer: 2. Phenotype
Question 3. Two crosses between the same pair of genotypes or phenotypes in which the sources of the gametes arc reversed in one cross, is known as:
- Test cross
- Reciprocal cross
- Dihybrid cross
- Reverse cross.
Answer: 2. Reciprocal cross
mcq on principles of inheritance and variation
Question 4. The genes controlling the seven pea characters studied by Mendel are now known to be located on how many different chromosomes?
- Seven
- Six
- Five
- Four
Answer: 4. Four
mcq on principles of inheritance and variation
Question 5. Which one of the following traits of garden pea studied by Mendel was a recessive feature?
- Round seed shape
- Axial flower position
- Green seed colour
- Green pod colour
Answer: 3. Green seed colour
Question 6. When a cluster of genes shows linkage behaviour they :
- Induce cell division
- Do not show a chromosome map,
- Show recombination during meiosis
- Do not show independent assortment.
Answer: 4. Do not show independent assortment
HBSE Class 12 Biology Heredity And Variation Notes
Question 7. Alleles represent :
- Different forms of a gene
- Same loci on homologous chromosomes
- Two or more forms
- All the above
Answer: 4. All the above
inheritance and variation mcq
Question 8. If a cross between two plants gives 50% tall and 50% dwarf progeny, then the parent’s genotype is:
- Tt x Tt
- Tt x tt
- TT x tt
- TT x Tt.
Answer: 2. Tt x tt
Question 9. How many different types of gametes can be formed by F, progeny, resulting from the cross AABBCC × aabbcc?
- 3
- 8
- 27
- 64.
Answer: 2. 8
Question 10. A person with blood group A has :
- Antigen A and antibody b
- Antigen B and antibody a
- Antigen A and antibody B
- No antibody and no antigen.
Answer: 1. Antigen A and antibody b
Question 11. Self-fertilising trihybrid plants form :
- Eight different gametes and 64 different zygotes
- Four different gametes and sixteen different zygotes
- Eight different gametes and sixteen different zygotes
- Eight different gametes and thirty-two different zygotes.
Answer: 1. Eight different gametes and 64 different zygotes
Mendelian Genetics Class 12 HBSE Important Questions
Question 12. When a tall and red flowered individual is crossed with a dwarf and white flowered individual, the phenotype of the progeny will be :
- Homozygous tall and red
- Heterozygous tall and red
- Homozygous tall and white
- Homozygous dwarf and white
Answer: 2. Heterozygous tall and red
Question 13. Genetic counsellors can identify heterozygous individuals by
- Height of individuals
- Colour of individuals
- Screening procedures
- All of these
Answer: 4. All of these
Question 14. If a homozygous red-flowered plant is crossed with a homozygous white-flowered plant, the offspring would be :
- All red flowered
- Half red flowered
- Half white flowered
- All white flowered.
Answer: 1. All red flowered
biology objective question in english
Question 15. Which Mendelian idea is depicted by a cross in which the F, generation resembles both the parents?
- Law of dominance
- Co-dominance
- Inheritance of one gene
- Incomplete dominance
Answer: 3. Inheritance of one gene
Question 16. Given below is a pedigree chart of a family with five children. It shows the inheritance of attached earlobes as opposed to the free ones. The squares represent the male individuals and circles the female individuals. Which one of the following conclusions drawn is correct?
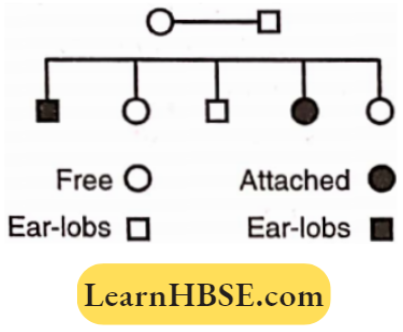
- The parents are homozygous recessive
- The trait is Y-linked
- The parents are homozygous dominant
- The parents are heterozygous.
Answer: 4. The parents are heterozygous
inheritance and variation mcq
Question 17. Which of the following terms represents a pair of contrasting characters?
- Allele
- Phenotype
- Homozygous
- Heterozygous.
Answer: 1. Allele
Question 18. Following are the statements, which are either true or false. Examine them and find out the incorrect answer. Mendel had selected Pisum sativum (garden pea) as his experi¬ mental tool because :
- The hybrids remain infertile
- The plants can be self-fertilized
- These small herbaceous plants can be easily cultivated
- There are several pairs of contrasting characters of allotrophic traits.
