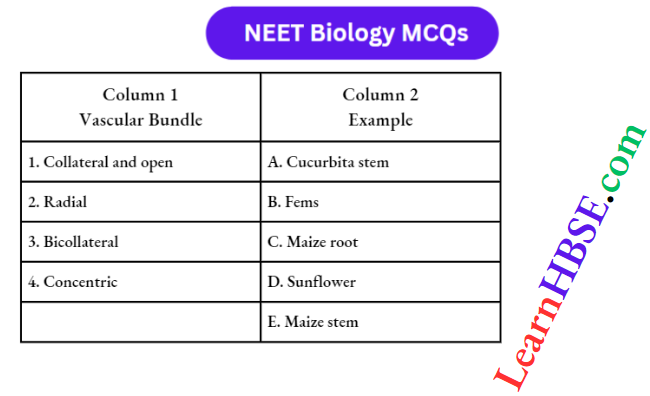
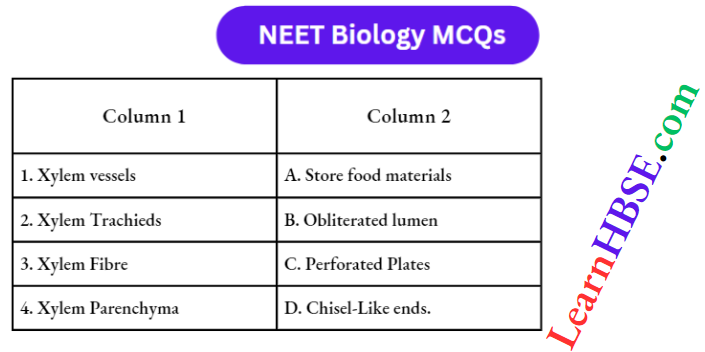
Question 1. The Nerve Fibres that conduct Impulses From The Peripheral To The Central Nervous System Are Called :
- Motor Nerve Fibres
- Mixed Nerve Fibres
- Afferent Nerve Fibres
- Efferent Nerve Fibres.
Answer: 3. Afferent Nerve Fibres
Question 2. The Nerve Fibres that carry Impulses From The Central Nervous System To The Muscles And Glands For Contraction And Secretion Are Called:
- Efferent Nerve Fibres
- Afferent Nerve Fibres
- Mixed Nerve Fibres
- Sensory Nerve Fibres.
Answer: 1. Efferent Nerve Fibres
nervous system questions
Question 3. When Sympathetic System Acts On A Particular Organ, Its Action Is :
- Stimulated
- Inhibited
- Transmitted
- Regulated.
Answer: 4. Regulated.

Question 4. The Simplest Form Of Nervous System That integrates rates of Body Activities Is Found In Cnidarians And Called :
- Nerve Trunk System
- Nerve Net System
- Ladder System
- Nerve Cord System.
Answer: 2. Nerve Net System
questions about nervous system
Question 5. Excitability And Conductivity Are The Outstanding Properties Of:
- Arteries
- Veins
- Neurons
- Nephrons.
Answer: 3. Neurons
Question 6. Dendrites Transmit The Impulses To :
- The Body Of Cell
- The Neurilemma
- The Myelin Sheath
- The Axon Only.
Answer: 1. The Body Of Cell
Question 7. Resting Potential Of Nerve Cells Is :
- -90 Mv
- -70-90 Mv
- -120 Mv
- -60 M V.
Answer: 2. -70-90 Mv
Question 8. Nerve Is:
- Group Of Nerve Fibres Bounded Together By Connective Tissue
- Group Of Nerve Fibres Bounded By A Membrane
- A Group Of Neuron Only
- None Of The Above.
Answer: 2. Group Of Nerve Fibres Bounded By A Membrane
questions about the nervous system
Question 9. Myelinated Fibres Are Nerve Fibres that are:
- Without Any Surrounding Sheath
- With A Surrounding Sheath
- Without Axon
- None Of The Above.
