Haryana Board Class 6 Maths Solutions For Chapter 2 Whole Numbers
- If we add 1 to a number we get successor of that number.
- The natural numbers along with zero form the collection of whole numbers.
- Whole numbers are closed under addition and also under multiplication is called closure property.
- Division means repeated subtraction.
- Division of whole number by ‘0’ is not defined.
- The addition of two numbers can be done in any order.
- We can multiply two whole numbers in any order.
- Addition and multiplication are commutative for whole numbers.
- ‘0’ is the additive identity of whole numbers.
- ‘1’ is the multiplicative identity for whole numbers.
- The numbers which we use for counting are known as natural numbers. It is denoted by ‘N’.
Set of natural numbers N = {1, 2, 3, 4, …………..} - The natural numbers along with the zero are called whole numbers. It is denoted by ‘W’.
Set of whole numbersW= {0, 1, 2, 3, ……………} - The number just before any natural number is called the ‘Predecessor’.
- The next number of any natural number is called the ‘Successor’.
- Every natural number has a successor. Every natural number except 1 has a predecessor.
- Every whole number has a successor. Every whole number except zero has a predecessor.
- All natural numbers are whole numbers and all whole numbers except zero are natural numbers.
- Whole numbers can be represented on a number line. Operations of addition, subtraction and multiplication can easily be performed on a number line.
- Addition corresponds to moving to the right on the number line, whereas subtraction corresponds to moving to the left. Multiplication corresponds to making jumps of equal distance from zero.
- “The sum of any two whole numbers is always a whole number”. This property is known as the closure property under addition for whole numbers.
Eg: If a, b are two whole numbers then their sum ‘a + b’ is also a whole number. - The product of any two whole numbers is always a whole number. This property is known as the ‘closure property under multi- plication for whole numbers’.
Eg: If a, b are two whole numbers, their product ‘a x b’ is also a whole number. - Whole numbers are closed under addition and multiplication. But, whole numbers are not closed under subtraction and division.
- Division by zero is not defined.
- If ‘a’ and ‘b’ are two whole numbers then ‘a + b = b + a’ this property is known as ‘Commutative Property’ under addition of whole numbers.
- If ‘a’ and ‘b’ are two whole numbers then ‘a x b = b x a’ this property is known as ‘Commutative Property’ under multiplication of whole numbers.
- Addition and multiplication are ‘Commutative’ over whole numbers. But whole. numbers are not commutative under subtraction and division.
- If a, b and c are three whole numbers then ‘a x (b + c) = (a x b) + (a x c)’ is known as ‘distributive property of multiplication over addition’.
- Addition and multiplication are ‘Associative’ over whole numbers. But whole numbers not associative under subtraction and division.
- If a, b and c are three whole numbers then ‘ax (b+c) = (a x b) + (ax c)’ is known as ‘distributive property of multiplication over addition’.
- Commutativity, associativity and distributivity of whole numbers are useful in simplifying calculations. We often use them without being aware of them.
- Pattern with numbers are not only interesting but also useful especially for mental calculations. They help us to understand properties of numbers better.
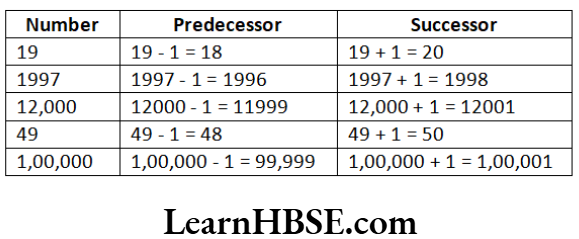
Question 1. Write the predecessor and successor of 19; 1997; 12,000; 49; 1,00,000
Solution.
Question 2. Is there any natural number that has no predecessor ?
Solution. Yes, the natural number 1 has no predecessor.
Question 3. Is there any natural number which has no successor? Is there a last natural number?
Solution. No, there is no natural number which has no successor. No, there is no last natural number..
Question 4. Are all natural numbers also whole numbers ?
Solution. Yes, all natural numbers are also whole numbers.
Question 5. Are all whole numbers also natural numbers ?
Solution. No, because the whole number ‘O’ is not natural number.
Question 6. Which is the greatest whole number?
Solution. There is no greatest whole number.
Haryana Board Class 6 Maths Whole Numbers solutions
Question 7. Find 4 + ; 2 + 6; 3 + 5 and 1 + 6 using the number line.
Solution.