Answer: 4. There are several pairs of contrasting characters of allotrophic traits
Laws Of Inheritance Class 12 HBSE Biology
Question 19. Cross between a homozygous black rough (BBRR) guinea pig and a homozygous white smooth guinea pig (bbrr) produced F, progeny all black and rough. Assuming that the black colour is dominant over white skin rough skin is dominant over smooth skin and the two genes involved are present on different chromosomes. The percentage of F2 individuals who are heterozygous for both gene pairs would be :
- 25%
- 50%
- 75%
- 35%.
Answer: 1. 25%
Question 20. The genetic ratio of 9:3:3:1 is due to:
- Segregation of characters
- Crossing over of chromosomes
- Independent assortment of genes
- Homologous pairing between chromosomes
Answer: 3. Independent assortment of genes
Question 21. When a cross is made between two species of the same genus, then the cross is known as :
- Intraspecific hybridization
- Interspecific hybridization
- Intergeneric hybridization
- Intervarietal hybridization.
Answer: 2. Interspecific hybridization
Question 22. Pure tall plants are crossed with pure dwarf plants. In the F1 generation, all plants were tall. All the plants of the F1 generation were selfed and the ratio of tall to dwarf plants obtained was 3:1. This is called :
- Dominance
- Inheritance
- Codominance
- Heredity
Answer: 1. Dominance
Genetic Disorders Class 12 HBSE Biology
Question 23. Epistasis is the:
- One pair of genes can completely mask the expression of another pair of genes
- One pair of genes independently controls a particular phenotype
- One pair of genes enhances the phenotype expression of another pair of gene
- Many genes collectively control a particular phenotype.
Answer: 1. One pair of genes can completely mask the expression of another pair of genes
Question 24. When one gene hides the effect of another gene, the interaction factor is known as:
- Epistatic factor
- Duplicate factor
- Complementary factor
- Supplementary factor
Answer: 1. Epistatic factor
Question 25. A genetically dwarf plant made tall by use of Gibberellin was crossed with a plant purely tall. Then the progenies would be :
- All dwarf
- All tall
- 50% tall and 50% dwarf
- May be tall or dwarf
Answer: 2. All tall
biology objective question in english
Question 26. Which of the following is considered a recessive character of Mendel?
- Round seed
- Wrinkled seed
- Axial flower
- Green pod.
Answer: 2. Wrinkled seed
Question 27. Which of the following characters chosen by Mendel are recessive?
- Green pod colour dwarf plant
- Tall plant and axial flowers
- Yellow pod colour and wrinkled seeds
- Dwarf plant and round seeds.
Answer: 3. Yellow pod colour and wrinkled seeds
Difference Between Dominance And Co-Dominance Class 12
Question 28. Which is the functional unit of inheritance?
- Gene
- Cistron
- Intron
- Chromosome
Answer: 1. Gene
Question 29. Heterosis requires :
- Crossing
- Selection
- Transformation
- Mutations
Answer: 1. Crossing
Question 30. The phenotypic ratio obtained in quantitative inheritance of a dihybrid cross is :
- 1: 2: 1
- 1: 4 : 6: 4: 1
- 1 :6: 15:20: 15:6: 1
- 9:3:3: 1.
Answer: 2. 1: 4 : 6: 4: 1
Question 31. Mating between two individuals differing in genotype to produce genetic variation is called :
- Mutation
- Introduction
- Hybridization
- Domestication.
Answer: 3. Hybridization
Question 32. Grain colour in wheat is determined by three pairs of polygenes. Following is the cross AABBCC (dark colour) and aabbcc (light colour), in the F2 generation what proportion of the progeny is likely to resemble either parent?
- None
- Half
- One third
- Less than 5 per cent.
Answer: 4. less than 5 per cent.
Question 33. The primary source of allelic variation is :
- Mutation
- Polyploidy
- Recombination
- Independent assortment
Answer: 3. Recombination
Chromosomal Mutations And Genetic Variation Class 12 HBSE
Question 34. To find out the different types of gametes produced by a pea plant having the genotype AaBb, it should be crossed to a plant with the genotype :
- aaBB
- AaBb
- AABB
- Aabb
Answer: 4. Aabb
Question 35. At a particular locus frequency of the ‘A’ allele is 0.6 that of the ‘A’ allele is 0.6 and that of ‘a’ is 0.4. What would be the frequency of heterozygotes in a random mating population at equilibrium?
