Plant Anatomy Question From Competitive Examinations
Question 1. In floating leaved plants, stomata occur on:
- Lower surface
- Upper surface
- Both sides
- Absent.
Answer: 2. Upper surface
plant anatomy mcqs
Question 2. Vascular bundles occur in a ring in:
- Monocot stem
- Leaf
- Root
- Dicot stems.
Answer: 4. Dicot stem.
Question 3. A.T.S. of the stem is stained first with safranin and then fast green. What would be the colour of the phloem?
- Red
- Green
- Orange
- Purple.
Answer: 2. Green
anatomy of flowering plants
Question 4. Passage cells occur in:
- Epidermis
- Cortex
- Endodermis
- Pericycle.
Answer: 3. Endodermis
Question 5. Casparian strips occur in:
- Longitudinal and radial walls of epidermal cells
- Longitudinal walls of xylem
- All walls of endodermis
- Radial walls of endodermis.
Answer: 4. Radial walls of endodermis.
morphology of flowering plants mcq class 11
Question 6. Loading of phloem is related to:
- Increase of sugar in phloem
- Elongation of phloem cell
- Separation of phloem parenchyma
- Strengthening of phloem fibre.
Answer: 1. Increase of sugar in phloem
Question 7. Roots of which plant contain a red pigment which has an affinity for oxygen:
- Canon
- Soyabean
- Mustard
- Radish.
Answer: 2. Soyabean
HBSE Class 11 Biology Plant Anatomy
Question 8. In the monocot root, we observe:
- Conjoint, collateral, closed, polyarch vascular bundle
- Exodermis, end arch, and tetrarch closed bundles
- Suberized exodermis, Casparian strip, passage cells cambium
- Suberized exodermis, polyarch xylem, pith.
Answer: 4. Suberized exodermis, polyarch xylem, pith.
Question 9. Dead cells that serve mechanical functions are:
- Sclerenchyma
- Companion cells
- Collenchyma
- Wood parenchyma.
Answer: 1. Sclerenchyma
Question 10. Annual rings are found in plants belonging to:
- Arabic region
- Temperate areas
- Tropics
- Near sea beaches.
Answer: 2. Temperate areas
Question 11. ‘Histogen theory’ was proposed by:
- Hanstein
- Eamu
- Esmam
- Schmidt.
Answer: 1. Hanstein
Question 12. In the diagram of the T.S. of Helianthus stem given below, certain parts have been indicated by alphabets; choose the answer in which these alphabets have been correctly matched with the parts which they
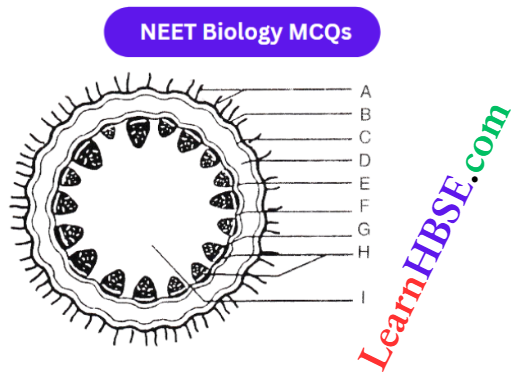
- A = Epidermis, B = Epidermal hairs
C = Parenchyma, D = Starch sheath
E = Hypodermis (collenchyma),
F = Vascular bundle
G = Bundle cap, H = Medulla or pith
I = Pith - A = Epidermis hairs, B = Epidermis
C = Hypodermis (Collenchyma),
D = Parenchyma
E = Starch sheath, F = Bundle cap
G = Vascular bundle, H = Medullary rays.
I = Medullary rays - A = Epidermal hairs, B = Epidermis
C = Hypodermis (collenchyma),
D = Starch sheath, E = Parenchyrna,
F = Vascular bundle, G = Bundle cap,
H = Medulla or pith, I = Medullary rays. - A = Epidermal hairs, B = Epidermis
C = Parenchyma, D = Hypodermis (Collenchyrnil)
E = starch sheath, F = Vascular bundle
G = Bundle cap, H = Medulla or pith
I = Medullary rays - C = Hypodermis (Collenchyma),
D = Parenchyma
E = Starch sheath, F = Bundle cap
G = Vascular bundle, H = Medullary rays.