Answer: 2. With A Surrounding Sheath
Question 10. During Synaptic Transmission Of Nerve Impulse, Neurotransmitter (P) Is Released From Synaptic Vesicles By The Action Of Ions (Q). Choose The Correct P And Q.
- P = Acetylcholine, Q = Ca–+
- P = Acetylcholine Q = Na+
- P = Gaba, Q =Na+
- P = Cholinesterase, Q = Ca++.
Answer: 3. P = Gaba, Q =Na+
Question 11. The Transmission Of Nerve Impulse Is A :
- Mechanical Process
- Biological Process
- Electrochemical Process
- Physical Process.
Answer: 3. Electrochemical Process
Question 12. The Potential Difference’betwecn Inside And Outside Of A Neuron Before Excitation Is Known As :
- Resting Potential
- Action Potential
- Spike Potential
- Reaction Potential.
Answer: 1. Resting Potential
Question 13. What Is The Difference Between The Conduction Of Electricity Through An Electric wire And That Of Nerve Impulse Through A nerve fibre
- Nerves Are Living
- Electricity Provides A Shock
- Nerve Impulse Is Sell Generated On Stimulation And Propagated
- All The Above.
Answer: 3. Nerve Impulse Is Sell Generated On Stimulation And Propagated
central nervous system test
Question 14. When Nene Is Stimulated, It Is Polarized. DepolarizaTion Is Maintained By The Following Ion :
- Ca++
- Cl–
- Mg++
- Organic Compounds, K+ And Na+.
Answer: 4. Organic Compounds, K+ And Na+.
Question 15. During Resting Conditions The Membrane Of the Axon Is :
- Impermeable To Na+ And K+ Ions
- Permeable To Both Na+ And K+ Ions
- More Penncable To K+ Than Na+ Ions
- More Permeable To K+ And Cl– Ions.
Answer: 3. More Penncable To K+ Than Na+ Ions
Question 16. The Tire Part Of Ommatidium That Is Functionally Similar To the Retina Is :
- Crystalline Cone
- Basement Membrane
- Rhabdome
- Vitrellae.
Answer: 3. Rhabdome
nervous system test
Question 17. The Simplest Form Of Nerve Network Is :
- Neuron
- Reflex Arc
- Peripheral Nervous System
- Autonomic Nervous System.
Answer: 2. Reflex Arc
Question 18. The Chemical Theory Of Transmission Attributes The Response Of Postsynaptic Cells To A Chemical Substance Released From:
- Axon
- Synapse
- Pre-Synaptic Nerve Terminal
- Dendrites.
Answer: 3. Pre-Synaptic Nerve Terminal
Question 19. Acetylcholine Is Most Closely Associated With Which Of The Following Systems?
- Autonomic Nervous System
- All The Neurons Except Those Of Sympathetic Nervous System
- Parasympathetic Nervous System
- Peripheral Nervous System.
Answer: 2. A11 The Neurons Except Those Of Sympathetic Nervous System
Question 20. The Sensory Ganglion Concerned With Spinal Reflex Lies In:
- Anterior Root Of Spinal Nerve
- Anterior Hom Of Spinal Nerve
- Posterior Root Of Spinal Nerve
- Posterior Hom Of Spinal Cord.
Answer: 3. Posterior Root Of Spinal Nerve
Question 21. Sodium Pump Of An Axon Is Operative At:
- Action Potential Period
- Resting Potential Period
- Refractory Period
- None Of The Above.
Answer: 1. Action Potential Period
Question 22. The Gap Between the Terminal Knobs Of An Axon And Dendrites Of The Cell Body Of Another Axon Is Known As:
- Synaptic Cleft
- Synapse
- Neural Crest
- Tight Junction.
Answer: 1. Synaptic Cleft
Question 23. Acetylcholine Is :
- Secreted By Nerve Cells In Synapse
- Produced By Liver
- A Delivery Enzyme
- Activates Enzymes.
Answer: 1. Produced By Liver
Question 24. Action Potential Is :
- Brief Change In Electric Charge
- Brief Change In Oxygen Concentration
- Brief Change In C02 Concentration
- Change In Direction Of Nerve.