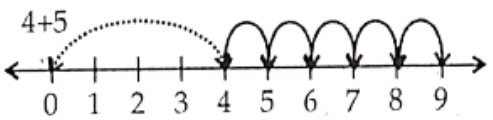
∴ 4 + 5 = 9
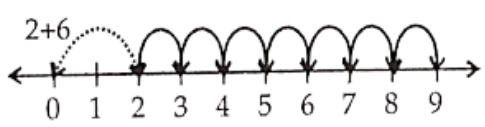
∴ 2 + 6 = 8
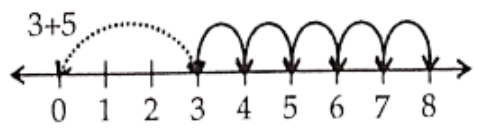
∴ 3 + 5 = 8
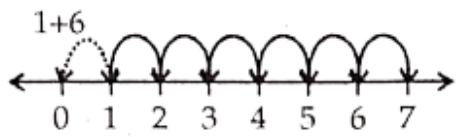
∴ 1 + 6 = 7
Question 8. Find 8 – 3; 6 – 2; 9 – 6 using number line.
Solution. 8 – 3
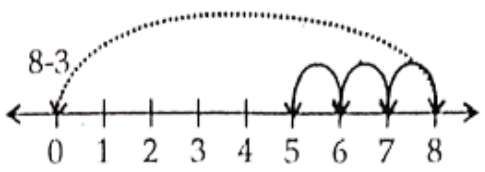
∴ 8 – 3 = 5
6 – 2
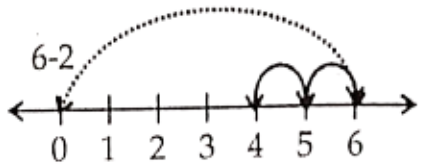
∴ 6 – 2 = 4
9 – 6

∴ 9 – 6 = 3
Properties of whole numbers Class 6 HBSE
Question 9. Find 2 x 6; 3 x 3; 4 x 2 using the number line.
Solution.
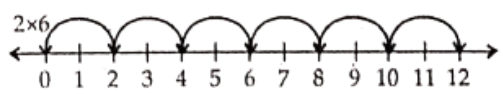
∴ 2 x 6 = 12
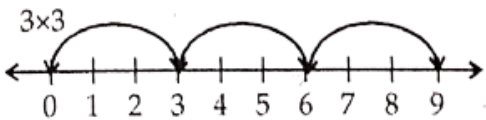
∴ 3 x 3 = 9
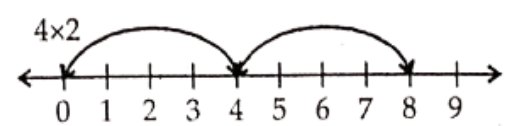
∴ 4 × 2 = 8
Chapter 2 Whole Numbers Exercise – 2.1
Question 1. Write the next three natural numbers af- ter 10999.
Solution. The next three natural numbers after 10999 are 11,000, 11,001 and 11,002.
Question 2. Write the three whole numbers occuring just before 10001.
Solution. The three whole numbers occurring just before 10001 are 10000, 9999 and 9998.
Question 3. Which is the smallest whole number?
Solution. The smallest whole number is 0.
Question 4. How many whole numbers are there between 32 and 53 ?
Solution. There are 20 whole numbers between 32 and 53. They are 33, 34, 35, 36, 37, 38, 39, 40, 41, 42, 43, 44, 45, 46, 47, 48, 49, 50, 51 and 52.
Question 5. Write the successor of:
(a) 2440701
(b) 100199
(c) 1099999
(d) 2345670
Solution. a) The successor of 2440701 is 2440701 + 1 = 2440702
b) The successor of 100199 is 100199 + 1 = 100200
c) The successor of 1099999 is 1099999 + 1 = 1100000
d) The successor of 2345670 is 2345670 + 1 = 2345671
Whole numbers and their operations Class 6
Question 6. Write the predecessor of:
(a) 94
(b) 10000
(c) 208090
(d) 7654321
Solution. a) The predecessor of 94 is 94 – 1 = 93
b) The predecessor of 10000 is 10000 – 1 = 9999
c) The predecessor of 208090 is 208090 – 1 = 208089
d) The predecessor of 7654321 is 7654321 – 1 = 7654320
Question 7. In each of the following pairs of numbers, state which whole number is on the left of the other number on the number line. Also write them with the appropriate sign (>, <) between them.
(a) 530,503
(b) 370,307
(c) 98765, 56789
(d) 9830415, 10023001
Solution. a) The whole number 503 is on the left of the whole number 530 on the num- ber line.