I = Medullary rays
Answer: 2. A = Epidermis hairs, B = Epidermis
Plant Anatomy Class 11 Notes
Question 13. In the diagram of the cross-section of the vascular bundle of the monocot stem given aside, different parts have been indicated by alphabets; choose the answer in which these alphabets have been correctly matched with the parts which they indicate
morphology of flowering plants class 11 mcq
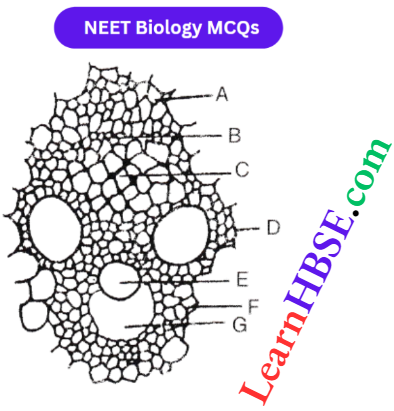
- A = Bundle sheath, B = Broken phloem,
C = Metaphloem, D = Metaxylem,
E = Protoxylem, F = xylem parenchyma,
G = Lysigenous cavity - A = Bundle cap, B = Metaphloem,
C = Protophloem, D = Protoxylem,
E = Metaxylefit, F = Lysigenous cavity,
G = Xylem parenchyma - A = Bundle sheath, B = Primary phloem,
C = Secondary phloem, D = Primary xylem,
E = secondary xylem, F = Xylem fibres,
G = Hydathode - A = Bundle cap, B = Metaxylem,
C = Metaphloem, D = Protoxylem,
E = Protophloem, F = Lysigenous cavity,
G = Xylem parenchyma.
Answer: 1. A = Bundle sheath, B = Broken phloem,
C = Metaphloem, D = Metaxylem,
E = Protoxylem, F = xylem parenchyma,
G = Lysigenous cavity
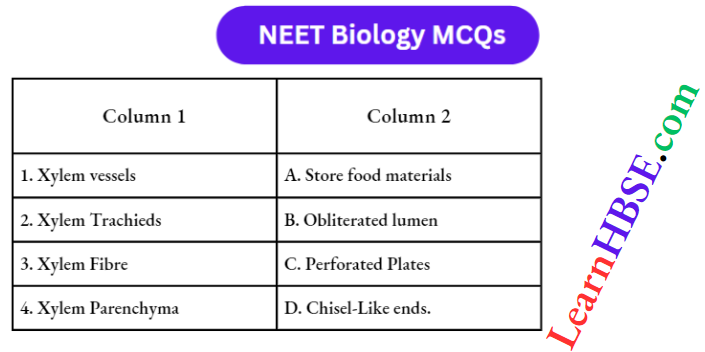
Question 14. Match the names of the structures listed under column-1 with the functions given under column 2. Choose the answer which gives the correct combination of the alphabet of the two columns:
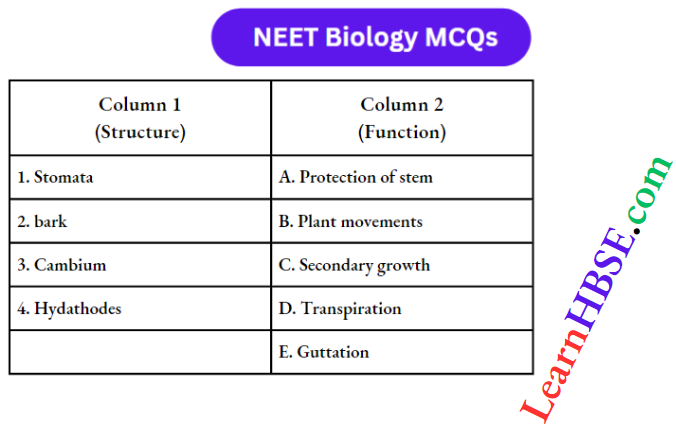
- 1=B, 2=D, 3=A, 4=C
- 1=D, 2=A, 3=C, 4=E
- 1=E, 2=C, 3=A, 4=D
- 1=A, 2=D, 3=t, 4=C.