Answer: 1. Brief Change In Electric Charge
Question 25. During the Refractory Period :
- Nerve Transmits Impulses Rapidly
- Nerve Transmits Impulses Very Slowly
- Nerve Never Transmits Impulses
- None Of The Above.
Answer: 3. Nerve Never Transmits Impulses
Question 26. Electrical Impulse Of The Eye Recorded Are :
- Encephalogram
- Electro-Cardiogram
- Electro-Retinogram
- None Of The Above.
Answer: 3. Electro-Retinogram
Question 27. Neurotransmitters Are Compounds That:
- Help In Transmission Of Impulse In Synapse
- Retard The Transmission Of Impulse In An Axon
- Retard The Transmission Of Impulse At Synapsis
- None Of The Above.
Answer: 1. Help In Transmission Of Impulse In Synapse
Question 28. The 3rd, 6th And 11th Cranial Nerves Are :
- Oculomotor, Trigeminal, Spinal
- Optic, Facial, Spinal
- Oculomotor, Abducens, Spinal
- Trochlear, Abducens, Vagus.
Answer: 3. Oculomotor, Abducens, Spinal
Question 29. Which Of The Following Cranial Nerves Is Present In Rabbit But Absent In Frog?
- Glossopharyngeal
- Hypoglossal
- Olfactory
- Optic
Answer: 2. Olfactory
Question 30. Nervous System Was, First Of All, Originated In :
- Leech
- Ascaris
- Hydra
- Tape Worm.
Answer: 3. Hydra
Question 31. Sympathetic Nerves In Mammals Arise From :
- Thoraco-Lumbar Nerves
- 3rd, 7th, 9th And 10th Cranial Nerves
- Sacral Nerves
- Cervical Nerves.
Answer: 1. Thoraco-Lumbar Nerves
Question 32. At The Nerve Synapse :
- Carbon Dioxide Is Released
- Oxygen Is Released
- Neuro-Transmitters Are Released
- Nothing Is Released.
Answer: 3. Neuro-Transmitters Are Released
Question 33. At The Nerve Cell Membrane, The Equilibrium Potential For Potassium Is :
- + 65 M V
- +35m V
- -90 M V
- -70 M V
Answer: 3. -90 M V
Question 34. The “Spike” Phase Of Action Potential Lasts For Roughly :
- 20 Milli Second
- 2 Milli Second
- 200 Milli Second
- 2000 Milli Second.
Answer: 2. 2 Milli Second
Question 35.The Chemical Thcoiy Of Ti.Msmissiou Iillrilnitcs The Response Of Postsvnaptic Coll To A Chemical Substance Released Item :
- Axon
- Synapse
- Pre-Synaptic Nerve Terminal
- Dendrites.
Answer: 3. Pre-Synaptic Nerve Terminal
Question 36. One None Is Stimulated, It Is Polarized. Depolarization Is Maintained By The Following Ion :
- Ca+
- Cl–
- Mg++
- K+.
Answer: 4. K+.
Question 37. During Resting Conditions The Membrane Of the Axon Is:
- Impermeable To Na+ And K+ Ion
- Permeable To Both Na+ And K+ Ions
- More Penncable To K+ Than Na+ Ion
- More Permeable To K+ And Cl– Ions.
Answer: 3. More Penncable To K+ Than Na+ Ion
Question 38. Conduction Of Nerve Impulse Along A Myelinated Nerve Is :
- Twisted
- Reversible
- Saltatory
- Continuous.
Answer: 3. Saltatory
Question 39. Somaesthetic Area Is Located In :
- Frontal Lobe
- Mid Lobe
- Parietal Lobe
- None.
Answer: 3. Parietal Lobe
Question 40. The Ends Of Bipolar Neurons In Retina Of Man Touch :
- Choroid Layer And Ganglion Cells
- Photosensitive Cells And Ganglion Cells
- Cornea And Retina
- Blind Spot And Yellow Spot.