∴ 503 < 530.
b) The whole number 307 is on the left of the whole number 370 on the num- ber line.
∴ 307 < 370.
c) The whole number 56789 is on the left” of the whole number 98765 on the number line.
∴ 56789 < 98765
d) The whole number 10023001 is on the right of the whole number 9830415 on the number line.
∴ 10023001 > 9830415.
Question 8. Which of the following statements are true (T) and which are false (F)?
a) Zero is the smallest natural number.
Solution. False (F)
b) 400 is the predecessor of 399.
Solution. False (F)
c) Zero is the smallest whole number.
Solution. True (T)
d) 600 is the successor of 599.
Solution. True (T)
e) All natural numbers are whole numbers.
Solution. True (T)
f) All whole numbers are natural numbers.
Solution. False (F)
Number line representation of whole numbers HBSE
g) The predecessor of a two digit number is never a single digit number.
Solution. False (F)
h) 1 is the smallest whole number.
Solution. False (F)
i) The natural number 1 has no predecessor.
Solution. True (T)
j) The whole number 1 has no predecessor.
Solution. False (F)
k) The whole number 13 lies between 11 and 12.
Solution. False (F)
l) The whole number 0 has no predecessor.
Solution. True (T)
m) The successor of a two digit number is always a two digit number.
Solution. False (F)
Haryana Board Class 6 Maths Solutions For Chapter 2 Whole Numbers Very Short Answer Questions
Question 1. Which is the smallest whole number?
Solution. ‘0’ is the smallest whole number.
Question 2. Are all natural numbers whole numbers ?
Solution. Yes, all natural numbers are whole numbers because all natural numbers along with zero are called whole numbers.
Question 3. Are all whole numbers natural numbers ?
Solution. No, all whole numbers are not natural numbers. Except zero the remaining all whole numbers are natural numbers.
Question 4. How many whole numbers are there in between 27 and 46?
Solution. The whole numbers lie between 27 and 46 are 28, 29, 30, 31, 32, 33, 34, 35, 36, 37, 38, 39, 40, 41, 42, 43, 44, 45.
There are 18 whole numbers in between 27 and 46:
Question 5. Mark the smallest whole number on the number line.
Solution. The smallest whole number is zero (0).
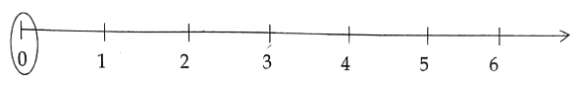
Distributive property of whole numbers Class 6
Question 6. Choose the appropriate symbol form < or > and place it in the blanks.
1) 8 > 7
2) 5 > 2
3) 0 < 1
4) 10 > 5
Question 7. Present the successor of 11 and predecessor of 5 on the number line.
Solution. The successor of 11 is 12 and the predecessor of 5 is 4.
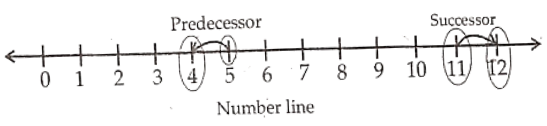
Haryana Board Class 6 Maths Solutions For Chapter 2 Whole Numbers Short Answer Questions
Question 8. Which of the statements are true (T) and which are false (F). Correct the false statements.
1) There is a natural number that has no predecessor.
Solution. True.
1 is a natural number that has no predecessor.
2) Zero is the smallest whole number.
Solution. True.
3) A whole number on the left of another number on the number line, is greater than that number.
Solution. False.
A whole number on the left of another number on the number line is smaller than that number.
Question 9. Show (1) 3+4 (2) 7-3 on number line.
1) 3+ 4
Solution. Consider 3 + 4
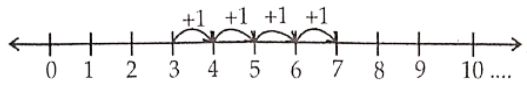
Start from 3. We add 4 to three. We make 4 jumps to the right on the number line as shown above then we will reach at 7
∴ 3 + 4 = 7
2) 7 – 3
Solution. Consider 7 – 3
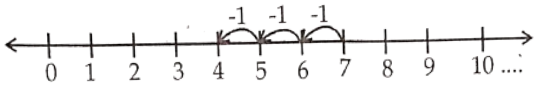
Start from 7. Since we subtract 3 from 7 we take 3 steps to the left on the number line as shown above then we will reach 4.