Answer: 2. 1=D, 2=A, 3=C, 4=E
Anatomy of Flowering Plants Class 11
Question 15. Match the types of vascular bundles listed under Column 1 with examples given under Column 2; choose the answer which gives the correct combination of the alphabets of the two columns:
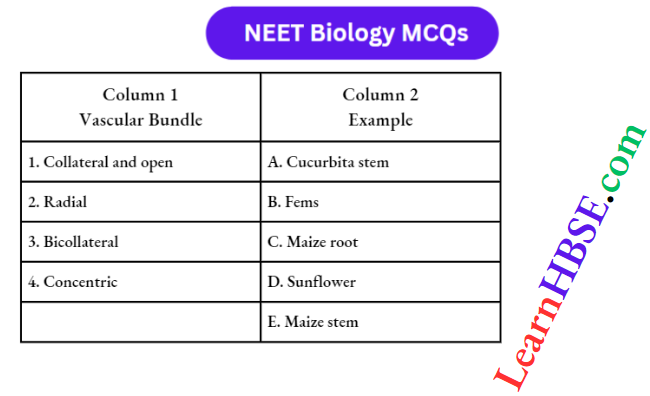
- 1=D, 2=C, 3=B, 4=A
- 1=D, 2=C, 3=A, 4=B
- 1=t, 2=D, 3=C, 4=A
- 1=D, 2=A, 3=C, 4=B
Answer: 1. 1=D, 2=C, 3=B, 4=A
Question 16. Terminal and axillary buds arise from:
- Apical meristem
- Parenchyma
- Lateral meristem
- Intercalary meristem.
Answer: 1. Apical meristem
Question 17. Intercalary meristem is located in:
- Latex
- Root
- Stem tip
- Petiole and internode.
Answer: 4. Petiole and internode.
Question 18. Which of the following is not a component:
- Vascular rays
- Medullary rays.
- Vessels
- Tracheids.
Answer: 2. Medullary rays.
Question 19. The primary cell wall is elastic due to the absence of:
- Suberin
- Culin
- Pectin
- Lignin.
Answer: 4. Lignin.
Types of Plant Tissues Class 11
Question 20. Vessels are found in:
- All angiosperms
- Most angiosperms, a few gymnosperms and pteridophytes.
- All angiosperms and a few gymnosperms
- Most angiosperms and a few gymnosperms.
Answer: 2. Most angiosperms, a few gymnosperms and pteridophytes.
Question 21. Four radial vascular bundles are formed in:
- Monocot root
- Dicot stem
- Dicot root
- Monocot stem.
Answer: 3. Dicot root
Question 22. Annual rings are formed basically due to:
- Marked variations in seasons
- Different kinds of development of phloem and xylem
- Uniform climate conditions
- Different kinds of phloem.
Answer: 1. Marked variations in seasons
Question 23. The commercial use fibres are obtained from:
- Interxylary fibres
- Xylem fibres
- Phloem fibres
- None of these.
Answer: 3. Phloem fibres
Question 24. Which one of the following tissues does not possess living protoplasm?
- Collenchyma
- Sclerenchyma
- Tracheids
- Parenchyma.
Answer: 2. Sclerenchyma
Question 25. The chief function of the sieve tube element is:
- To translocate the organic materials from source to sink
- To conduct minerals
- To conduct water from roots to leaves
- To help the plants in forming wood.
Answer: 1. To translocate the organic materials from source to sink
Question 26. Cambium activity is highest in:
- Spring
- Winter
- Autumn
- Rains.