Answer: 2. Photosensitive Cells And Ganglion Cells
Question 41. Glands Of Swammerdam Are Rich In :
- Calcium
- Acetylcholine
- Dopamine
- Gonadotrophin.
Answer: 1. Calcium
Question 42. Sensory Neuron In A Vertebrate Reflex Are Located In :
- Grey Matter Of Spinal Cord
- White Matter Of Spinal Cord
- Ventral Root Ganglion
- Dorsal Root Ganglion.
Answer: 4. Dorsal Root Ganglion.
Question 43. Which One Of The Following Nerves Is Not Related To The Movement Of Eye Ball?
- Oculomotor
- Abducens
- Trochlear
- Glossopharyngeal.
Answer: 4. Glossopharyngeal.
Question 44. The Benzodiazepine Drug Known As Valium Produces Relaxation By Aiding The Binding To Receptor Proteins Of Inhibitory Neurotransmitters:
- Ach
- Gaba
- Dopamine
- Glycine.
Answer: 2. Gaba
Question 45. Which One Of The Following Is The Effect Of Parasympathetic Nervous System?
- Increasing Blood Pressure
- Secretion Of Digestive Juice
- Dilating Pupil
- Increasing Cardiac Output.
Answer: 2. Secretion Of Digestive Juice
Question 46. Which Of The Following Is the Function Of Pons Varolii?
- Site Of Cardiac Centre
- Perceiving Centre For Crude Sensation
- Controls Hunger And Thirst
- Transmits Impulses From One Side Of Ceubellum To The Other Side.
Answer: 4. Transmits Impulses From One Side Of Ceubellum To The Other Side.
Question 47. The Cervical Plexus Is Formed By
- Anterior Rami Of First Two Cervical Nerves
- Anterior Rami Of First Three Cervical Nerves
- Anterior Rami Of First Two Cervical And First Two Thoracic Nerves
- Anterior Rami Of Hist Four Cervical Nerves.
Answer: 4. Anterior Rami Of First Two Cervical And First Two Thoracic Nerves
Question 48. Presynaptic Membrane Permits :
- Influx Of Na+ Ions
- Influx Of Ca+3 Ions
- Influx Of Na+ And K+ Ions
- Start Of Original Impulse.
Answer: 2. Influx Of Ca+2 Ions
Question 49. Heart Beat Is Regulated By :
- Cns
- Ans
- PNS
- Spinal Cord.
Answer: 2. Ans
Question 50. Brain Reserves How Many Percent Of Total 02 Consumed By Body?
- 10%
- 20%
- 30%
- 40%.
Answer: 2. 20%
Question 51. The Refractory Centre Which Rfor Exampleulates Respiration Is Located In :
- Medulla Oblongata
- Cerebral Peduncle
- Vagus Nerve
- Cerebellum.
Answer: 1. Medulla Oblongata
Question 52. Which Brain Structure In Rabbit Is Directly Vision Related ?’
- Hippocampus
- Corpus Callosum
- Corpus Albicans
- Corpora Quadrigeminum.
Answer: 4. Corpora Quadrigeminum
Question 53. Most Of The Neurons Of Our Body Are :
- Unipolar
- Bipolar
- Pseudo-Unipolar
- Multipolar.
Answer: 4. Multipolar.
Question 54. Body Coordination Is Exhibited By :
- Blood Vascular System
- Nervous System
- Endocrine System
- Nervous And Endocrine System.
Answer: 4. Nervous And Endocrine System.
Question 55. The Sodium-Potassium Pump :
- Transports Na+ And K+ Out Of The Neuron
- Transports Na+ Into The Neuron And K+ Out
- Transports K+ Into The Neuron And Na+ Out
- Transports Na+ And K+ Into The Neuron.
Answer: 3. Transports K+ Into The Neuron And Na+ Out
Question 56. When A Neuron Shows A Stable Resting Potential, The Concentration Of Na+ Is :
- 10 Times Higher Inside The Cell Than Outside
- 10 Times Higher Outside The Cell Than Inside
- 30 Times Higher Inside The Cell Than Outside
- 30 Times Higher Outside The Cell Than Inside.