∴ 7 – 3 = 4.
Question 10. Show (1) 5 x 2 (2) 4 x 3 on number line.
Solution. Consider 5 x 2 = 2 + 2 + 2 + 2 + 2
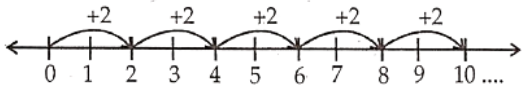
Start from 0. Move 2 units to the right each time, making 5 such moves we reach 10.
So, 5 x 2 = 10
2) 4 × 3
Solution. Consider 4 x 3 = 3 + 3 + 3 + 3
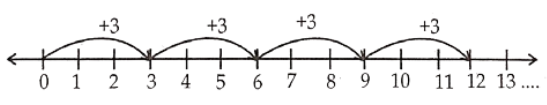
Start from 0. Move 3 units to the right each time, making 4 such moves we reach 12.
So, 4 x 3 = 12
Question 11. Find the sum of the predecessor of 300 and successor of 427.
Solution. The predecessor of 300 is 299.
The successor of 427 is 428.
∴ The required sum = 299 + 428
= 727
Haryana Board Class 6 Maths Solutions For Chapter 2 Whole Numbers Long Answer Questions
Question 12. Show these on number line:
1) 5+3
Answer.
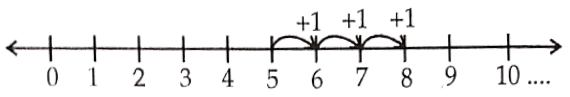
5 + 3 = 8
2) 5 – 3
Answer.
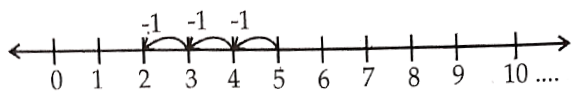
5 – 3 = 2
Word problems on whole numbers for Class 6 HBSE
3) 3 + 5
Answer.
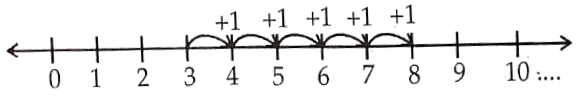
3 + 5 = 8
4) 10 + 1
Answer.
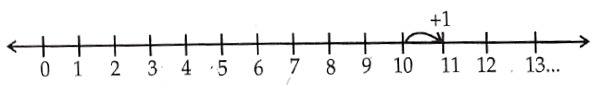
10 + 1 = 11
5) 8 – 5
Answer.
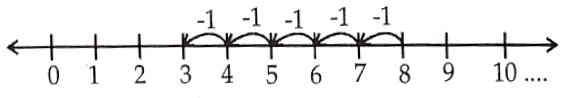
8 – 5 = 3
Question 13. Find the following using number line.
1) 6 + 7 + 7
Solution.
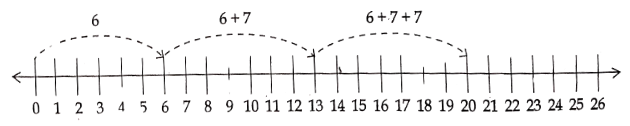
Start from 0, reach 6; we make 7 jumps from 6 to the right on the number line as shown above. We will reach 13.
Again start from 13, make 7 jumps to the right on the number line as shown above. We will reach 20.
6 + 7 + 7 = 20
2) 18 – 9
Solution.
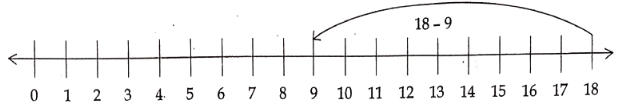
Start from 0, reach 18. Since we subtract 9 from 18, Start from 18. We take 9 steps to the left on the number line as shown above. We will reach 9.
18 – 9 = 9
Identity elements in whole numbers Class 6
3) 5 x 3
Solution.
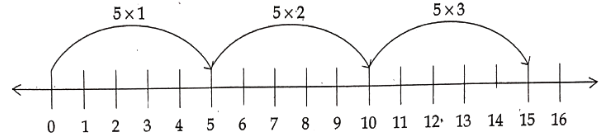
Start from 0, move 5 units to the right each time making 3 such moves. We will reach 15.