- 0.16
- 0.48
- 0.36
- 0.24.
Answer: 2. 0.48
Question 36. Test cross involves :
- Crossing the F1 hybrid with a double recessive genotype
- Crossing between two genotypes with the dominant trait
- Crossing between two genotypes with a recessive trait
- Crossing between two F1 hybrids.
Answer: 1. Crossing the F1 hybrid with a double recessive genotype
Question 37. In Mendel’s experiments with the garden pea, round seed shape (RR) was dominant over wrinkled seeds (rr), and yellow cotyledon (YY) was dominant over green cotyledon (yy). What are the expected phenotypes in the F2 generation of the cross RRYY × rryy
- Only wrinkled seeds with green cotyledons
- Round seeds with yellow cotyledons, and wrinkled seeds with yellow cotyledons
- Only wrinkled seeds with yellow cotyledons
- Only round seeds with green cotyledons.
Answer: 2. Round seeds with yellow cotyledons, and wrinkled seeds with yellow cotyledons
Question 38. How many different kinds of gametes will be produced by a plant having the genotype AABbCC?
- Nine
- Two
- Six
- Three.
Answer: 2. Two
Question 39. In maize, hybrid vigour is exploited by :
- Harvesting seeds from the most productive plants
- Inducing mutations
- Bombarding the protoplast with DNA
- Crossing of two inbred parental lines.
Answer: 4. Crossing of two inbred parental lines
Question 40. The phenotype of an organism is the result of:
- Environmental changes and sexual dimorphism
- Genotype and environment interactions
- Mutations and linkages
- Cytoplasmic effects and nutrition.
Answer: 2. Genotype and environment interactions
DNA Replication And Transcription Class 12 HBSE
Question 41. Which one of the following is an example of polygenic inheritance?
- Pod shape in garden pea
- Skin colour in humans
- Flower colour in Mirabilis jalapa
- Production of male honey bee
Answer: 2. Skin colour in humans
Question 42. A common test to find the genotype of a hybrid is by :
- Crossing of one F2 progeny with a female parent
- Studying the sexual behaviour of F2 progenies
- Crossing of one F1 progeny with a male parent
- Crossing of one F2 progeny with a male parent.
Answer: 2. Studying the sexual behaviour of F2 progenies
Question 43. Two genes R and Y are located very close on the chromosomal linkage map of a maize plant. When RRYY and rryy genotypes are hybridized, the F2 segregation will show :
- Segregation in the expected 9 : 3 : 3: 1 ratio.
- Segregation in 3: 1 ratio.
- A higher number of the parental types.
- Highernumberoftherecombinant types.
Answer: 2. Segregation in 3: 1 ratio
Question 44. Inheritance of skin colour in humans is an example of:
- Point mutation
- Polygenic inheritance
- Codominance
- Chromosomal aberration.
Answer: 2. Polygenic inheritance
Question 45. In pea plants, yellow seeds are dominant to green. If a heterozygous yellow-seeded plant is crossed with a green-seeded plant, what ratio of yellow and green-seeded plants would you expect in Ff generation?
- 9: 1
- 1 : 3
- 3: 1
- 50:50
Answer: 4. 50:50
Question 46. A human male produces sperms with the genotypes AB, Ab, aB, and ab about two diallelic characters in equal proportions. What is the corresponding genotype of this person?
- AaBB
- AABb
- AABB
- AaBb
Answer: 4. AaBb
Question 47. When a cross is conducted between a black-feathered hen and a white-feathered cock, blue-feathered fowls are formed. When these fowls are allowed for interbreeding, in F, generation, there are 20 blue fowls. What would be the number of black and white fowls?
- Black 10, white 10
- Black 10, white 20
- Black 20, white 10
- Black 20, white 20
Answer: 1. Black 10, white 10
Question 48. Grain colour in wheat is determined by three pairs of polygenes. Following the cross AABBCC (dark colour) x aabbcc light colour), in the F2 generation what proportion of the progeny is likely to resemble either parent?
