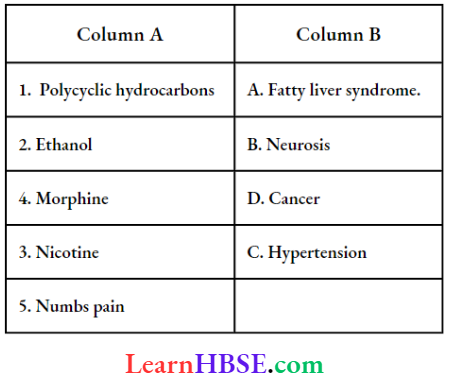
Question 1. Rabies is also called:
- Infantile paralysis
- Lock Jaw
- Hydrophobia
- Amoebiasis.
Answer: 3. Hydrophobia
Question 2. Rubeola virus causes:
- Smallpox
- Measles
- Chickenpox
- Influenza.
Answer: 2. Measles
Question 3. Black Death or Great Mortality is the name given to:
- Plague
- Malaria
- Cholera
- Cancer.
Answer: 1. Plague
human health and disease pyq
Question 4. A person with blood group ‘O’ can receive blood transfusion from persons with blood groups:
- O and A B
- O, A and B
- O only
- AB only.
Answer: 3. O only
Question 5. After which animal is the ‘Rh’ factor named?
- Dragon fly
- Monkey
- Man
- Rat.
Answer: 2. Monkey

Question 6. The universal recipient in blood transfusion belongs to the group:
- A
- O
- AB
- B.
Answer: 3. AB
Question 7. Rh factor is connected with:
- Carbohydrate metabolism in the body
- Initiation of protein synthesis
- Blood clotting
- Blood of man.
Answer: 4. Blood of man
Question 8. Haemophilia is a disease caused by deficiency of:
- Water in plasma
- RBCs
- WBCs
- Thromboplastin.
Answer: 4. Thromboplastin.
Question 9. Rh negative individuals are:
- Homozygous dominant (RR)
- Heterozygous (Rr)
- Homozygous recessive (rr)
- Possess only one gene (R or r).
Answer: 3. Homozygous recessive (rr)
Question 10. Which of the following is a genetic trait?
- Albinism
- Leucoderma
- Tuberculosis
- Diphtheria.
Answer: 1. Albinism
Question 11. The Rh factor was discovered by:
- William Harvey
- Landsteiner and Weiner
- James Watson
- Robert Hooke.
Answer: 2. Landsteiner and Weiner
Question 12. Universal donor in blood transfusion belongs to the blood group:
- A
- O
- AB
- B.
Answer: 2. O
Question 13. A woman with blood group O marries a man with blood group A. The child conceived to such a woman will:
- Survive with normal health
- Survive with slight anaemic conditions
- Will not survive long
- Will die soon after birth.
Answer: 1. Survive with normal health
Question 14. Which of the following is biologically incompatible marriage because of the danger of erythroblastosis foetal?
- Rh– man and Rh– woman
- Rh+ man and Rh+ woman
- Both Rh positive
- Both Rh negative.
Answer: 2. Rh+ man and Rh+ woman
Question 15. Down’s Syndrome has karyotype make-up as:
- 44 + 3x
- 44 + xxy
- 45 + xx in female
- 44 + xy or 44+ xx in female.
Answer: 3. 45 + xx in female
Question 16. If a man is Rh+ and the lady is Rh– then:
- The first child will die
- The first child will survive
- No child will be bom
- None of these.
Answer: 2. The first child will survive
Question 17. If a human mother has blood group ‘O’, the foetus in the womb would die, the blood group of the foetus is
- A
- B
- AB
- No effect in any case.
Answer: 4. No effect in any case.
Question 18. To a person of blood group AB blood groups of A and B are given separately, what will happen:
- Clumping occurs with A
- Clumping occurs with B
- Clumping occurs with both
- Clumping does not occur.
Answer: 4. Clumping does not occur.
Question 19. Which of the following diseases is genetically similar to haemophilia?
- Albinism
- Colour blindness
- Phenylketonuria
- None of the above.
Answer: 2. Colour blindness
Question 20. The disease Erythroblastosis foetal in human embryos is caused by to:
- Disadjustment of blood groups
- Disadjustment of Rh factor
- Both of these
- None of these.
Answer: 2. Disadjustment of Rh factor
Question 21. ABO blood groups were discovered by:
- Landsteiner
- Darwin
- Harvey
- Weiner.
Answer: 1. Landsteiner
Question 22. The second Rh+ child conceived to an Rh– the woman will:
- Die immediately
- Surely survive
- Survive with serious malformations
- Usually die at an early stage.
Answer: 1. Die immediately
Question 23. Persons with blood group ‘O’ lack:
- Antigens
- Antibody ‘a’
- Antibody ‘b’
- Haemophilia.
Answer: 1. Antigens
Question 24. Foetal sex can be determined by examining cells from amniotic fluid looking for
- Barr bodies
- Chiasmata
- Sex chromosome
- Kinetochores.