Answer: 2. 10 Times Higher Outside The Cell Than Inside
Question 57. In The Resting State Of The Neural Membrane, Diffusion Due To Concentration Gradients, If Allowed, Would Drive
- Na+ Into The Cell
- Na+ Out Of The Cell
- K+ Into The Cell
- K+ And Na+ Out Of The Cell.
Answer: 1. Na+ Into The Cell
Question 58. The Resting Potential Of Neurons Is 70 Mv. It Is Mainly Due To :
- Excess Of Chloride Ions Inside
- Excess Of Protein Ions Inside
- Na+ Ions Outside
- K+ Ions Inside.
Answer: 3. Na+ Ions Outside
Question 59. A Nerve Impulse Which Travels Through Nerve Fibre Only It Its Membrane Suddenly Becomes More Permeable To Ions Of:
- Chloride
- Potassium (K+)
- Sodium (Na+)
- Magnesium (Mg++).
Answer: 3. Sodium (Na+)
Question 60. An Action Potential, For A Given Axon, Is:
- Different In Size Each Time It Occurs
- Always The Same Size
- Larger When Information Has To Be Conveyed Faster
- Smaller When Information Goes To A Gland Rather Than A Muscle.
Answer: 2. Always The Same Size
Question 61. Which Of The Following Increases When An Action Potential Is Initiated?
- Diffusion Of Sodium Ions Into The Neuron
- Diffusion Of Sodium Ions Out Of The Neuron
- Diffusion Of Potassium Ions Out Of The Neuron
- Diffusion Of Potassium Ions Into The Neuron.
Answer: 1. Diffusion Of Sodium Ions Into The Neuron
Question 62. When An Action Potential Abruptly Drops From Positive To Nfor Exampleative, This Is Because :
- Potassium Gates Are Inactivated And Sodium Gates Are Opened
- Sodium Gates Are Inactivated And Potassium Gates Are Opened
- Both Potassium And Sodium Gates Are Inactivated
- Both Potassium And Sodium Gates Are Opened.
Answer: 2. Sodium Gates Are Inactivated And Potassium Gates Are Opened
Question 63. A Nerve Impulse Leaves A Neuron Via :
- Dendrite
- Cyton
- Axon
- Nucleus.
Answer: 3. Axon
Question 64. Synapse Is A Gap Between Adjacent :
- Muscle Fibres
- Nerve Cells
- Nerve Cell Bodies
- None Of The Above.
Answer: 2. Nerve Cells
Question 65. A Nerve Which Conveys Impulses From A Tissue To Nerve Centre Is Called :
- Efferent
- Mixed
- Motor
- Afferent.
Answer: 4. Afferent.
Question 66. The “Spike” Phase Of The Action Potential Lasts For Roughly :
- 2 Milliseconds
- 20 Milliseconds
- 200 Milliseconds
- 2000 Milliseconds.
Answer: 1. 2 Milliseconds
Question 67. The Speed At Which Impulses Are Conducted Increases With :
- Increasing the Diameter Of The Soma
- Increasing the Diameter Of The Axon
- Increasing Number Of Dendrites
- Increasing Branching Of The Dendrites.
Answer: 2. Increasing the Diameter Of The Axon
Question 68. Saltatory Conduction Of Nerve Impulses Occurs In :
- A myelinated Fibres
- Myelinated Fibres
- Both A And B
- None Of The Above.
Answer: 2. Myelinated Fibres
Question 69. Synaptic Fatigue Is Due To :
- Exhaustion Of Neurotransmitter
- Release Of More Adrenaline
- Release Of More Acetylcholine
- None Of The Above.
Answer: 1. Exhaustion Of Neurotransmitter
Question 70. Secretion Of Parasympathetic Nerve Endings Is :
- Noradrenaline
- Glycine
- Acetylcholine
- Hydroxy-Triptamine.
Answer: 3. Acetylcholine