Answer: 1. Spring
Difference Between Plant Anatomy and Morphology
Question 27. In the leaf, vascular bundles are found in
- Veins
- Palisade tissue
- Upper epidermis
- Lower epidermis
- Spongy mesophyll.
Answer: 1. Veins
Question 28. The quiescent centre in the root meristem series is a
- Site for storage of food which is utilized during maturation
- Reservoir of growth hormones
- Reserve for replenishment of damaged calls of the meristem
- Region for absorption of water.
Answer: 3. Reserve for replenishment of damaged calls of the meristem
Question 29. In a dicotyledonous stem, the sequence of tissues from the outside to the inside is:
- Phellem – Pericycle – Endodermis – phloem
- Phellem – Phloem – Endodermis – Pericycle
- Phellem – Endodermis – Pericycle – Phloem
- Pericycle – Phellem – Endodermis – Phloem.
Answer: 3. Phellem – Endodermis – Pericycle – Phloem
Question 30. Jute fibres deteriorate because they have:
- High cellulose
- Low cellulose
- High lignin
- Low lignin.
Answer: 3. High lignin
Question 31. Wood is:
- Primary xylem
- Secondary xylem
- Primary phloem
- Secondary phloem.
Answer: 2. Secondary xylem
Question 32. Cork cambium results in the formation of cork which becomes impermeable to water due to the accumulation of:
- Resins
- Suberin
- Lignins
- Tannins.
Answer: 2. Suberin
Question 33. Companion cells in plants are associated with:
- Vessels
- Sperms
- Guard cells
- Sieve elements.
Answer: 4. Sieve elements.
Question 34. In a plant organ which is covered by periderm and in which the stomata are absent, some gaseous exchange will take place through:
- Lenticels
- Trichomes
- Aerenchyma
- Pneumatophores
Answer: 1. Lenticels
Question 35. In a woody dicotyledonous tree, which of the following parts will mainly consist of primary tissues?
- Stem and root
- All parts
- Shoot tips and root tips
- Flowers, fruits and leaves.
Answer: 3. Shoot tips and root tips
Question 36. Which of the following statements is not true?
- Cork cambium is otherwise called phellogen
- Cork is otherwise called Phellem
- The secondary cortex is otherwise called the periderm
- The Cork cambium, cork and secondary cortex are collectively called Phelloderm
- 3 and 4 only
- 1 and 2 only
- 2 and 3 only
- 2 and 4 only
- 1 and 4 only.
Answer: 1. 3 and 4 only
Question 37. Bicollateral conjoint vascular bundles have
- Xylem and phloem, which are arranged alternately on different radii
- The xylem and phloem, are situated at the same radius and it has two groups of phloem along the two sides of the xylem (inside and outside)
- Xylem and phloem in the same radius but it has only one group phloem outside the xylem
- Phloem surrounds the xylem tissues xylem surrounds the Phloem tissues.
Answer: 2. The Xylem and phloem, are situated at the same radius and it has two groups of phloem along the two sides of the xylem (inside and outside)
Question 38. Math the following in column 1 with column 2 and choose the correct combination.
- 1-D, 2-C, 3-B, 4-A
- 1-C, 2-B, 3-A, 4-D
- 1-B, 2-A, 3-4, 4-C
- 1-A, 2-B, 3-C, 4-D
- 1-C, 2-D, 3-B, 4-A.
Answer: 5. 1-C, 2-D, 3-B, 4-A.
Question 39. Casparian thickenings are found in the cells of:
- Pericycle of the root
- Endodermis of the root
- Pericycle of the stem
- Endoermis of the stem.
Answer: 2. Endodermis of the root
Question 40. A portion of apical meristem that gives rise to xylem tissue is called:
- Protoxylem
- Metaxylem
- Procambium
- Tracheid
Answer: 3. Procambium
Question 41. For a critical study of secondary growth in plants, which one of the following pairs is suitable?