Answer: 1. Barr bodies
Question 25. The causes of diseases like peptic ulcers, hypertension, coronary heart diseases, and liver cirrhosis are:
- Certain viruses and bacteria
- Excess of fats in food
- Excessive use of alcoholic drinks
- Not yet identified.
Answer: 3. Excessive use of alcoholic drinks
Question 26. Trisomic condition of Down’s syndrome arises due to:
- Triploidy
- Non-disjunction
- Translocation
- Dicentric bridge formation.
Answer: 2. Non-disjunction
Question 27. Condition of sex chromosomes in male children with Down’s syndrome will be:
- XY
- XXY
- XX
- XO.
Answer: 1. XY
Question 28. Phenylketonuria (PKU) is:
- A nutritional disorder due to protein deficiency
- An inborn error of metabolism due to a recessive autosomal gene mutation
- A sex-linked disorder which is more common in males than in females
- None of the above.
Answer: 2. An inborn error of metabolism due to a recessive autosomal gene mutation
Question 29. Chromosomes of Klinefelter’s syndrome usually have:
- One X
- XXY
- 2X only
- No Y.
Answer: 2. XXY
Question 30. XO chromosome abnormality is:
- Turner’s syndrome
- Klinefelter’s syndrome
- Criminal syndrome
- Down’s syndrome.
Answer: 1. Turner’s syndrome
Question 31. Tay Sach’s disorder is:
- A chromosomal disorder in young children
- The result of severe protein deficiency in diet damages the muscle development in growing children
- An inherited disorder in which the spinal cord and brain are severely damaged within a few months of birth leading to paralysis and mental retardation, and finally the infant’s death in 3 or 4 years
- A genetic abnormality which appears at the age of 25-30 years and damages the bones.
Answer: 3. An inherited disorder in which the spinal cord and brain are severely damaged within a few months of birth leading to paralysis and mental retardation, and finally the infant’s death in 3 or 4 years
Question 32. Active immunity is due to:
- Memory cells
- Killer T-cells
- Helper T-cells
- Suppressor T-cells.
Answer: 1. Memory cells
Question 33. Passive immunity is provided through:
- Exogenous supply of antigens
- Exogenous supply of antibodies
- Endogenous supply of antigens
- Endogenous supply of antibodies.
Answer: 2. Exogenous supply of antibodies
Question 34. B-cells produce antibodies in response to instruction received from:
- Killer T-cells
- Suppressor T-cells
- B-lymphocytes
- All of the above.
Answer: 4. All of the above.
Question 35. Opsonisaiion is carried out by:
- IgM
- IgG
- IgA
- IgD and IgE.
Answer: 2. IgG
Question 36. Lysis of foreign cells is mediated through:
- IgM and IgG
- IgG and IgA
- IgA and IgD
- IgD and IgE.
Answer: 1. IgM and IgG
Question 37. T-cells have a life of:
- 4-5 days
- 4-5 weeks
- 4-5 months
- 4-5 years.
Answer: 4. 4-5 years.
Question 38. Antigenic determinant sites bind to which portions of an antibody molecule?
- Light chains
- Heavy chains
- Intermediate chains
- Both (1) and (2).
Answer: 4. Both (1) and (2).
Question 39. The cells that actually release the antibodies are:
- Helper T-cells
- Cytotoxic T-cells
- Mast cells
- Memory cells.
Answer: 3. Mast cells
Question 40. Types of T-cells are
- Killer cells and helper cells
- Killer cells and suppressor cells
- Killer, helper and suppressor cells
- Killer, helper and depressor cells.
Answer: 3. Killer, helper and suppressor cells
Question 41. Interferon is a protein that:
- Inactivates a virus
- Protects unattacked cells from virus
- Prevents viruses from taking over the cellular machinery
- All of the above.
Answer: 2. Protects unattacked cells from virus
Question 42. The most modern technique of vaccine preparation is:
- Extraction of antigens from pathogens
- Multiplication of antigens through DNA technique
- Weakening of pathogens through chemical treatment
- Attenuation of the pathogen through heat.
Answer: 2. Multiplication of antigens through DNA technique
Question 43. AIDS testing on normal individuals is done by:
- Separation of virus
- Reduction in immunity of the individual
- Identification of antibodies
- Identification of antigen-toxin.
Answer: 3. Identification of antibodies
Question 44. When people are born without B-cells or T-cells, they suffer from:
- Autoimmune diseases
- Immunodeficiency diseases
- Both of these
- None of these.
Answer: 2. Immunodeficiency diseases
Question 45. Which of the following is incorrect:
- Skin is a tough outer layer, so it prevents entry of bacteria and viruses
- Skin secretes oil and sweat by the glands which makes the surface basic and thus kills the microbes
- Skin secretes lysozyme along with sweat which prevents infection
- Some bacteria are present on the skin which release acids and other metabolic wastes that inhibit the growth of pathogens.
Answer: 2. Skin secretes oil and sweat by the glands which makes the surface basic and thus kills the microbes
Question 46. Which one of the following diseases is due to an allergic reaction?
- Enteric fever
- Hay fever
- Skin cancer
- Goitre.
Answer: 2. Hay fever