- Half
- Less than 5%
- One third
- None of the above
Answer: 3. One third
Question 49. Match the genetic phenomena with the respective ratios
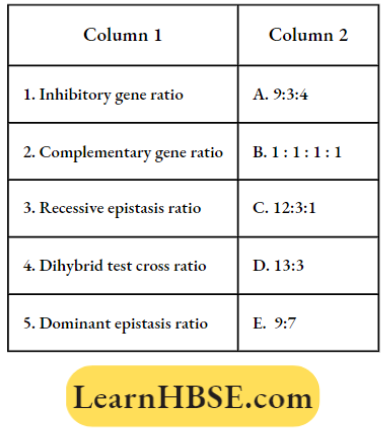
- 1=E,2=D,3=C,4=B,5=A
- 1=A,2=B,3=D,4=C,5=E
- 1=D,2=E,3=A,4=,5=C
- 1=E,2=D,3=A,4=B,5=C,
Answer: 3. 1=D,2=E,3=A,4=,5=C
Question 50. A pedigree analysis ![]() represents
represents
- Unrelated mating
- Consanguinous mating
- Affected parents
- Siblings
- Non-identical twins.
Answer: 2. Consanguinous mating
Question 51. Indicate, the inheritance of which of the following is controlled by multiple alleles:
- Colour blindness
- Sickle cell anaemia
- Blood group
- Phenylketonuria
Answer: 3. Blood group
Question 52. Which of the following is related to haemophilia?
- A recessive gene responsible for present in the X chromosome
- A dominant gene responsible for present in the autosomal chromosome
- A responsible dominant gene present in the Y chromosome
- A responsible dominant gene presents the autosomal chromosome
Answer: 1. A recessive gene responsible for present in the X chromosome
Question 53. F2 generation in a Mendelian cross showed that both genotypic and phenotypic ratios are the same as 1 : 2: 1. It represents a case of:
- Dihybrid cross
- Monohybrid cross with complete dominance
- Monohybrid cross with incomplete dominance
- Co-dominance
Answer: 3. Monohybrid cross with incomplete dominance
Question 54. A normal-visioned man whose father was colour-blind marries a woman whose father was also colour-blind. They have their first child as a daughter. What are the chances that this child would be colour-blind?
- Zero per cent
- 25%
- 50%
- 100%.
Answer: 1. zero per cent
Examples Of Polygenic Inheritance Class 12 Biology
Question 55. A man having the genotype EEFfGgHH can produce P number of genetically different sperms and a woman of genotype liU.MmNn can generate (J number of genetically different eggs. Determine the values of P and Q.
- P = 4, Q = 4
- P = 4. Q = 8
- P = 8. Q = 4
- P = 8. Q = 8.
Answer: 2. P = 4. Q = 8
Question 56. In an organism, a tall phenotype is dominant over a recessive dwarf phenotype, and the alleles are designated as T and t, respectively. Upon crossing two different individuals, a total of 250 offspring were obtained, out of which 124 displayed tall phenotype and the rest were dwarf. Thus, the genotype of the parents was
- TTxTT
- TT x tt
- Tt x Tt
- Tt x ti.
Answer: 4. Tt x ti
Question 57. When yellow round heterozygous pea plants are self-fertilized, the frequency of occurrence of the RrYY genotype among the offspring is
- 9/16
- 3/16
- 2/16
- 1/16
Answer: 3. 2/16
Question 58. ABO blood groups are determined by three different alleles. How many genotypes and phenotypes are possible?
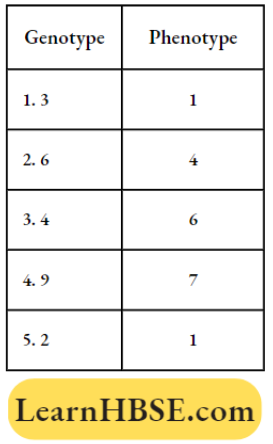
Answer: 2
Question 59. If two persons with ‘An AB’ blood group marry and have a sufficiently large number of children, these children could be classified as ‘A’ blood group: ‘AB’ blood group: ‘B’ blood group in a 1:2:1 ratio. The modern technique of protein electrophoresis reveals the presence of both ‘A’ and ‘B’ type proteins in ‘AB’ blood group individuals. This is an example of:
- Incomplete dominance
- Partial dominance
- Complete dominance
- Codominance
Answer: 4. Codominance
Question 60. The incorrect statement about Haemophilia is :
- It is a recessive disease
- It is a dominant disease
- A single protein involved in the clotting of blood is affected
- It is a sex-linked disease
Answer: 2. It is a dominant disease