- Teak and pine
- Deodar and fern
- Wheat and maidenhair fern
- Sugarcane and sunflower.
Answer: 1. Teak and pine
Question 42. Passage cells are thin-walled cells found in:
- Phloem elements serve as entry points for substances for transport to other plant parts.
- Testa of seeds to enable the emergence of growing embryonic axis during seed germination.
- The central region of style through which the pollen tube grows towards the ovary.
- Endodermis of roots facilitating rapid transport of water from cortex to pericycle.
Answer: 4. Endodermis of roots facilitating rapid transport of water from cortex to pericycle.
Question 43. One of the characteristics of a sieve tube is:
- It is a part of phloem
- The function is the transport of inorganic solutes
- It is a dead cell
- A sieve plate is not present.
Answer: 1. It is a part of phloem
Question 44. In the following pairs where do you get lignin in both the elements?
- Tracking and collenchyma
- Sclerenchyma and sieve tube
- Sclerenchyma and trachea
- Parenchyma and endodermis.
Answer: 3. Sclerenchyma and trachea
Question 45. Which of the following statements is true?
- Uneven thickening of the cell wall is characteristic of sclerenchyma
- Periblem forms the cortex of the stem and the root
- Tracheids are the chief water-transporting elements in gymnosperms
- Companion cells are devoid of the nucleus at maturity
- The commercial cork is obtained from Quercus suber
- (1) and (4) only
- (2) and (3) only
- (3) and (4) only
- (1), (2) and (3) only.
- (2), (3) and(5).
Answer: 5. (2), (3) and(5).
Question 46. The waxy material deposited in the Casparian strip of the endodermis is:
- Pectin
- Suberin
- Cellulose
- Lignin
- Hemicellulose.
Answer: 2. Suberin
Question 47. The vascular cambial ring of a dicot stem is:
- Primary in origin
- Secondary in origin
- Embryonic in origin
- Tertiary in origin
- Partly primary and partly secondary in origin
Answer: 5. Partly primary and partly secondary in origin
Question 48. Consider the following statements:
- In a dicot root, the vascular bundles are collateral and endarch
- The innermost layer of the cortex in a dicot root is the endodermis
- In a dicot root, the phloem classes are separated from the xylem by parenchymatous cel1s that are known as the conjunctive tissue of these statements given above
- (1) is true, but (2) and (3) are false
- (2) is true, but (1) and (3) are false
- (1) is true, but (2) and (3) are false
- (3) is true, but (1) and (3) are false
- (3) is true, but (1) and (2) are false
Answer: 5. (3) is true, but (1) and (2) are false
Question 49. Ground tissue includes:
- Axe tissues external to endodermis
- All tissues except the epidermis and vascular bundles
- Epidermis and cortex
- All tissues are internal to the endodermis.
Answer: 2. All tissues except the epidermis and vascular bundles
Question 50. The cork cambium, cork and secondary cortex are collectively called:
- Phelloderm
- Phellogen
- Periderm
- Phellem
Answer: 3. Periderm
Question 51. The common bottle cork is a product of:
- Pheliogen
- Xylem
- Vascular cambium
- Dermatogen.
Answer: 1. Pheliogen
Question 52. Closed Vascular bundles lack:
- Conjunctive tissue
- Cambium
- Pith
- Ground tissue
Answer: 2. Cambium
Question 53. Water-containing cavities in vascular bundles are found in:
- Maize
- Cycas
- Pinus
- Sunflower.
Answer: 1. Maize
Question 54. Companion cells are closely associated with:
- Vessel elements
- Trichomes
- Guard cells
- Sieve elements.
Answer: 4. Sieve elements.
Question 55. Interfascicular cambium develops from the cells of:
- Xylem parenchyma
- Endodermis
- Pericycle
- Medullary rays.
Answer: 4. Medullary rays.
Question 56. The age of a tree can be estimated by:
- Biomass
- Number of annual rings
- Diameter of its heartwood
- Its height and girth
Answer: 2. Number of annual rings