5 x 3 = 15
Haryana Board Class 6 Maths Solutions For Chapter 2 Whole Numbers Objective Type Questions
Choose the correct answer :
Question 1. Natural numbers are represented by
- I
- W
- N
- O
Answer. 3. N
Question 2. The successor of 16 is
- 17
- 15
- 18
- 16
Answer. 1. 17
Question 3. The predecessor of 25 is
- 26
- 25
- 24
- 27
Answer. 3. 24
Question 4. The smallest whole number is
- 0
- 1
- 2
- 3
Answer. 1. 0
Question 5. Which number has no predecessor in natural numbers?.
- 0
- 1
- 2
- 3
Answer. 2. 1
Question 6. ……. + 25 = 25
- 1
- 0
- 2
- 25
Answer. 2. 0
Question 7. The number just before a number is called.
- Predecessor
- Successor
- Both A & B
- None
Answer. 1. Predecessor
Question 8. The next number of any natural number is called.
- Predecessor
- Successor
- Both A & B
- None
Answer. 2. Successor
Question 9. The predecessor of the smallest natural number
- 0
- 1
- 2
- None
Answer. 4. None
Question 10. The successor of the greatest whole number
- 0
- 1
- 100
- cannot find
Answer. 4. cannot find
Question 11. Which of the following whole number does not have predecessor
- 0
- 1
- 99
- None
Answer. 1. 0
Question 12. Whole numbers are represented by
- I
- W
- N
- R
Answer. 2. W
Question 13. Additive identity of whole numbers is
- 1
- 2
- -1
- 0
Answer. 4. 0
Question 14. Multiplicative identity of whole numbers is
- 1
- 2
- -1
- 0
Answer. 1. 1
Question 15. Taking ‘2 steps four times’ represented by
- 2 + 4
- 4 + 2
- 4 x 2
- 2 × 4
Answer. 3. 4 x 2
Question 16. The sum of smallest natural number and smallest whole number is
- 0
- 1
- 2
- Not defined
Answer. 2. 1
Question 17. Division by zero is
- 0
- 1
- same number
- Not defined
Answer. 4. Not defined
Question 18. The sum of first 5 natural numbers
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 10
Answer. 2. 15
Question 19. The sum of first 5 whole numbers
- 14
- 15
- 10
- 16
Answer. 3. 10
Question 20. ……..+46 = 46
- 1
- 0
- 46
- 2
Answer. 2. 0
Question 21. Set of whole numbers
- {1, 2, 3, 4,……}
- {0,1,2,3,…………….}
- {-3, -2, -1, 0, 1, 2, 3,…….}
- None
Answer. 2. {0,1,2,3,…………….}
Question 22. Smallest whole number
- 0
- 1
- -1
- Not exist
Answer. 1. 0
Question 23. The predecessor of 1000 is
- 1001
- 999
- 1000
- 998
Answer. 2. 999
Question 24. The successor of 9999 is
- 9998
- 9999
- 10000
- 10001
Answer. 3. 10000
Question 25. Which number has no predecessor?
- 1 in natural numbers
- 0 in whole numbers
- Both A & B
- Neither A nor B
Answer. 3. Both A & B
Question 26. Which of the following represents the given number line?
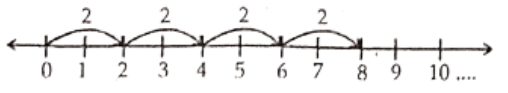
4 + 2 = 6
4 x 2 = 8
2 × 4 = 8
10 – 2 = 8
Answer. 2. 4 x 2 = 8
Question 27. The difference of predecessor of 1000 and successor of 998 is……..
1
2
3
0
Answer. 4. 0
Chapter 2 Whole Numbers Fill in the blanks:
Question 28. The numbers 1, 2, 3 ….. which we use for counting are known as …………..
Answer. natural numbers
Question 29. The natural numbers along with the zero form the collection of ……… numbers.
Answer. whole
Question 30. The number just before a number is called the …………..
Answer. predecessor
Question 31. The next number of any natural number is called its …………
Answer. successor
Question 32. 3, 4 relation between these numbers is …………..
Answer. 4 > 3
Question 33. The sum of any two whole numbers is always a ………..
Answer. whole number
Question 34. …… by zero is not defined.
Answer. Division
Question 35. Every whole number has a ………
Answer. Successor
Question 36. We add …….. to a whole number we get the same whole number.
Answer. 0
Question 37. Every number can be arranged as a …………..
Answer. line
Question 38. ………… is the smallest whole number.
Answer. 0
Question 39. The number of whole numbers between 1 and 2 is ……..
Answer. 0
Question 40. 2021 ÷ 0 is ……..
Answer. Not defined
Question 41. ……. is the additive identiy.
Answer. 0
