Respiratory System Questions And Answers
Question 1. What advantage over an aquatic organism does a terrestrial organism have with regard to obtaining oxygen for respiration?
Answer:
Respiratory System Questions
The advantage over an aquatic organism does a terrestrial organism have with regard to obtaining oxygen for respiration
Aquatic organisms obtain oxygen for their respiration from water. Water has about 1% oxygen in a dissolved state. Terrestrial organisms obtain oxygen directly from the air. The oxygen content of air is 21%. So terrestrial organisms are in a favourable position to obtain the required oxygen without too much work.
On the other hand, aquatic animals which extract oxygen from water have to perform more vigorous and rapid breathing to obtain the required oxygen. A fish will breathe 100 times/ min as compared to 14-20/min in humans.
Class 10 Biology Respiration
Question 2. What are the different ways in which glucose is oxidized to provide energy in various organisms?
Answer:
The different ways in which glucose is oxidized to provide energy in various organisms
There are three common methods by which glucose is catabolised to release energy-aerobic respiration, lactic acid anaerobic respiration and alcoholic anaerobic respiration.
Respiratory Questions
Aerobic Respiration. Glucose is completely oxidised with oxygen as a terminal oxidant. It yields carbon dioxide and energy. The energy yield is 686 kcal/2870 kJ per mole of glucose. About 38 ATP molecules are formed for storing energy. The process occurs partly in cytoplasm and partly in mitochondria.
![]()
Lactic Acid Anaerobic Respiration. Glucose is incompletely catabolised to form two molecules of lactic acid without involving the use of oxygen. It occurs in many bacteria and skeletal muscles during vigorous exercise. Only about 50 kcal/210 kJ of energy is released from which 2 ATP molecules are formed. The process occurs exclusively in the cytoplasm.

Respiration in Biology Class 10 Notes
Ethyl Alcohol Anaerobic Respiration. A molecule of glucose is catabolised to form two molecules of ethyl alcohol. Two molecules of carbon dioxide are evolved. The energy yield is about 50 kcal/210 kJ, equivalent to 2ATP molecules. Oxygen is not required. Respiration occurs inside the cytoplasm. Mitochondria are not required.
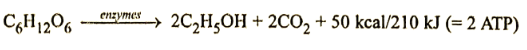
Aerobic and Anaerobic Respiration Class 10
Question 3. How are oxygen and carbon dioxide transported in human beings?
Answer:
Transport of Oxygen. It occurs through blood. 97% of oxygen combines with haemoglobin to form oxyhaemoglobin (Hb4O8). The remaining 3% dissolves in blood plasma. In the tissues, oxyhaemoglobin breaks down to release oxygen. The deoxygenated blood travels to the lungs for reoxygenation.
Transport of Carbon Dioxide. Carbon dioxide produced in cellular respiration passes into the blood. 70% of carbon dioxide forms sodium bicarbonate inside the plasma. 23% of carbon dioxide combines with haemoglobin to produce carbaminohaemoglobin. The remaining 7% gets dissolved in blood plasma. Blood-carrying carbon dioxide reaches alveoli where carbon dioxide diffuses into alveolar air.
Respiration in Plants and Animals Class 10
Question 4. How are the lungs designed in human beings to maximize the area for the exchange of gases?
Answer:
Lungs designed in human beings to maximize the area for the exchange of gases as follows
Human Respiratory System, Class 10 pdf
After entering a lung, each bronchus divides and redivides repeatedly to form segmental bronchi and then each segmental bronchus produces different ranks of bronchioles. The terminal bronchioles form respiratory bronchioles.
The latter form alveolar sacs that are studded with bunches of alveoli. It is estimated that a human lung has about 300 million alveoli. The total alveolar surface of the two lungs is about 80 m2 or roughly 40 times the surface area of the human body. Such a large surface area is most suitable for rapid gaseous exchange between the blood and the alveolar air.
